A broad variety of waste products, including municipal solid waste, building and excavation debris, and industrial chemicals are disposed of in landfills. Landfill gas (LFG) is a natural consequence of organic waste degradation in landfills. If not adequately handled, these gases can be detrimental to the ecosystem as well as public health. Consequently, their monitoring becomes crucial.

Image Credit: Roman Mikhailiuk/Shutterstock.com
A landfill is a defined piece of land where garbage is discarded before being buried with soil or any other substance. To create a landfill, the facility must be conceived, developed, and maintained in a manner that minimizes environmental impacts and safeguards public health. Lining landfills with materials such as clay or durable plastic is essential. This stops trash and liquid (leachate) from leaking into the land and water nearby. Typically, trash is deposited in designated sections of a landfill. These regions are known as "cells." As one cell is occupied, another one is prepped, and yet another is completed or repaired.
Leachate and Landfill Gases
Leachate is the liquid generated at a landfill. As chemicals from decomposing garbage interact with other garbage, leachate can become poisonous. Leachate is captured and disposed of in a wastewater treatment facility to prevent it from polluting local waterways.
Gases from landfills mainly consist of methane, carbon dioxide, and trace quantities of many other gases that emit a rotten odor. Because methane is combustible and can cause fires, some landfills incinerate the gas or convert it into energy.
One ton of biodegradable waste generates around 400–500 cubic meters of landfill gas. Consequently, landfill gas emissions are analyzed for several years after the facilities have ceased receiving trash.
Why is Gas Analysis at Landfills Essential?
Gases from landfills can contribute to pollution, the release of greenhouse gases, and ozone layer depletion. By analyzing the gases emitted by a landfill, authorities can take measures to limit their harmful effects, such as absorbing and eliminating methane or minimizing the discharge of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Additionally, the collection and utilization of methane gas enable landfills to be a source of sustainable energy. Authorities can examine the viability of extracting methane for energy reasons by analyzing methane levels at a landfill.
Different Methods of Landfill Gas Analysis
There are numerous techniques and methods for qualitative and quantitative landfill gas analysis, and the appropriate one for a particular facility will rely heavily on various factors such as the type of debris and waste, the ambient conditions adjacent to the site, the regulatory prerequisites, and the site owner's financial plan.
Inserting gas sampling probes into a landfill to gather specimens of the gases being released is a typical technique often termed "subsurface monitoring". The quantities of the various gases in the mixture can then be determined using a gas chromatograph or other specialist equipment.
The process of near-surface monitoring consists of installing a network of gas monitoring wells at various points throughout the landfill site. These wells are outfitted with instruments capable of detecting the presence and quantity of gases in their surroundings. The data obtained by the detectors may be remotely transferred to a centralized monitoring and analysis system, which can be used to monitor variations in landfill gases over time and identify any concerning trends or patterns.
Soil gas monitoring systems detect the gas concentration in the soil's vapor space. Utilizing instruments or boreholes, soil gas concentrations are determined at deep. The method of ambient air monitoring examines the levels of volatile organic chemicals (VOCs) and pollutants in the air surrounding a landfill.
Another technique, "emissions monitoring" measures the rate at which gases are released from a stationary source, such as flares or the landfill's surface. There is also a range of remote-sensing landfill gas analysis technologies, like thermal imaging cameras and laser sensors that may be utilized at dump sites. These technologies have abolished the use of physical sampling or the deployment of monitoring wells and may be implemented to identify the number of landfill gases.
