Hound is a unique particle characterization tool that integrates microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) to efficiently quantify, size, and identify particles based on their distinct chemical or elemental characteristics.
By consolidating these diverse capabilities into a single instrument, Hound swiftly compiles comprehensive data about your particles within minutes.
- Count
- Shape
- Size
- Elemental ID
- Chemical ID
Capabilities
Round Them Up
Hound lets users prep their sample for all particle characterization. Users can capture prominent and visible particles by plucking them from the solution, or pouring the entire sample through a filter round if they are small.
If users wish to keep them suspended, they must pipette the sample onto a wet round. No matter what functions best for the samples, the gold-coated surfaces catch everything and remove all the background noise.
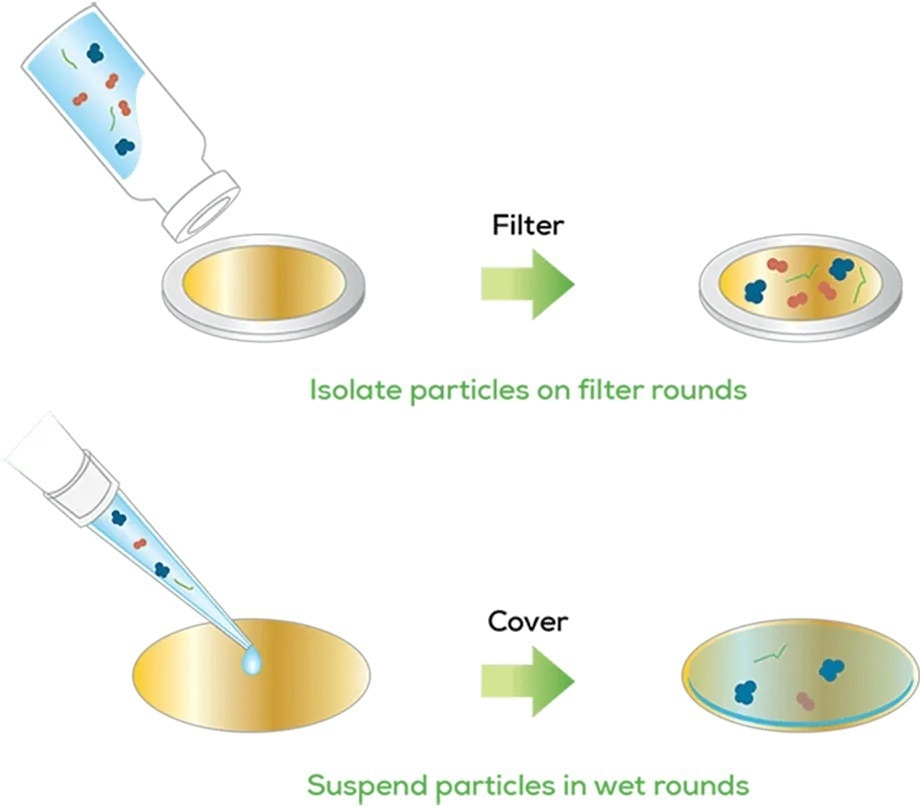
Image Credit: Unchained Labs
Track Them Down
After successfully capturing the particles, Hound’s automated system promptly detects and measures them. Utilizing either bright-field or dark-field imaging ensures no particles go unnoticed, even those with challenging characteristics like translucency, such as proteins.
Within a matter of minutes, Hound conducts a thorough scan, providing detailed reports on the size, shape, morphology, and fibrous properties of all identified particles.
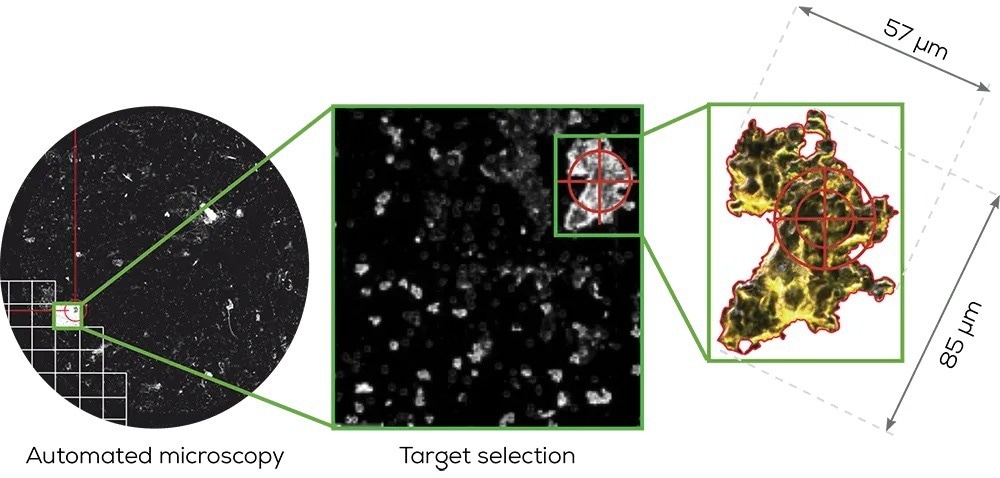
Image Credit: Unchained Labs
Identify the Unknowns
If users cannot understand their particle by size and shape, Hound has additional features to characterize it. Raman 785 nm is the workhorse laser that can ID the majority of the particles.
