This case study explores the feasibility of a solution that utilizes Fine Ceramics as a substitute for the cap material that protects electronic devices. In this solution, a gyro sensor (image stabilization sensor) is installed onto a ceramic base.
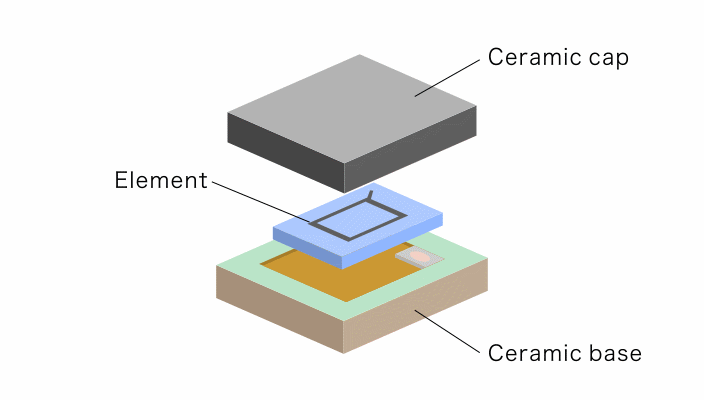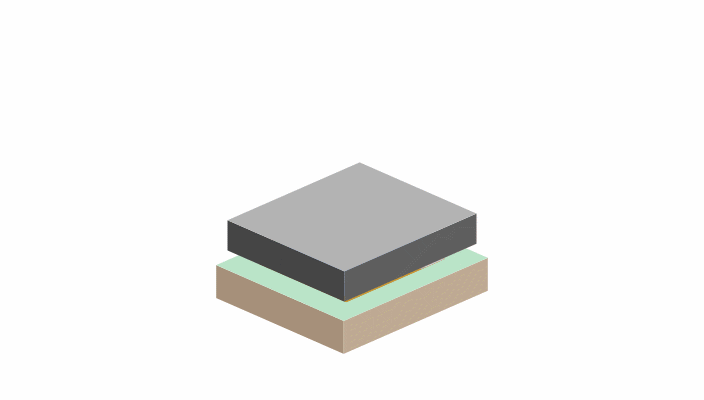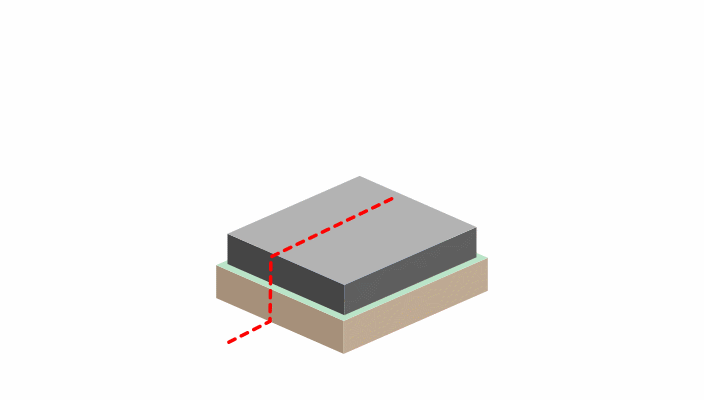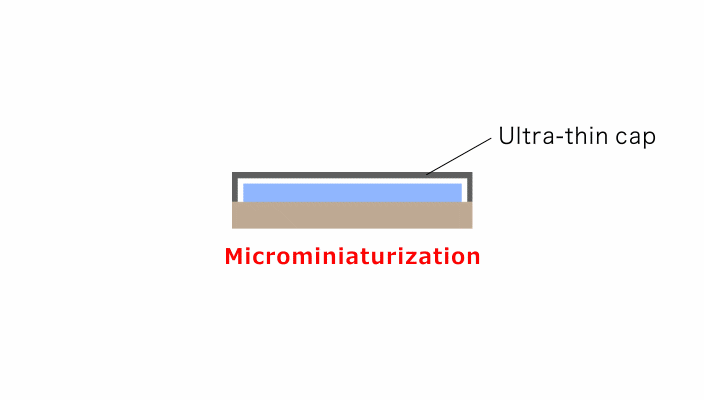
Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.
Challenge: Balancing Metal Strength with Cap Thickness Requirements
To diminish the height and size of electronic devices, the use of thinner caps was investigated.
