A new world record of 8 TeV collision energy has been set by the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), a highest-energy particle accelerator built by CERN. This represents the commencement of observation of physics data for the year 2012.
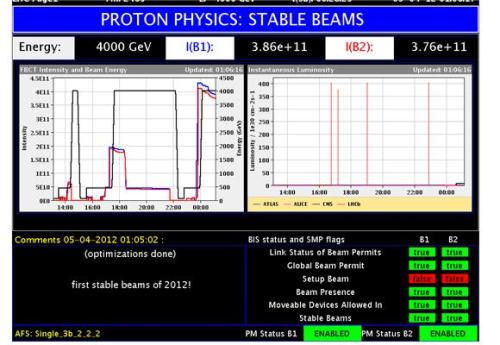 Collision of two 4 TeV proton beams
Collision of two 4 TeV proton beams
The team was able to observe stable beams, when two TeV proton beams collided at the four interaction points of the LHC. This considerably increases the discovery potential of the instrument.
Steve Myers, Director for Accelerators and Technology at CERN, stated that they have been successful in operating the two beams at 3.5 TeV for last two years and this gave them the confidence to amplify the energy in 2012 with no risk to the LHC. Sergio Bertolucci, Research Director at CERN, added that the improvement in energy means maximizing the LHC’s discovery potential and therefore, 2012 seems to be a new era for particle physics.
Though the enhancement in the collision energy is comparatively low, it contributes to an added discovery potential for few hypothetical particles. Based on the prediction supersymmetry, a theory in particle physics, some of these particles will be produced abundantly at the higher energy. Standard Model Higgs particles will be created in a large quantity at 8 TeV energy than at 7 TeV.
Currently, the machine is scheduled to operate till the end of 2012 and then it will be shutdown to organize it for running at 6.5 TeV per beam in late 2014. The ultimate aim of the LHC team is to increase the total collision energy to 7 TeV.