Sponsored by Metrohm AGReviewed by Olivia FrostOct 26 2023
Both potassium bicarbonate and potassium chloride are used in effervescent tablets to prevent low potassium levels in the blood.1
Image Credit: luchschenF/shutterstock.com
Utilizing the United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP-NF) monographs enables pharmaceutical labs and manufacturers to meet strict quality regulations regarding drugs and formulations.
The USP is participating in an international program to modernize many current monographs.
The monograph titled “Potassium Bicarbonate and Potassium Chloride Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution” involves various methods to determine these effervescent tablets' sodium, potassium, and chloride content.2
The USP has approved ion chromatography (IC) with suppressed conductivity detection to quantify chloride content in these potassium chloride and potassium bicarbonate effervescent tablets.2
The Metrosep A Supp 16 - 100/4.0 (L91) column separates chloride as required. This technique is validated in line with USP General Chapter Chromatography, system suitability.3
Sample and Sample Preservation
Samples are analyzed using a solution of the corresponding effervescent tablets, with no additional sample preparation being necessary.
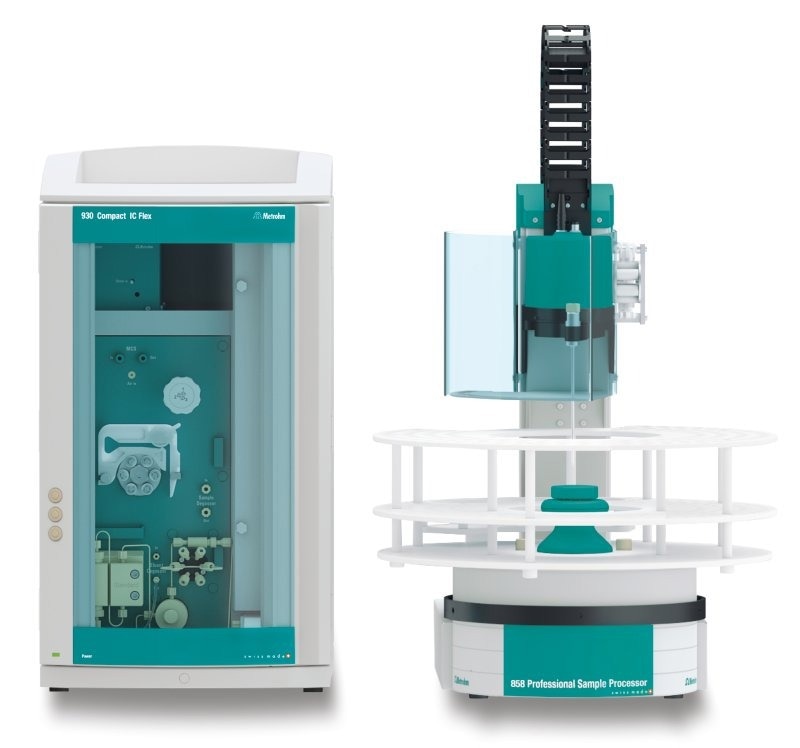

Figure 1. Instrumental setup including a 930 Compact IC Flex Oven/SeS/PP and an 858 Professional Sample Processor. Image Credit: B&W Tek
Experimental
A total of 50 g (equivalent to the weight of 10 tablets) of finely powdered potassium chloride and potassium bicarbonate effervescent tablets for oral solution is added to a 2000 mL volumetric flask to prepare a sample stock solution (4434.52 μg/mL chloride). The powder is then dissolved in 200 mL of ultrapure water (UPW).
The volumetric flask is filled to the mark once the effervescence ends. A small volume (1.692 mL) of this stock solution is removed, added to a 500 mL volumetric flask, and filled to the mark with UPW.
This final sample solution holds 15.0 μg/mL chloride. The 15 μg/mL working standard solution is prepared using a USP Potassium Chloride RS standard.
Samples and standard solutions are directly injected into the IC using an 858 Professional Sample Processor, as shown in Figure 1. A Metrosep A Supp 16 – 100/4.0 column separates chloride from other anions.
This anion-exchange column comprises a strong ion exchanger made from monodisperse porous polystyrene/divinyl benzene beads and quaternary amines. The column meets the criteria for specific USP techniques employing the USP chromatographic column packing L91.
A six-point linear calibration curve with a concentration range of 2.25 to 22.50 μg/mL chloride is used to calibrate. Subsequently, the sample is analyzed in duplicate.