When the thickness of a conventional metal cap is reduced to meet dimensional specifications, it loses the rigidity necessary to endure impact from the outside, which can create a short circuit.
A resin coating on the inner wall of the metal cap is then essential to prevent short-circuiting electrical conductivity.
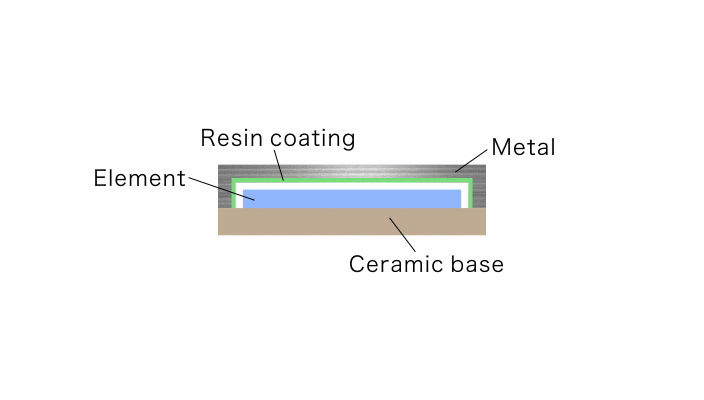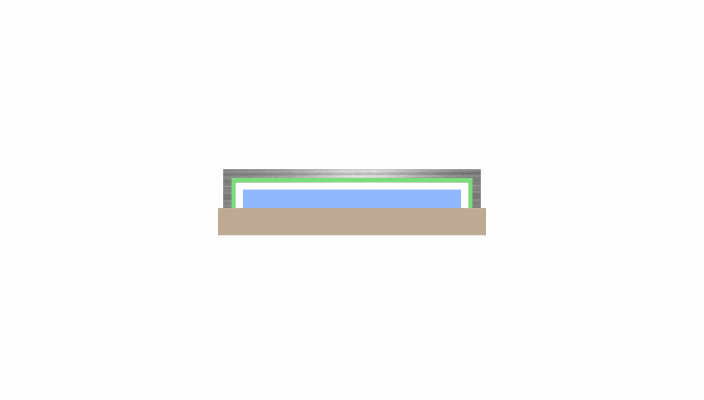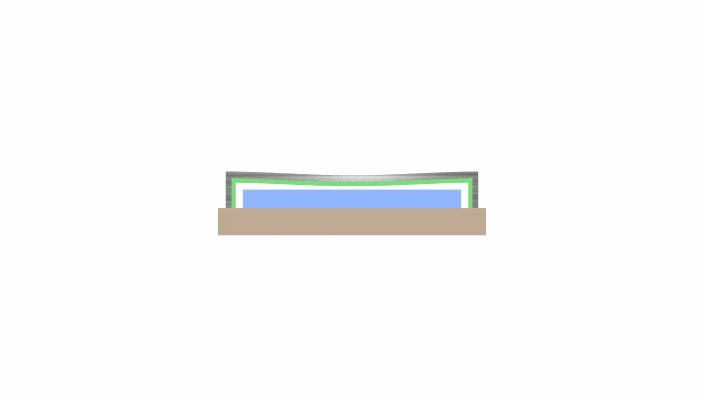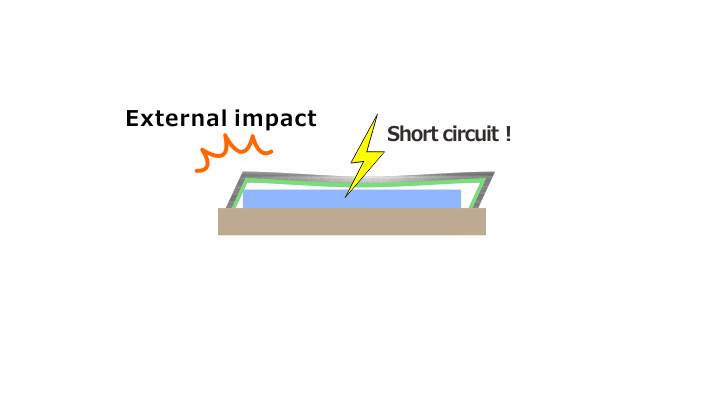
Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.