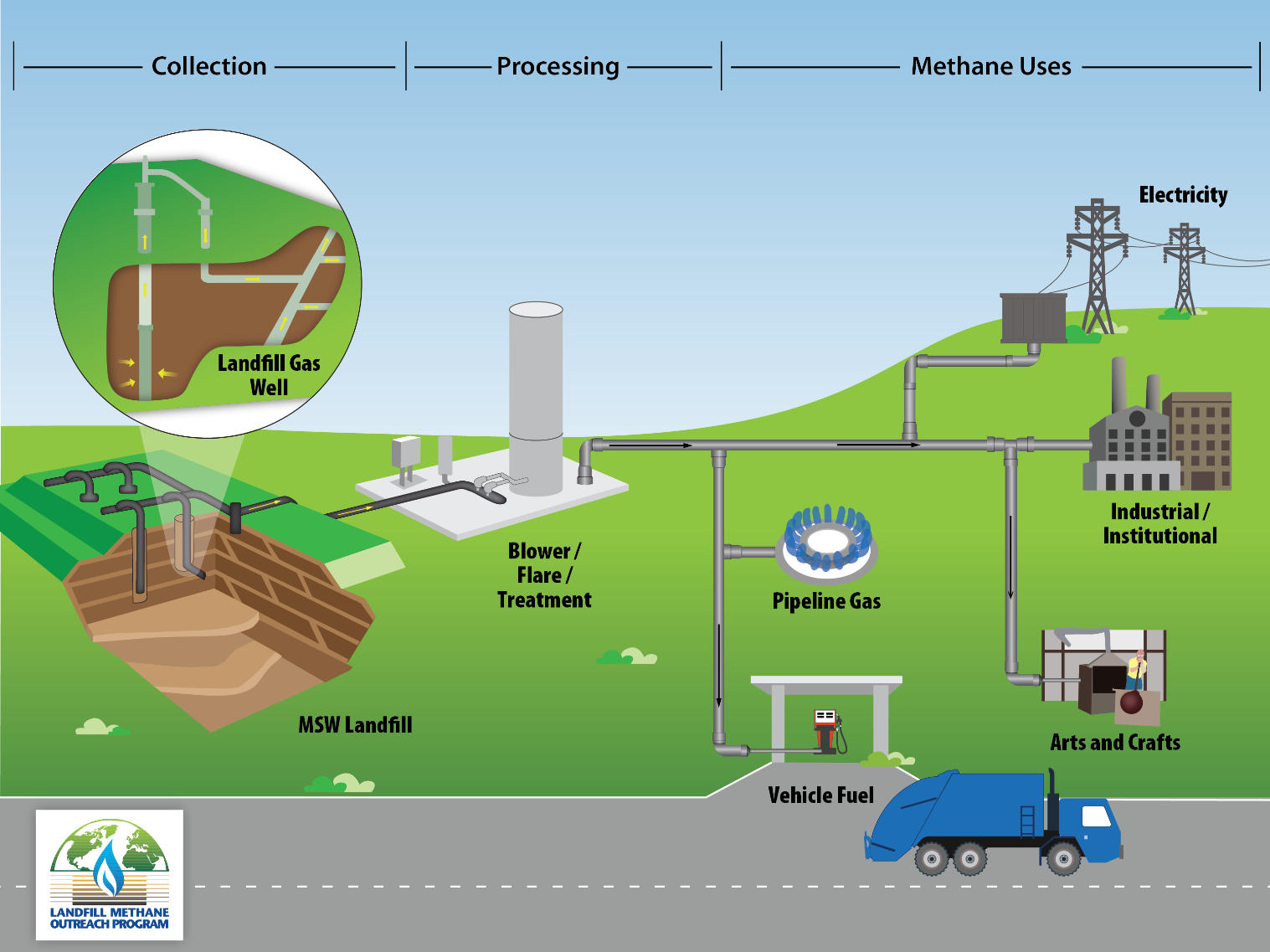
The illustration depicts the gathering and treatment of LFG to generate methane for numerous applications Image Credit: United States Environmental Protection Agency epa.gov/lmop/ basic-information-about-landfill-gas
Equipment for Landfill Gas Analysis
Some general equipment has been mentioned previously for use at landfill sites. These include gas sampling probes, gas chromatographs, monitoring wells, infrared cameras, and laser-based gas monitoring instrumentation.
However, several companies manufacture specialized instruments which are frequently utilized in landfill gas analysis.
Geotech offers a variety of LFG measurement and analysis techniques for periodic ground gas monitoring in boreholes for comprehensive site evaluations below ground level. The Landtec GEM™ 5000 Portable Gas Analyzer is intended particularly for monitoring Landfill Gas (LFG) collection and control systems in landfills. The GEMTM 5000 collects and analyses landfill gas samples for methane, carbon dioxide, and oxygen, with possibilities for further analyses. It determines balance gas, flow (SCFM), and calorific value with six times the accuracy and twice the speed of previous methods. Its modest weight and small size are significant benefits for reliable portable landfill gas readings.

Image Credit: Engineer studio/Shutterstock.com
Furthermore, RKI Eagle 2 is a portable landfill gas meter of the second generation, that can monitor up to six gas mixtures in real time. In addition, the Ion Science GasClam® 2 is the first in-situ drilling gas meter capable of detecting a broad spectrum of gases often encountered in environmental boreholes. It is designed for situations in which measurements are logged at user-defined frequencies and may be examined inside the GasClam program or exported for analysis in Excel or other CSV-supported apps.