Table 1. Requirements for the IC method for chloride determination as per USP Monograph «Potassium Bicarbonate and Potassium Chloride Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution» 2. Source: B&W Tek
| Column with L91 packing |
Metrosep A Supp 16 - 100/4.0 |
| Eluent |
15 mmol/L sodium carbonate,
1.5 mmol/L sodium hydroxide |
| Flow rate |
0.8 mL/min |
| Temperature |
45 °C |
| Injection volume |
20 μL |
| Detection |
Suppressed conductivity |
Results
In line with the USP Monograph titled “Potassium Bicarbonate and Potassium Chloride Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution,” the IC assay for chloride content was validated.2 The chloride determination in the sample was calculated with 101.2% accuracy, as shown in Figure 2. This value satisfies the acceptance criteria.
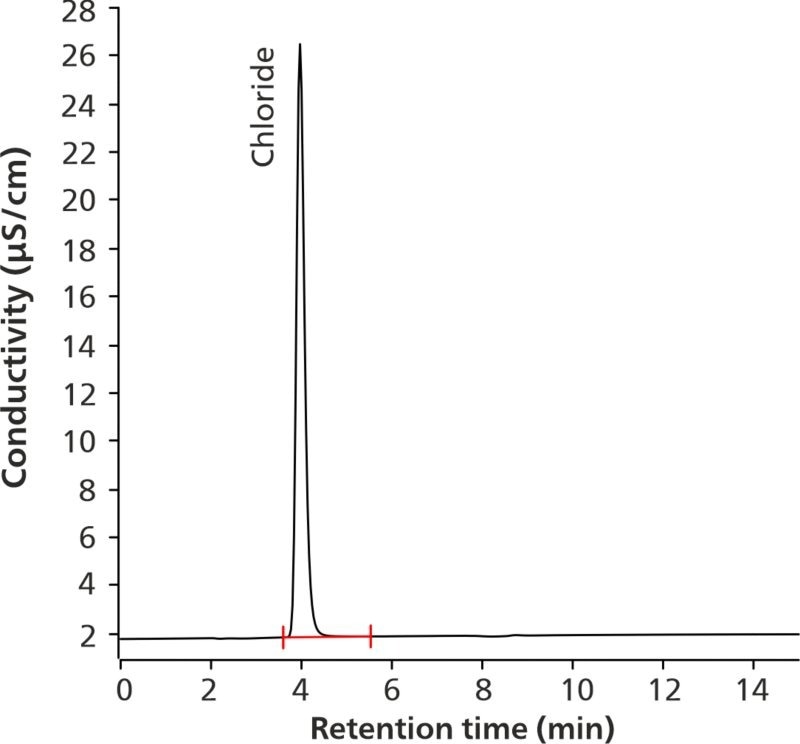
Figure 2. Chromatogram of 15.0 μg/mL chloride in the sample solution (101.1% recovery of the nominal concentration). Image Credit: B&W Tek
All analytical quality requirements were fulfilled, for example, the correlation coefficient for chloride was determined to be 0.9998, and the relative standard deviation of repeated standard solutions was 0.05% (n = 6), as displayed in Table 2.
Table 2. Analytical quality criteria for method acceptance according to USP Monograph «Potassium Bicarbonate and Potassium Chloride Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution» 2. Source: B&W Tek
| Parameter |
Actual |
USP requirement |
Status |
| % RSD |
0.05 |
NMT 0.5 |
Pass |
| Tailing factor |
1.27 |
NMT 2.0 |
Pass |
| Recovery |
101.2% |
90–110% |
Pass |
| Resolution |
2.48 |
NLT 1.5 |
Pass |
Conclusion
The USP officially includes the presented method of using IC for chloride in potassium chloride and potassium bicarbonate effervescent tablets for oral solution.2
Chloride is separated using the Metrosep A Supp 16 - 100/4.0 column, which is a strong anion exchanger, corresponding to packing material L91. The robustness and reliability of this technique were shown, following the guidelines of the USP General Chapter.3
The setup detailed in this article is appropriate for the quantification of chloride, in accordance with the USP requirements. Additional USP techniques are presented in the flyer titled “Bring your USP methods up to date!”4
References and Further Reading
- Kardalas, E.; Paschou, S. A.; Anagnostis, P.; et al. Hypokalemia: A Clinical Update. Endocr Connect 2018, 7 (4), R135–R146. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-18-0109.
- Potassium Bicarbonate and Potassium Chloride Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution; Monograph; U.S. Pharmacopeia/National Formulary: Rockville, MD. https://doi.usp.org/USPNF/USPNF_M67253_01_01.html.
- Chromatography, General Chapter; U.S. Pharmacopeia/National Formulary: Rockville, MD. https://www.usp.org/sites/default/files/usp/document/harmonization/gen-chapter/harmonization-november-2021-m99380.pdf.
- Metrohm AG. Bring Your USP Methods up to Date!, 2023. 8.000.5436EN

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by B&W Tek.
For more information on this source, please visit B&W Tek.