Scientists from HSE Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (HSE MIEM) and the Institute of Non-Classical Chemistry in Leipzig have suggested a new theoretical model of supercapacitors that considers the properties of a cation. This significantly affects the electric differential capacitance of supercapacitors.
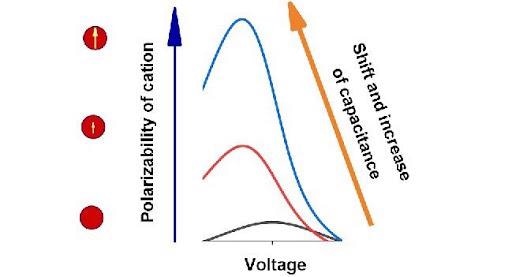 Growth of polarizability or permanent dipole moment of cations leads to considerable growth of differential capacitance. Image Credit: Yury A. Budkov et al.
Growth of polarizability or permanent dipole moment of cations leads to considerable growth of differential capacitance. Image Credit: Yury A. Budkov et al.
This is the first study of its kind in electrochemistry. The researchers think that the model will enable engineers to make more strong energy sources in the future. The study outcomes were published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. The study was done with the help of a grant by RSF.
Supercapacitors are devices that have the ability to store energy in an electric double layer on the surface of an electrode (for instance, electrodes of gold, carbon, platinum, and work like this). A supercapacitor, or ionistor, is a hybrid of a capacitor and an accumulator and has various benefits in comparison.
It features both a high speed of electric power accumulation and greater capacitance. By the value of capacitance per unit mass, supercapacitors surpass ordinary capacitators significantly, while electric voltages are much lower.
“Capacitance is the main characteristic, which demonstrates how much electric power the electric double layer can accumulate.”
The effective distance between a supercapacitor’s “plates,” which are a layer of ions and a metal electrode, measures only a few nanometers in the electric double layer. That is how a supercapacitor can accumulate huge electric power even at lower applied voltages.
The researchers performed an analysis to find out how the properties of a cation (positively charged ion) in ionic liquid affect the differential capacitance of a supercapacitor.
The present theoretical models explain ions in supercapacitors as non-structured charged particles, without indicating the variation of one ion from another. However, in the case of ionic liquids, not only are the charge and size of each ion essential but so are properties such as dipole moment on a cation and static polarizability.
“Dipole moment is a product of absolute value of dipole charges and the distance between them (dipole length). Electronic polarizability is a value that determines the particle’s ability to get an induced dipole moment in the external electrical field.”
The scientists examined how differential capacitance acts based on the voltage provided by the growing permanent dipole moment and static polarizability of cations for electrolyte solutions and ionic liquids.
In both instances, the growth of permanent dipole moment or polarizability of cations results in significant growth of differential capacitance at negative voltage. The researchers described such behavior of differential capacitance with extra attraction of a cation that consists of a permanent or induced dipole moment to an electrode in an inhomogeneous electric field.
We have demonstrated something very important. Capacitance, which is the main characteristic that demonstrates how much energy an electric double layer can accumulate, is sensitive to the changes in dipole moment and polarizability of an organic cation.
Yury Budkov, Professor, HSE Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics
“This gives the experimentalist (electrochemical engineer) an opportunity, if they want to achieve bigger capacities, to choose an ionic liquid in which the cation has higher dipole moment or polarizability,” added Budkov.
According to the researchers, their study is basic and will enable chemical engineers to make more accurate calculations in developing supercapacitors. Supercapacitors are utilized as power sources in various industries, right from housing services to alternative power sources, to electronic and mobile devices, to digital equipment. They serve as a separate or a standby power source for memory chips, electronic clocks, and microcontrollers.
We are going to develop software that would allow us to forecast capacitance properties of various ionic liquids and electrolyte solutions on specific electrodes–carbon, gold and platinum. The software will also consider the effect related to dielectric properties of ions.
Yury Budkov, Professor, HSE Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics
Journal Reference:
Budkov, Y. A., et al. (2021) Theory of Ionic Liquids with Polarizable Ions on a Charged Electrode. Journal of Physical Chemistry C. doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c05548.