In this interview, individuals from H.C Starck Solutions talks about how their molybdenum and tungsten metal, composite and laminate products are used in thermal management applications in the power industry.
What materials does H.C. Starck Solutions provide for thermal management?
H.C. Starck Solutions is a long-established and leading manufacturer of technology metals including molybdenum (Mo) and tungsten (W). Nearly everything we do leverages our expertise in these materials. For thermal management, we provide materials solutions based on pure Mo or pure W, and Mo and W composites and laminates with copper.
What properties make these metals so useful in these applications?
The expansion of H.C. Starck Solutions materials at elevated temperatures is similar to that of the silicon-based semiconductor device to which it is mounted.
Without such material and device matching, there is a serious risk of premature failure due to temperature-induced strain in the system.
Further, the refractory materials provided by H.C. Starck Solutions have good thermal conductivity, drawing heat away from the device, which is especially important in high power devices where overheating will limit the device’s service life.

Copper/molybdenum/copper laminates from H.C. Starck Solutions
Are the various products you supply (composites, laminates, etc) tailored for specific types of application? How do you select the right product for a particular product or application?
Our responsibility as a design partner is to try to best match our product with the requirements of the customers by balancing mechanical and thermal properties with price and service lifetime considerations.
One example comes to mind from the past year. Nearly all the products we supply are coated with metals such as gold, silver, nickel, ruthenium and rhodium for solder-wetting, etch-resistance, protective layers and/or electrical contacts. The coatings are applied in our own world class manufacturing facility in the United Kingdom, which is a real specialty area of our expertise, and I am proud to say that we are a market-leader in this field.
A large, multinational customer had a requirement to extend the service life of their system from 15 years to 20 years. After analysing the requirements, H.C. Starck Solutions undertook a development project to optimize the characteristics of the coated layer and its interaction with the other components in the system. H.C. Starck Solutions was able to enhance the properties of our product, thus enabling our customer to offer additional value to their end user customer.
How are the challenges in thermal management evolving in the modern power industry?
For decades thermal management has been an issue as miniaturization and increased functionality and power densities have driven designers to seek better solutions. So the next 10 years will be a continuation of these historical trends.
Cost and manufacturability have likewise been important concerns in the past and will continue to be important considerations far into the future. Despite the current low price for oil, we see increased adoption of alternative energy technologies as a long run trend. Alternative energy technologies often have a component of thermal management that necessitates attention and creative solutions.
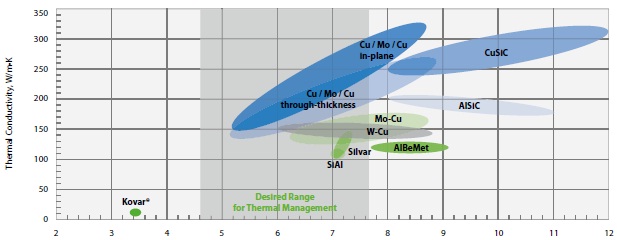
Thermal management materials by in-plane coefficient of thermal expansion
How do you think the market for thermal management technology will develop over the next few years?
Aside from the technologies that H.C. Starck Solutions offers the market, there are competing technologies in metal matrix composites such as AlSiC. Diamond-based materials also offer very interesting properties but at a price point that currently puts them out of reach for most applications.
With that said, designers have many options to address their thermal management requirements. I think we will see more options brought to market in the coming years as material innovations push thermal management technology forward, while the ongoing trends of miniaturization and increased power densities provide a market pull for new technologies.
What unique solutions can H.C. Starck Solutions provide that sets you apart from other suppliers?
H.C. Starck Solutions is unique not only in the products we make but also in the way we serve the market. We are vertically integrated and have several joint ventures with mines, allowing us a secure raw material supply chain for many years to come. Vertical integration also allows for excellent control of properties and the ability to tailor properties to meet specific market needs.
Finally, I would add that H.C. Starck Solutions has a global operation with factories in Asia, North America, and Europe, and we are a major supplier of technology metals, which are used in global applications from electronics like mobile devices to aerospace, oil and gas exploration, renewable energy, transportation, chemical processing, communication, lighting, heat treatment, and medical and security diagnostic equipment to name a few.
About H.C. Starck Solutions
The H.C. Starck Group is a leading global supplier of technology metals and advanced ceramics. The company operates modern manufacturing facilities in Europe, America, and Asia and serves growing industries such as the electronics, chemicals, automotive, medical technology, aerospace, energy technology, and environmental technology industries, as well as engineering companies and tool manufacturers.
On December 31, 2017, the H.C. Starck Group had 2,600 employees in the United States, Canada, Great Britain, Germany, China, Japan, and Thailand.
H.C. Starck’s products are predominantly based on technology metals: Tantalum, Niobium, Tungsten, and Molybdenum.
The Fabricated Products Division converts technology metal powders into customized semi-finished and finished products through pressing, sintering, rolling, melting and thermo-mechanical processing and surface treatment.
The Tungsten Division provides high performance products for the mechanical engineering and tool making, automotive and energy industry, aviation industry, and the chemical industry, for example:
- tungsten carbides for carbide tools and wear parts
- tungsten and cast tungsten carbides for oil and gas drilling
- tungsten metal powders for heavy metal alloys
- tungsten chemicals as precursors for catalysts
The Advanced Ceramic Components (CER) Division manufactures specialized technical ceramic parts and films. CER produces engineering parts such as sealing rings, functional parts including fuel cells for solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) systems and products for dental applications as well as for armor and wear protection. Furthermore, CER focuses on technological developments to expand the portfolio toward product applications in the semiconductor industry.
In 2018 H.C. Starck sold the division Surface Technology & Ceramic Powders to the Swedish Höganäs Group, effective March 1st and the division Tantalum and Niobium to the JX Nippon Mining & Metals Group, effective July 1st.
The group is led by a two-member Executive Board: Dr. Jens Knöll (Chairman of the Executive Board), Dr. Jan Lösch (Member of the Executive Board).
H.C. Starck was founded in Berlin in 1920. Since 2007, the company is owned by financial investors Advent International and The Carlyle Group.
H.C. Starck is registered in Goslar (Germany) and the Group’s headquarters is located in Munich (Germany).

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by H.C. Starck Solutions.
For more information on this source, please visit H.C. Starck Solutions.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the interviewee and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited (T/A) AZoNetwork, the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and Conditions of use of this website.