For over five decades, Kyocera’s Fine Ceramic materials, components, semiconductor packages, and electronic devices have been instrumental in advancing space exploration.
Kyocera has a robust legacy of delivering advanced ceramic components for space and astronomy applications. These applications auxiliary power units, astronomical instruments, satellites, space probes, telescope components, and space vehicles.
Throughout the years, Kyocera has cultivated a robust collaboration with JAXA. This includes the development of components integral to the Hayabusa mission, which involved a robot spacecraft collecting a sample from a nearby asteroid.
Kyocera has identified Fine Cordierite as a superior and advanced ceramic for an assortment of applications, including structural components and satellite mirrors. Kyocera remains steadfast in its commitment to consistently innovate and create new value at the forefront of technology.
Ceramic Materials for Space & Astronomy Applications
- Low Thermal Expansion Ceramic "Fine Cordierite"
- Facilitating High Precision and Lightweight Components

Optical Mirror with Light-Weight Design. Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.
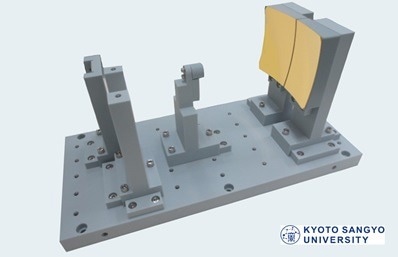
Low Thermal Expansion Optical System. Image Credit: ©Kyoto Sangyo University
-
Silicon Carbide and SiSiC
- High Stiffness and High Thermal Conductivity
- Applicable to Optical Mirror and Structural Components

SiC Optical Mirror. Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.

SiSiC Structural Parts. Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.
- Features of High Strength, High Rigidity, and Excellent Light Transmission

Machined Sapphire Products. Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.

Sapphire Window with Ultra-High Vacuum Property. Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.
- Assembly of Ceramic and Metal Parts for Ultra-High Vacuum Applications
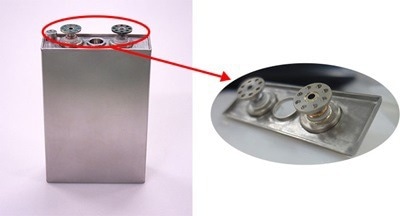
Lithium-ion Battery Seal for Hayabusa. Image Credit: © The Furukawa Battery Co., Ltd.

Metallized Products for Liquid Hydrogen. Image Credit: Kyocera International, Inc.
Camera Lens Spacer: Fine Cordierite Structural Components
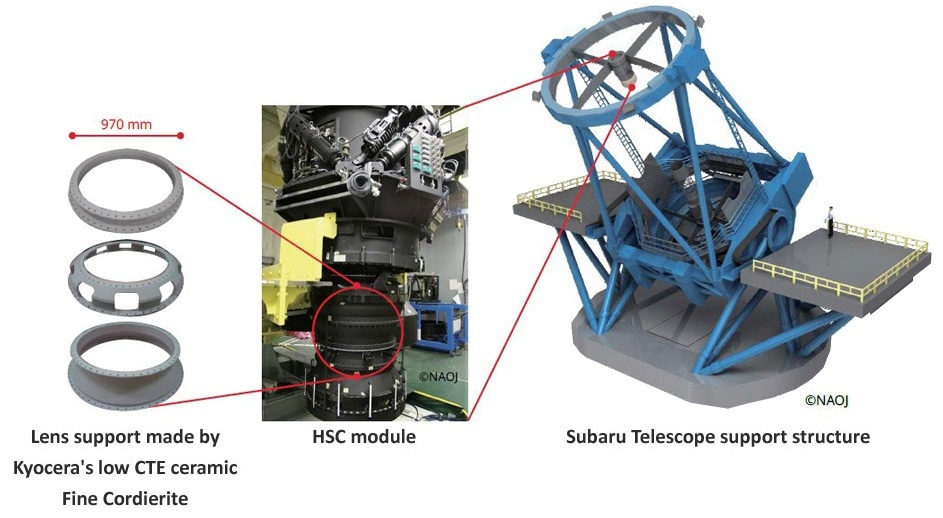
Image Credit: NAOJ
"10n World": Fine Ceramics Supporting Space Observation 13 Billion Light-Years Away
Video Credit: NAOJ
The Subaru Telescope, an 8.2-meter (320-inch) optical infrared flagship telescope managed by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), is located at the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii.
In 2012, when NAOJ integrated a new super wide-angle camera (Hyper Suprime-Cam, or HSC) into the Subaru Telescope, there were two design criteria for adaptive optics. One was to create a larger lens aperture and the other was to reduce the weight of the lens.
Kyocera’s cordierite emerged as the optimal material to accomplish the design requirements for the lens support. Cordierite’s superior characteristics allowed for a sleek design with ample material strength and rigidity to support the lens structure while minimizing deformation caused by temperature fluctuations.

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Kyocera International, Inc.
For more information on this source, please visit Kyocera International, Inc.