Die swell has been used in the plastics industry as a qualitative measure of polymer melt elasticity for quality control. It can also be used in an extrusion process for analysis of extrudate smoothness.
Die swell is the expansion of extrudate after exiting the die. It takes place as a result of the molecular orientation generated by the flow in the die (with the greatest extension occurring near the wall) and recoiling after exiting the die (contracting in the direction of flow and expanding perpendicular to the flow). This phenomenon is produced by plastic materials memory - as the extrudate exits the die, it tries to return to its initial molecular coil shape.
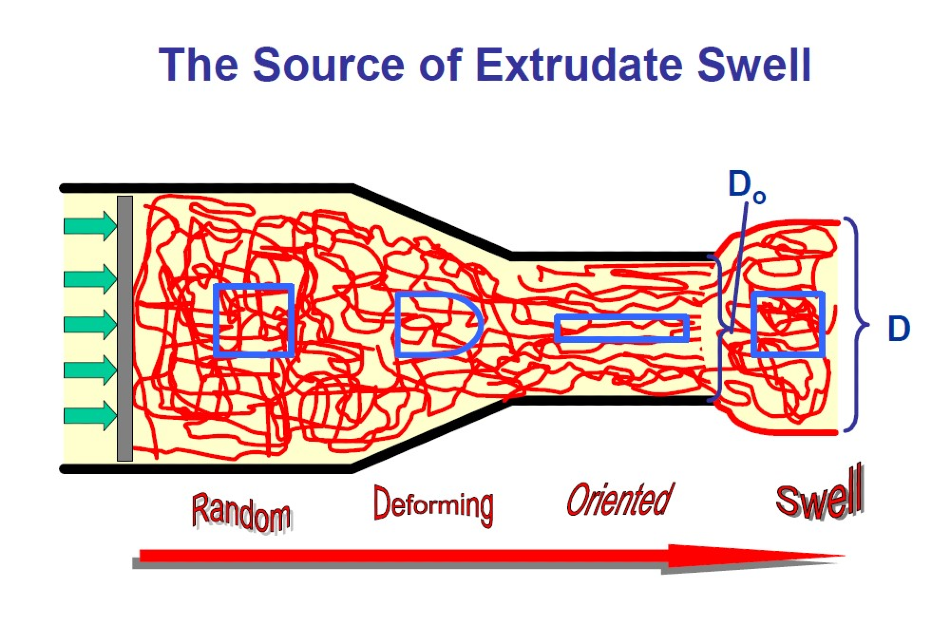
Image Credit: Dynisco
Dynisco LCR capillary rheometer can measure the diameter of the extrudates using a CCD element detection and laser beam. This accessory element has the following specification: resolution of 2.75 mm, light source of 800 nm laser, response time of 1.4 ms, accuracy of +/- 0.003 mm, and measuring range of 0.13 – 23 mm.
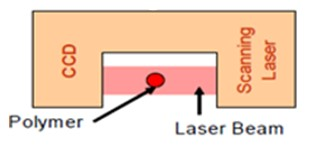
Image Credit: Dynisco
There are two ways to measure the swell die using the capillary rheometer. Relaxed die swell can be measured after the piston is stopped between viscosity measurements (Position and Delay sec test type) whilst running die swell can be measured while the piston is moving during a viscosity measurement (Steady State test type).
Relaxed die swell can be used to predict the part dimensions, while running die swell can be used to predict the die swelling condition of extrusion process. Die swell can also be used to analyze the extrudate smoothness (part finish) because the extrudate distortion (e.g. melt fracture, shark skin, etc) can produce cyclical or noisy die swell measurements.
The die swell ratio percentage can be calculated using the equation below when the diameter of the die is known:
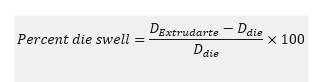
The die swell ratio percentage versus sheer rate for three different high density polyethylene samples is shown in Figure 1.
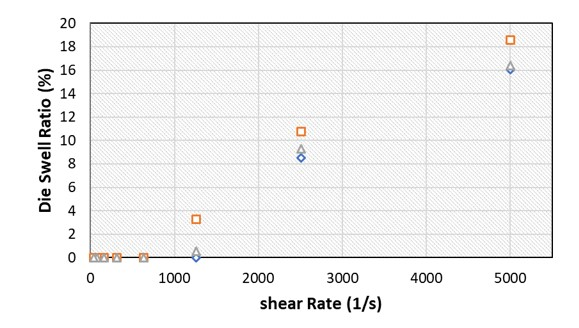
Figure 1. Die swell ratio percentage versus shear rate for three PP samples. Image Credit: Dynisco
The die swell ratio decreases with the decreasing sheer rate, as expected. This is because for lower sheer rates, viscoelastic plastic materials forget their elastic memory and, as a result, die swell decreases.
Die swell can be troubleshooted using longer die, a larger diameter die, decreasing the sheer rate, increasing the temperature or tapering the die.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Azadeh Farahanchi, Rheological Scientist, Ph.D.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Dynisco.
For more information on this source, please visit Dynisco.