Another company, PRM Filtration, combines robust, fixed-position, periodic, gas-monitoring instruments into its Landfill Gas (LFG) products. Its stationary Landfill Gas Analyzer monitors CH4, O2, and CO2. The Siemens ULTRAMAT is a multi-component gas analyzer that is ideally suited for Landfill Gas operations. Computerized calibration reduces the requirement for reference gases. There are IR, UV, H2S, and O2 sensors available, and the enhanced menu-driven navigation makes service staff operations more efficient.
Esders manufactures the GOLIATH Biogas – 201057 which is a robust, explosion-proof gas measuring device with an inbuilt membrane pump and a rechargeable NiMH battery designed for biogas, landfill gas, and sewage gas. Several other companies offer various products all over the world continuously improving landfill gas analysis capabilities.
Latest Research
The latest research published in Proceedings Volume 12163, International Conference on Statistics, Applied Mathematics, and Computing Science studied a massive landfill in Beijing, and analysis of landfill gases as per the data of 18 years from 2003 to 2020 was performed. The estimation and verification were done by utilizing two prediction models: Scholl-Canyon and LandGEM.
Using the Scholl-Canyon model, the maximum landfill gas quantities emerged in 2009. Then, a gradual falling pattern emerged following the volume maximum. According to the LandGEM model, gas output grew over the whole research period. In 2009, landfill gas production hit a turning point and thereafter gradually rose.
Based on a comparison of real landfill gas production statistics from 2009 to 2020, landfill gas output has decreased sharply since 2009 and steadied since 2013. The estimation result from the LandGEM model cannot match the real data on landfill gas production. However, the real landfill gas production data shows a similar pattern to the Scholl-Canyon model's projection data.
Recent Trends in Landfill Gas Analysis
There have been numerous noteworthy recent breakthroughs in the domain of landfill gas analysis. There has been an increase in the usage of autonomous and remote monitoring systems in landfills in recent years. The utilization of "Smart Gas monitoring and Collection Systems" has effectively reduced greenhouse gas emissions from landfills.
Utilizing data analytics and visualization technologies to better comprehend and regulate landfill gas emissions is another major development. Specifically, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being applied in landfill gas analysis equipment to enhance the precision and effectiveness of gas detection and analysis. AI and ML algorithms may be used to evaluate data obtained from landfill gas monitoring systems to forecast future gas emissions and anticipate any difficulties or concerns.
Landfill Gas Market Trend
Fortune Business Insights has published a market study of Landfill gases. In 2020, as per the report, the worldwide landfill gas (LFG) market was worth $3.29 billion. It is anticipated to increase at a CAGR of 6.3% from $3.40 billion in 2021 to $5.21 billion in 2028, from 2021 to 2028. As a result of the COVID epidemic, however, a negative market trend of 5.3 percent was estimated for 2020. Nonetheless, governments are utilizing landfill gas for energy production, which is anticipated to offer the industry a big boost.
In short, landfill gas analysis is essential for the safety of human health and the environment and considerable research is being done to reduce the concentration of landfill gases and manufacture efficient equipment for rapid and accurate analysis.
More from AZoM: An Overview of Flue Gas Analysis
References and Further Reading
Derbyshire County Council, 2023. How landfill sites work. [Online]
Available at: https://www.derbyshire.gov.uk/environment/rubbish-waste/waste-strategy/landfill/how-landfill-sites-work/how-landfill-sites-work.aspx
East Sussex County Council, 2023. What is a landfill site?. [Online]
Available at: https://www.eastsussex.gov.uk/rubbish-recycling/how-we-manage-our-waste/landfill-sites/what-is-a-landfill-site
Envirotech, 2022. What Is Landfill Gas Monitoring?. [Online]
Available at: https://www.envirotech-online.com/news/gas-detection/8/breaking-news/what-is-landfill-gas-monitoring/59367
Esders, 2022 GOLIATH Biogas. [Online]
Available at: https://www.esders.com/products/201057/goliath-biogas/
Fortune Business Insights, 2022. Landfill Gas Market. [Online]
Available at: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/landfill-gas-market-105683
Geotech, n.d. Landfill Gas Monitors. [Online]
Available at: https://www.geotechenv.com/landfill_gas_monitors.html
PRM Filtration, n.d. Gas Flow Instrumentation. [Online]
Available at: https://www.prmfiltration.com/gas-flow-instrumentation/
United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2022. Basic Information about Landfill Gas. [Online]
Available at: https://www.epa.gov/lmop/basic-information-about-landfill-gas
Lu, P. et. al. (2022). Estimation and verification of landfill gas production by two typical prediction models in Gao Antun landfill. In International Conference on Statistics, Applied Mathematics, and Computing Science (CSAMCS 2021) .12163, 642-647. SPIE.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.