Nippon Steel Corporation and Kobe Steel, Ltd. announce that they plan to begin construction of a plant to recycle steel mill dust into direct reduced iron. As part of the objectives to enhance and expand their alliance, the two companies decided to carry out the project through a joint venture and undertook preparations to start the new business.
Construction of the plant will commence as outlined below:
1. Purpose of the Joint Business
(1) Resource Recycling of Byproduct from Steelmaking Process
(Producing Competitive Iron Units)
The joint venture plans to stably produce competitive iron units by recycling steel mill dust, a byproduct from the steelmaking process. Due to the sharp increase in steel demand centered on emerging countries, raw material prices have escalated. This business would be an extremely effective approach to secure competitive iron units in a business environment of unstable raw material prices and availability.
(2) Promotion of Regional Recycling and Zero Emissions
Through the joint business, both Nippon Steel and Kobe Steel will be able to promote steel dust recycling and zero emissions in the local region beyond the framework of each individual company by integrating the process technology established by Kobe Steel(1) and operation know-how established by Nippon Steel on the recycling and effective utilization of steel dust.
In addition to the new business, Nippon Steel will be able to use its existing dust recycling plants at its Hirohata Works to recycle steel mill dust generated from the steelmakers, including alliance partners, located in the Kansai region.
2. Outline of the Joint Business
(1) Nippon Steel and Kobe Steel will use steel mill dust and iron ore fines from their steel mills as raw materials to recycle iron into direct reduced iron (DRI) and recover zinc. For this purpose, a joint venture company has been established within Nippon Steel's Hirohata Works.
Outline of the Joint Venture
Name: Nittetsu Shinko Metal Refine Co., Ltd.
Capital: 900 million yen
Equity share: Nippon Steel 70%, Kobe Steel 30%
Location: Nippon Steel Hirohata Works (in Himeji, Hyogo Prefecture)
Established: October 2008 (Received approval to recycle steel dust in March 2009)
(2) Nittetsu Shinko Metal Refine will construct a direct reduction plant utilizing Kobe Steel's FASTMET(r) Process within Nippon Steel's Hirohata Works. Nittetsu Shinko Metal Refine will recycle the steel mill dust it receives and use it to produce DRI. The DRI will be supplied to Nippon Steel and Kobe Steel, with a portion also going to Sanyo Special Steel Co., Ltd., a group company of Nippon Steel.
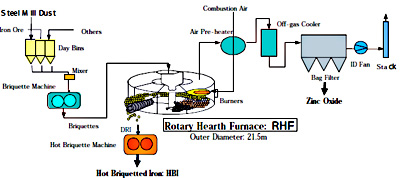
(3) In the FASTMET Plant, steel mill dust is heated to a high temperature in a doughnut-shaped Rotary Hearth Furnace (RHF) and quickly undergoes reduction to make DRI, which is then formed into hot briquetted iron (HBI). At the same time, the zinc in the steel mill dust is recovered. As the steel mill dust and zinc are effectively recycled, the DRI can be used as an alternative or supplement to scrap and iron ore as the main raw material, and the recycled zinc can reduce the use of zinc ore. Recycling also promotes zero emissions. .
Outline of Capital Investment
Main equipment: Rotary Hearth Furnace, hot briquette machine
Treatment capacity: Approximately 220,000 metric tons per year
Total investment: Approximately 10 billion yen (for the RHF & related equipment)
Planned start-up: October 2011
The new RHF will raise the number of RHFs at Hirohata Works to four. In conjunction with the construction of the new RHF, Nippon Steel plans to utilize the Nos. 1, 2 and 3 RHFs currently in operation at Hirohata Works to additionally process the steel mill dust from alliance partners Sumitomo Metal Industries, Ltd. and Nisshin Steel Co., Ltd.
This joint business will be a countermeasure for the decreasing quality and higher prices of raw materials. Nippon Steel and Kobe Steel intend to smoothly go forward with the new joint business, while continuing to actively strengthen and promote their cooperative relationship.