Induction heating is widely used in various aerospace and defense manufacturing applications. Its popularity arises from its versatility and efficiency, among other advantages, spanning a wide array of applications, including preheating for welding, brazing, heat staking, heat treatment, and much more.
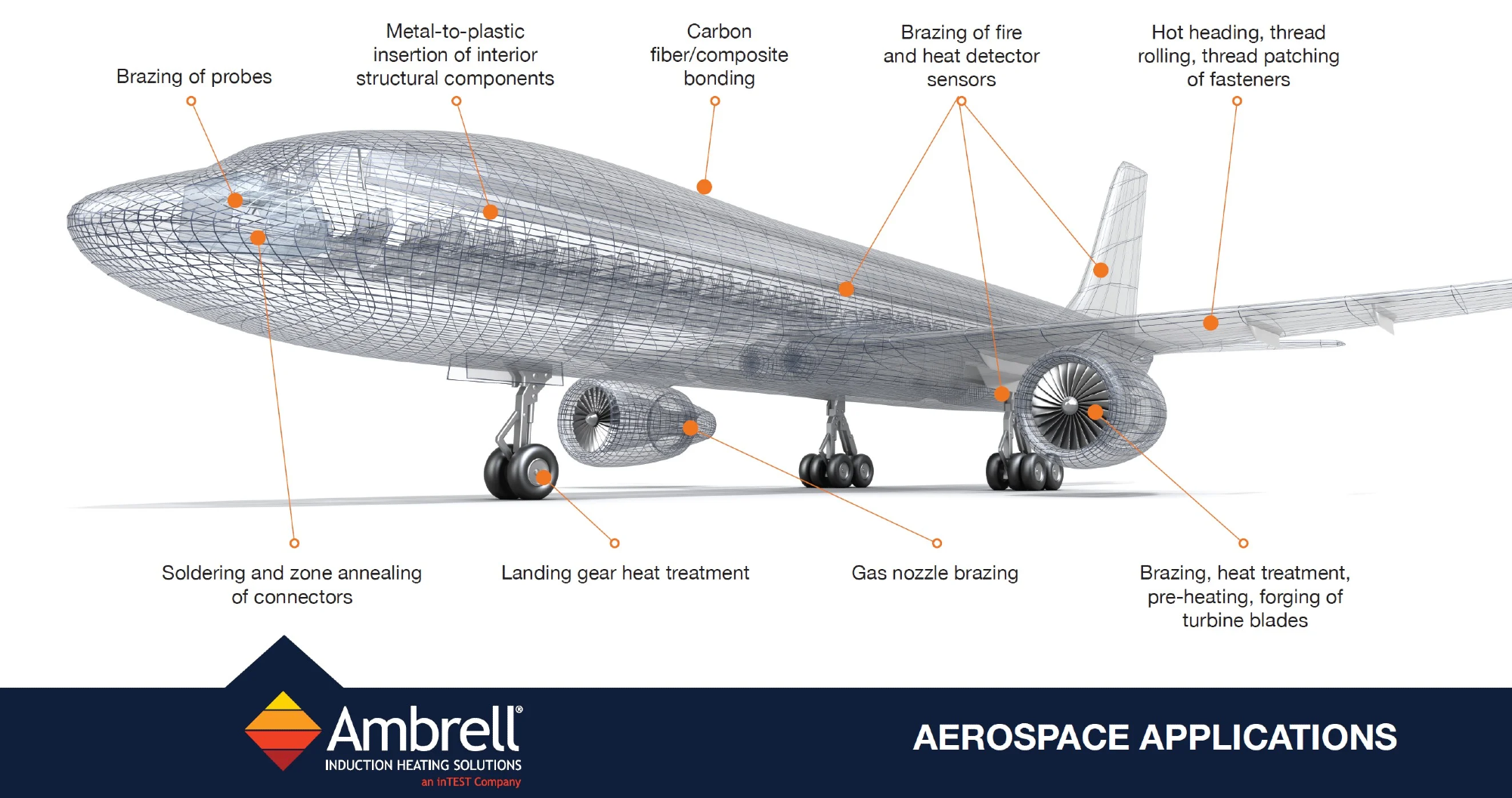
Image Credit: Ambrell Induction Heating Solutions
What is Induction Heating?
Induction heating represents a non-contact heating method that employs electromagnetic induction to warm electrically conductive materials.
A coil carries an alternating current, generating a magnetic field. When a conductive object is introduced into this field, it induces an electric current within the object. The object's resistance to this current generates heat, subsequently heating the part.
Primary Benefits of Induction Heating for Aerospace Manufacturing
Induction heating offers several key advantages for aerospace manufacturing, including:
- Efficiency: Induction heating boasts remarkable efficiency, with as much as 90% of electrical energy being converted into heat. This starkly contrasts other conventional heating techniques, which often fall short of this level. This efficiency translates into energy savings and environmentally friendly benefits.
- Accuracy: Induction can precisely target specific areas of a workpiece, avoiding the unnecessary heating of non-relevant sections. This precision is crucial in aerospace manufacturing, where precision tolerances are paramount.
- Repeatability: Induction heating is highly repeatable, ensuring uniform results every time. This consistency is vital for maintaining the quality of aerospace components.
- Speed: Induction heating rapidly warms materials, often outpacing alternative heating methods, thereby reducing production cycle times.
- Cleanliness: Induction heating is a clean process devoid of fumes or smoke, contributing to its safety and environmental friendliness.
Applications of Induction Heating in Aerospace Manufacturing
Induction heating serves a range of applications in aerospace manufacturing, including:
- Brazing: Induction heating is employed for brazing aerospace components, providing a robust and dependable joining method that is suitable for various aerospace needs.
- Heat treatment: Aerospace components such as landing gears, turbine blades, and engine parts benefit from induction heating for heat treatment, enhancing their durability, strength, and hardness.
- Preheating for Welding: Induction heating is used to preheat components before welding, notably turbine blades, offering swift, precise, and repeatable preheating that reduces cycle times.
- Other applications: Induction heating finds use in other aerospace manufacturing processes, including curing composites, soldering, annealing connectors, heat-staking internal structural components, bonding materials, and fitting parts through shrinkage.
Examples of Induction Heating in Aerospace Manufacturing
Outlined below are some examples showcasing the use of induction heating in aerospace manufacturing:
- Heat-treating landing gears and turbine blades
- Carbon fiber/composite bonding
- Various brazing applications, such as brazing probes, heat detector sensors, and gas nozzles
Ambrell offers complimentary application testing at THE LAB, allowing users to validate the feasibility of their applications before making a system purchase.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Ambrell Induction Heating Solutions.
For more information on this source, please visit Ambrell Induction Heating Solutions.