The development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) is gaining momentum because of their potential use as target-directed therapeutic agents in cancer treatment. The Drug Antibody Ratio (DAR) is one of the key factors for effective ADC design.
The DAR defines the level of the appended drug which directly affects both potency and potential toxicity of the therapeutic, and can have considerable effects on characteristics such as aggregation and stability. Hence determining DAR is essential in the development of innovative ADC therapeutics.
Drawbacks in Existing Drug-Antibody Component Analysis
UV spectroscopy or Mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF or ESI-MS) is typically used for DAR determination. UV absorption-based calculations are often complex due to similarities in extinction coefficients of the small molecule and antibody. Although mass spectrometry is a powerful technique for Mw determination, it relies on homogenous ionization and recovery between compounds. This does not always exist for ADCs.
Analysis Using ASTRA 6 Software Tool
This article describes a DAR determination technique based on SEC-MALS in combination with UV absorption and differential refractive index detection. UV traces for two model ADCs are depicted in Figure 1. Molecular weights of the entire ADC complexes are calculated directly from light scattering data.
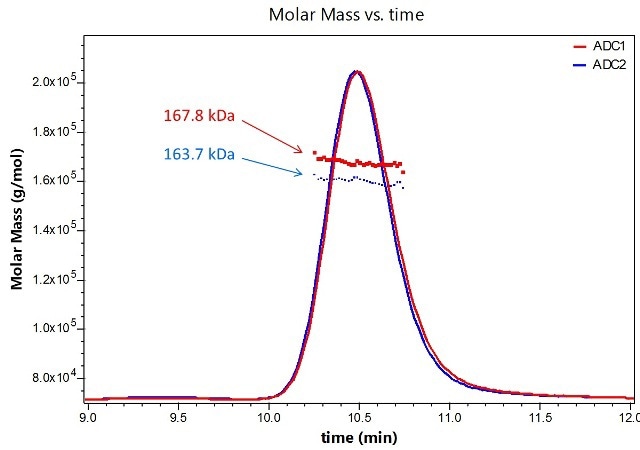
Figure 1. Molar masses for two distinct ADC formulations are determined using SEC-MALS analysis.
Component analysis is programmed within the ASTRA 6 software package through the use of the differential refractive index increments (dn/dc) and extinction coefficients, which are taken from the literature or empirically calculated for each species, to compute the molar mass of the entire ADC complex and for each component of the complex.
Here, alkylation of an antibody is done with a compound possessing a nominal molecular weight of 1250 Da, as illustrated in Figure 2. All antibody fractions have similar molar masses, meaning that the overall differences between the two formulations reveal distinct average DARs which are in line with the values acquired by orthogonal techniques.
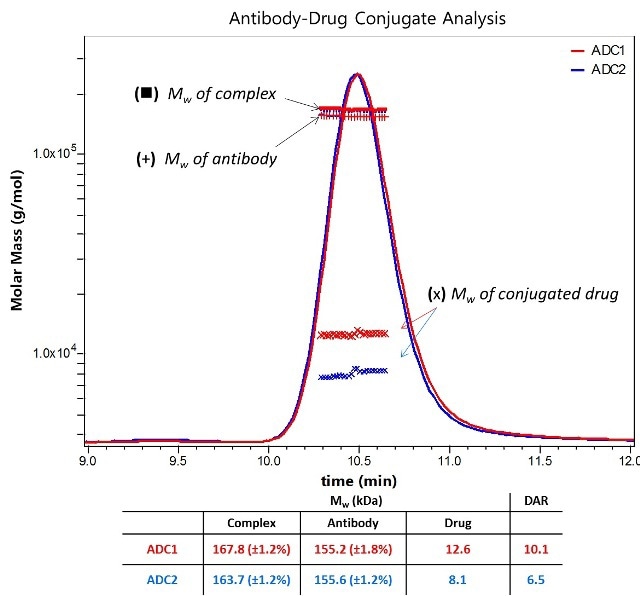
Figure 2. Molar Masses for the antibody and total appended drug are calculated in the ASTRA software package based on prior knowledge of each component’s extinction coefficient and dn/dc, allowing determination of DAR based on a nominal Mw of 1250 Da for an individual drug.
The total amount of attached pendant groups is represented by the molar mass traces for the conjugated moiety, while the horizontal trends represent that modification is homogenous across the population eluting in that peak.
About Wyatt Technology
Quality at Wyatt Technology begins by listening attentively to their customers. Wyatt strives to make all customer contact a positive experience. Regardless of whether the customer issue is one of service, innovation or product quality, Wyatt's aim is to delight the customer. Wyatt set and maintain the highest standards for production consistency, while incorporating flexibility and innovation into each process. Seeking innovative ways to improve work habits and adopt the best practices.
Wyatt focuses on a number of specific industries:
- Biotechnology
- Chemical
- Pharmaceutical
- Academic
- Government
- Medical Devices.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Wyatt Technology.
For more information on this source, please visit Wyatt Technology.