Conditions
- Thin material with superior rigidity
- Mass producible for use in electronic components
Solution: Adoption of High-Rigidity Alumina
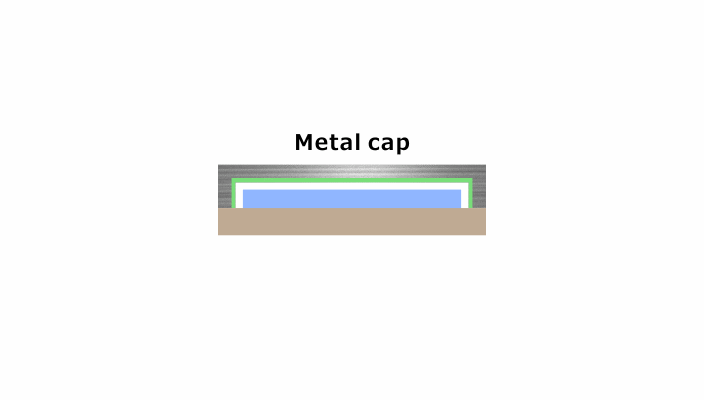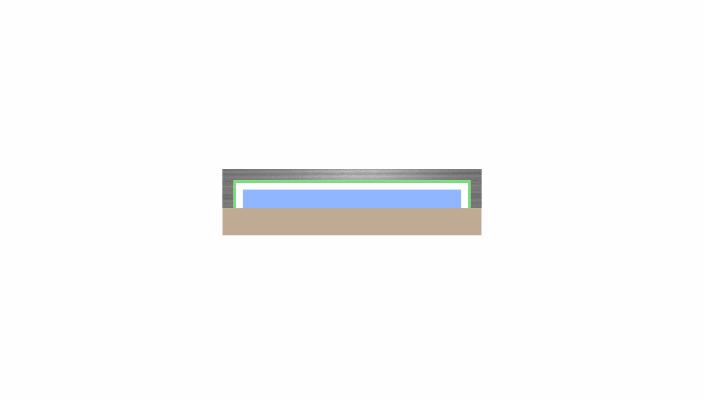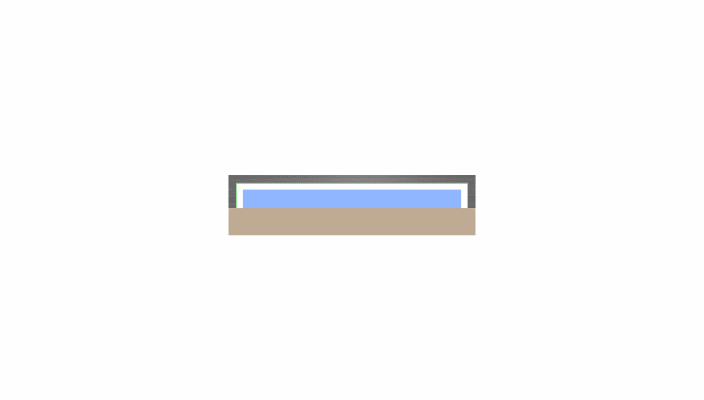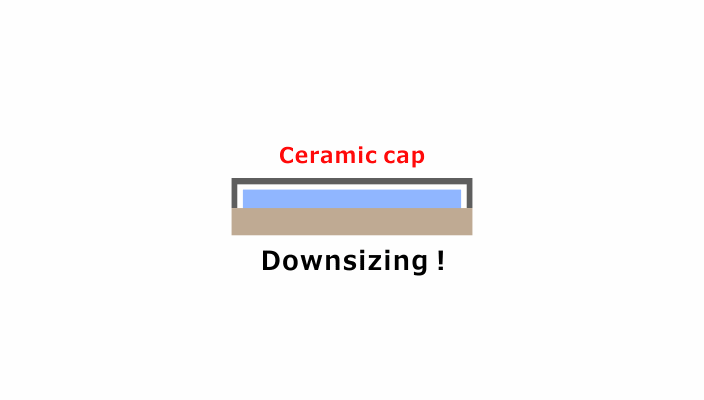
Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.
Kyocera's solution replaces the standard metal cap material with high-rigidity Alumina Fine Ceramics.
Result: Successful Size Reduction by Cap Thinning
Transitioning from metal to high-rigidity Fine Ceramics allowed for a reduction in cap thickness and height, thus contributing to the miniaturization of electronic devices.
