|
Stress is defined as the force per unit area. Thus, the formula for calculating stress is:
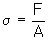
Where σ denotes stress, F is load and A is the cross sectional area. The most commonly used units for stress are the SI units, or Pascals (or N/m2), although other units like psi (pounds per square inch) are sometimes used.
Forces may be applied in different directions such as:
• Tensile or stretching
• Compressive or squashing/crushing
• Shear or tearing/cutting
• Torsional or twisting
This gives rise to numerous corresponding types of stresses and hence measure/quoted strengths. While data sheets often quote values for strength (e.g compressive strength), these values are purely uniaxial, and it should be noted that in real life several different stresses may be acting.
Tensile Strength
The tensile strength is defined as the maximum tensile load a body can withstand before failure divided by its cross sectional area. This property is also sometimes referred to Ultimate Tensile Stress or UTS.

Typically, ceramics perform poorly in tension, while metals are quite good. Fibres such as glass, Kevlar and carbon fibre are often added polymeric materials in the direction of the tensile force to reinforce or improve their tensile strength.
Compressive Strength
Compressive strength is defined as the maximum compressive load a body can bear prior to failure, divided by its cross sectional area.

Ceramics typically have good tensile strengths and are used under compression e.g. concrete.
Shear Strength
Shear strength is the maximum shear load a body can withstand before failure occurs divided by its cross sectional area.
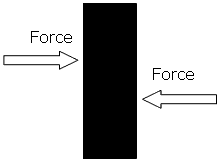
This property is relevant to adhesives and fasteners as well as in operations like the guillotining of sheet metals.
Torsional Strength
Torsional strength is the maximum amount of torsional stress a body can withstand before it fails, divided by its cross sectional area.
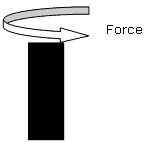
This property is relevant for components such as shafts.
Yield Strength
Yield strength is defined as the stress at which a material changes from elastic deformation to plastic deformation. Once the this point, known as the yield point is exceeded, the materials will no longer return to its original dimensions after the removal of the stress.
|