The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), a prominent global research institution specializing in particle physics, gained widespread recognition in 2012 for the discovery of the Higgs boson.
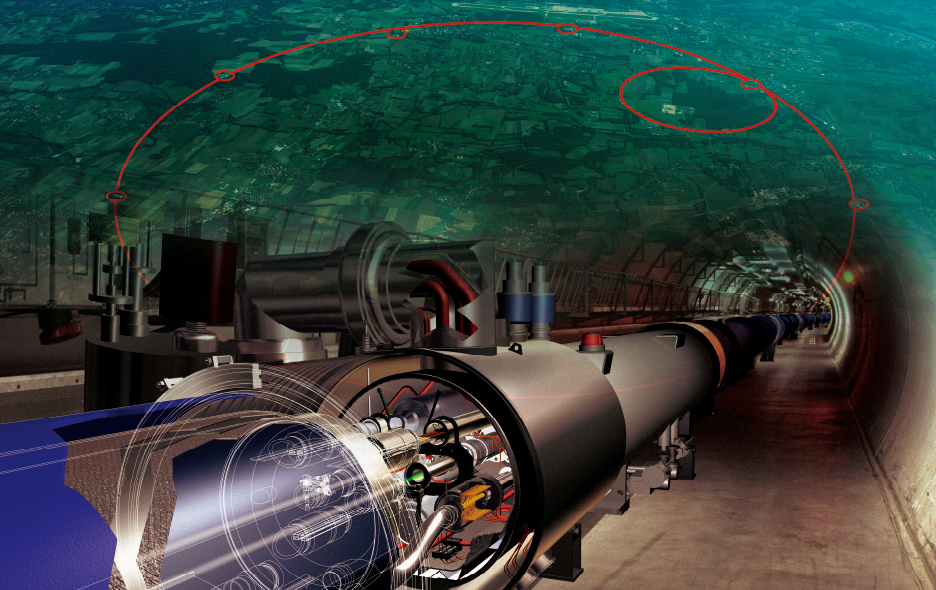

The Large Hadron Collider. (Photo: Courtesy of the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN))
CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is situated in an underground tunnel 100 meters below the surface with a circumference of 27 km. It is employed in experiments that propel protons to nearly the speed of light before colliding head-on.
Kyocera's Fine Ceramic components perform a pivotal role in controlling protons and measuring experimental outcomes, enabled by their unparalleled reliability and distinctive attributes that ensure elevated levels of airtightness, insulation, and heat resistance.
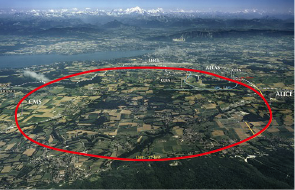
The Large Hadron Collider with a 27-km circumference. Image Credit: CERN

Fine Ceramic chamber. Image Credit: Kyocera International Inc.

Feedthrough. Image Credit: Kyocera International Inc.

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Kyocera International, Inc.
For more information on this source, please visit Kyocera International, Inc.