Imec announces that it has developed an ultra-thin hybrid floating gate cell with demonstrated functionality. The results, which are presented at this week’s 2012 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM, San Francisco, USA, December 10-12, 2012), are an important step for further scaling of NAND Flash technology towards the 10nm half pitch node and beyond.
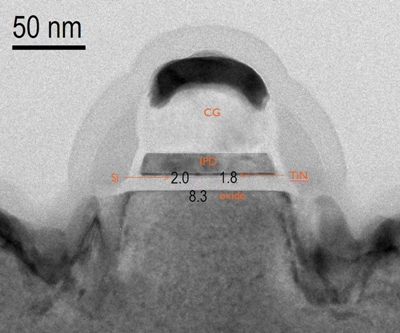 TEM of Ultra thin Hybrid Floating Gate (HFG) with high-k Inter Gate Dielectric (IGD) extending Flash scaling beyond 1x node.
TEM of Ultra thin Hybrid Floating Gate (HFG) with high-k Inter Gate Dielectric (IGD) extending Flash scaling beyond 1x node.
The increasing need for high density flash memory has driven the scaling of the technology down to the 19nm half pitch node which is currently in production. However, from such dimensions on, the Control Gate (CG) can no longer be wrapped around the Floating Gate (FG), urging for a planar floating gate architecture. But planarising the technology results in a reduced coupling of the CG and FG. Consequently, the performance degrades due to leakage through the Interpoly dielectric (IPD). In order to recover the performance in planar devices, imec has developed a Hybrid Floating Gate (HFG) architecture featuring a low work function material at the bottom and a high work function material at the top. The functionality has been successfully demonstrated in integrated cells. Moreover, to limit the cell to cell interference occuring in a high-density NAND array, imec scaled down the thickness of the hybrid floating gate to only 4nm.
Jan Van Houdt, Director of the Flash memory program at imec: “Flash memory is the state-of-the-art technology in all mobile devices, ranging from cell phones, digital cameras, USB sticks, MP3 players and tablets, to solid state drives. To address the exploding demand for memory capacity in such devices, imec is pushing the roadmap of the current Flash technology. We are excited to have demonstrated this functional ultra-thin hybrid floating gate cell technology, as an enabling solution for our partners to scale Flash memory down to 10nm and further increase the memory capacity in next-generation mobile devices”.
These results were obtained in cooperation with imec’s key memory partners INTEL, Micron, Samsung, SanDisk, Toshiba and SK Hynix.