For protein aggregates or particles that fluoresce, switch to Raman 532 nm. If the particle contains metals, the LIBS laser can determine the particle depending on its elements.
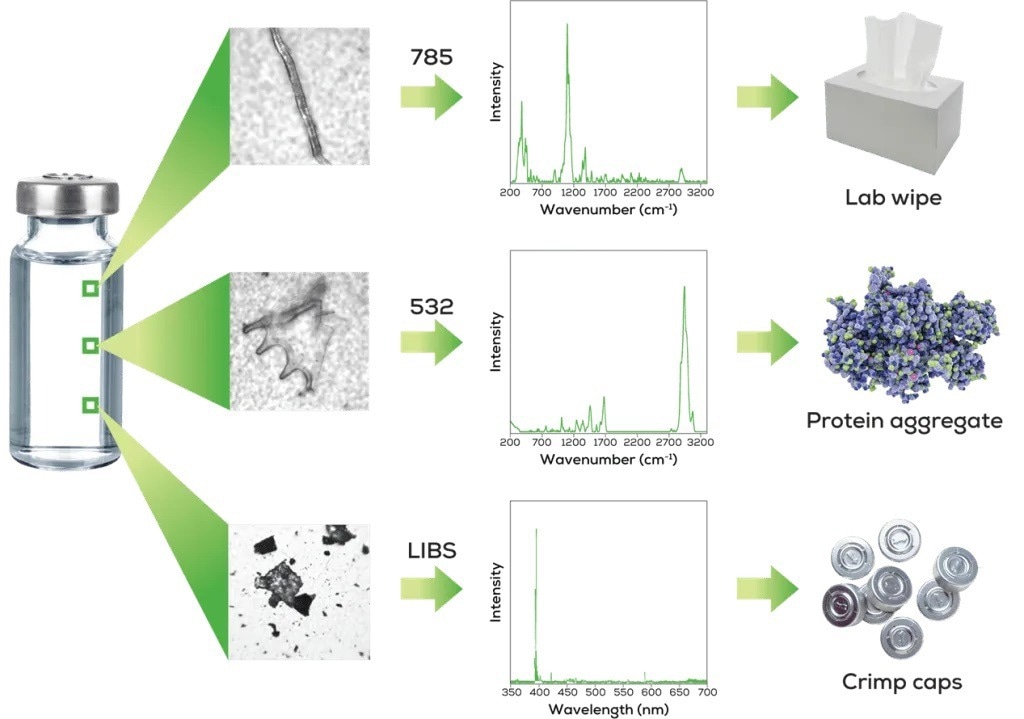
Image Credit: Unchained Labs
Teach Hound New Tricks
Raman and LIBS capture the signature from their particles. Such special fingerprints can be saved to a customizable reference database–so users can ID it immediately.
Users’ images and spectra are stored for reference and reports, and 21 CFR Part 11 software tools help users retain compliance via data collection and analysis.
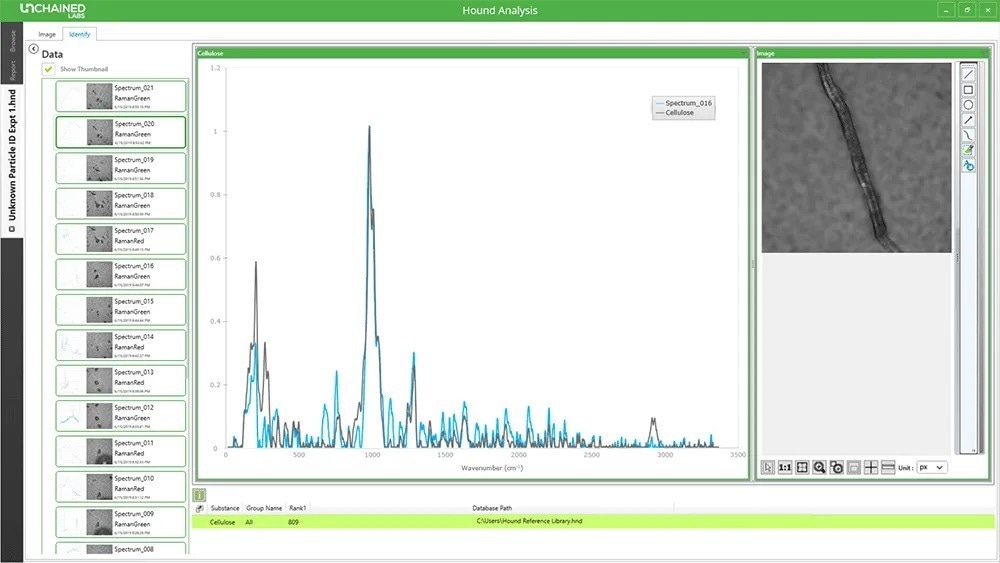
Image Credit: Unchained Labs
Pick the Desired Hound
Source: Unchained Labs
| Configuration |
Proteins |
Organics |
Inorganics |
Metals |
| Raman 785 nm + 532 nm + LIBS |
Best |
Best |
Best |
Best |
| Raman 785 nm + 532 nm |
Best |
Best |
Good |
N/A |
| Raman 785 nm |
Good |
Good |
Good |
N/A |