Poly (cyclohexene propylene carbonate) is a solid polymer. It is an amorphous, clear, readily processible plastic possessing long term mechanical stability.
Technical Name Poly (cyclohexene propylene carbonate)
Chemical Structure
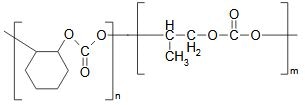
Image Credit: Empower Materials
Molecular Weight Available Approximately 150,000 - 200,000
Applications
- Binder applications for metal, ceramics or glass powders
- Decomposable channel former
- Pore former
Typical Physical Properties
| Property |
Value |
| Density (g/cm3) |
1.04 |
| Decomposition Temperature (°C) |
250 (onset estimate) |
| Glass Transition Temperature (°C) |
90-100 |
| Solubility |
Upon request |
Product Delivery Form It is available as a film, granulate or in solution form.
Benefits
- Upon decomposition, QPAC®100 leaves less than 10 ppm ash residue, resulting in outstanding mechanical and/or electrical properties
- Low temperature decomposition is exceptional for thermal sensitive materials and is more efficient than other binders
- QPAC®100 has a higher Tg than QPAC®25 and QPAC®40 offering more stability at higher temperatures
- Decomposition can occur in a wide range of atmospheres including oxygen, air, nitrogen, argon, hydrogen and vacuum
TGA FOR QPAC®100
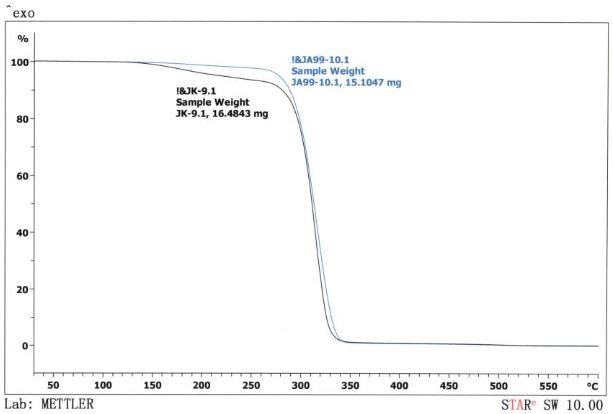
Image Credit: Empower Materials