Employing an electrically insulating Fine Ceramic material for the cap has also eliminated the need for resin coating, allowing further reduction in clearance within the device.
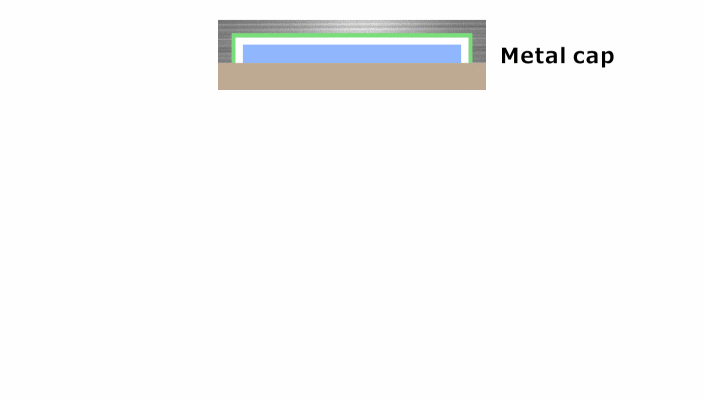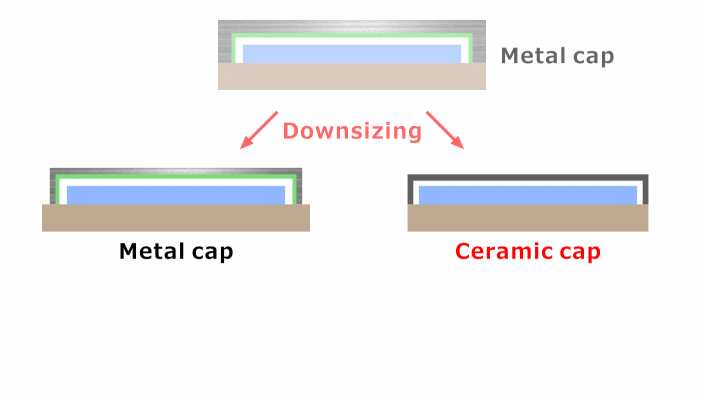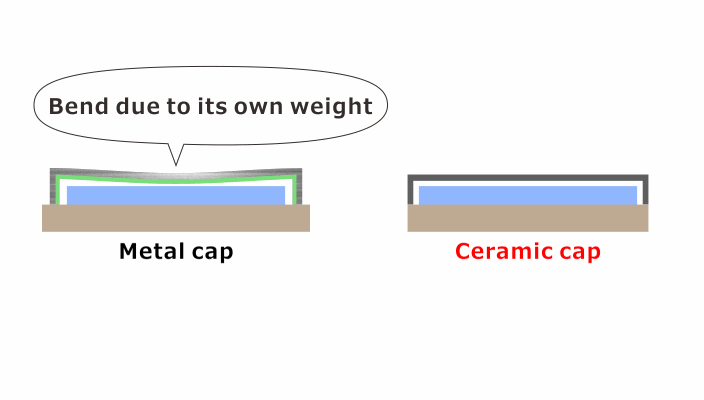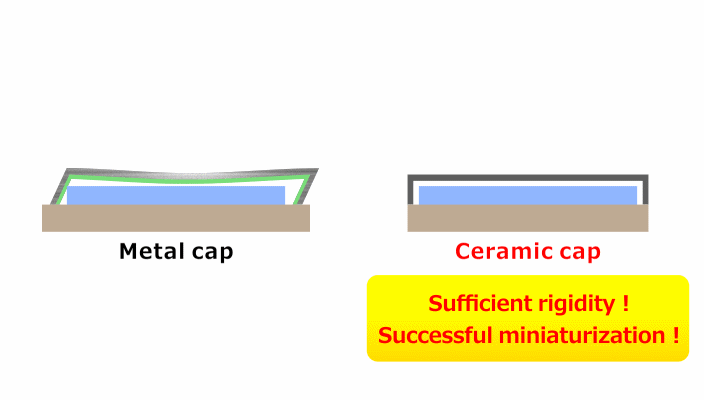
Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.
*Structures in the pictures and animation have been simplified.
*Material property can change depending on operating conditions.

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Kyocera International, Inc.
For more information on this source, please visit Kyocera International, Inc.