A research team led by Cun-Zheng Ning, who serves as Professor of electrical engineering at the Arizona State University, has synthesized a new compound crystal material dubbed erbium chloride silicate in the single-crystal nanowire form, paving the way to design future-generation computers, enhance internet capabilities, improve the quality of the sensor and solid-state lighting technology and improve the conversion efficiency of the silicon-based solar cells.
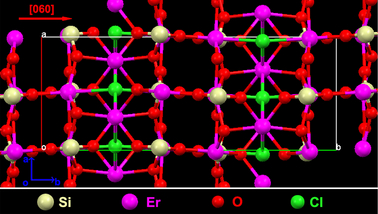 The image, called a “ball-and-stick modal,” illustrates the crystal structure of the new erbium crystal compound developed at ASU’s Nanophotonics Lab. The four different colors represent the four elements that were combined to produce the new material.
The image, called a “ball-and-stick modal,” illustrates the crystal structure of the new erbium crystal compound developed at ASU’s Nanophotonics Lab. The four different colors represent the four elements that were combined to produce the new material.
Erbium releases photons at 1.5 µm of wavelength, to be used as a dopant in optical fibers to augment the signal of telephones and Internet. The innovative erbium compound has erbium atoms 1,000 folds more than that of in other erbium materials, enabling the integration of several devices into a chip-scale system, Ning said. When incorporated with silicon, the new compound crystal material can integrate communication and computing capabilities to the low-cost silicon system, while improving the internet and computing functions at the same time, he said.
The novel erbium material can increase the solar cell conversion efficiency by transforming two or more photons that carry less energy into a single photon with more energy. When silicon absorbs this single, high-energy photon, the conversion efficiency of the solar cell will get increased. The material’s color-conversion capability of converting ultraviolet light into visible light makes it suitable for producing white light for solid-state lighting equipment.
The usual method involves the doping of host materials, including silicon, silicon oxide and other glasses and crystals, with erbium. In the new crystal material, erbium is integrated as an element of a homogenous compound. As it has more number of erbium atoms, the material delivers improved optical activity to generate powerful lighting. Ning stated that the synthesis of the material in the superior quality single-crystal form makes it to have better optical quality when compared to other doped materials.
The research team discovered the innovative material accidently during its experiment to dope erbium with silicon nanowires. The team is now working on the application of the innovative erbium compound to improve the conversion efficiency of the solar cells to produce tiny optical amplifiers for chip-scale photonic devices for high-speed internet and computers. From its initial findings, the team discovered that the new material has unique properties and high optical quality, Ning said. More about the material is yet to be discovered, he concluded.