Lubricating products such as greases need to be workable in all environments that the application may be used. This can include extremely low temperatures such as farming equipment in Siberia, or vehicles used at the South Pole (-40ºC).

Image Credits: maxuser/shutterstock.com
Cooling Effects
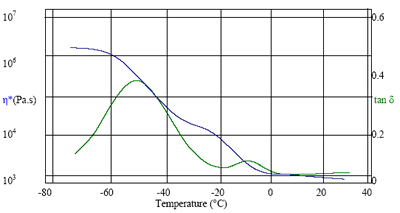
When cooled, the different fractions in the grease will freeze up individually and a corresponding peak should be evident in the Tan δ value. In parallel with the tan δ peak, the complex viscosity (η*) will of course increase.
|
|
|
Figure 1. Variation in viscosity and phase changes with temperature.
|
Interpretation Of Results
The oscillation results above clearly show the freezing points of each component from the peaks of the tan delta curve at c.-10ºC and c.-50ºC. The viscosity also shows two individual ‘drops’ tying in with the phase changes. The sample’s workability at any particular temperature can therefore be seen from the complex viscosity.
Measuring Temperature Induced Phase Changes
This mechanically assessed phase change is likely to be around 10ºC higher than that measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), because the phase change is frequency dependent and a DSC sample is at rest.
However, as most lubricant manufacturers need to determine the working range of a grease material at low temperatures, the Tg (or freezing point) measured by rheometry is often much more pertinent.
Conclusion
The melting point and glass transition temperatures can be accurately measured for any grease or lubricant compound using the Bohlin CVO where the transition occurs between -150ºC and 550ºC.
Measurement Conditions
|
Samples
|
Grease and high molecular weight lubricants
|
|
Geometry
|
PP15 serrated and a forced gas Extended Temperature Cell with a Low Temperature Extension unit (uses Liquid N2)
|
|
Single Frequency Oscillation
|
|
|
Strain
|
0.005
|
|
Frequency
|
1 Hz
|
|
Initial stress
|
100 Pa
|
|
Temperature range
|
30ºC to -70°C (or working temperature)
|

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Malvern Panalytical.
For more information on this source, please visit Malvern Panalytical.