The latest study in the journal Pharmaceutics focuses on electrospun nanofibers which contain natural biocompatible compounds that ensure their effectiveness for the treatment of burnt human skin.

Study: Electrospun Fibers Loaded with Natural Bioactive Compounds as a Biomedical System for Skin Burn Treatment. Image Credit: Bhakpong/Shutterstock.com
Electrospun nanofibers are gaining popularity in research since bioactive compounds may be readily deposited into the nanocomposites, resulting in improved burst regulation and pharmaceutical durability.
Importance of Electrospinning Fibers
Burns continue to be a serious public health issue across the world. Heat (flame or scorching), cold, chemicals, radioactivity, or abrasion can all induce burn damage.
Electrospinning is a popular and novel encapsulation process. It is a straightforward and adaptable method for manufacturing bioactive fibers. These fibers have diameters ranging from a few nanometers to micrometers, with tunable permeability, elevated interface region, and morphology that enhances metabolic processes, skin rehabilitation, and hemostasis, as well as preventing the spread of infection, and characteristics that allow possible applications in biochemical regeneration and drug delivery mechanisms.
Limitations of Electrospinning
Electrospinning has major benefits over other injury and burn therapy methods now in use. Despite these evident benefits, electrospinning may have certain operational drawbacks or restrictions, such as limited cell penetration and insufficient mechanical durability for higher load implementations. The bioactive materials utilized also have certain limitations. A few of the bioactive molecules are chemically reactive, insoluble, prone to oxidative breakdown, or have a low bioavailability.
Categories of Electrospun Fibers
Many aspects influence the electrospinning method, including experimental parameters, solution characteristics, and testing environment. As a consequence, various categories of such fibers are present for variable uses.
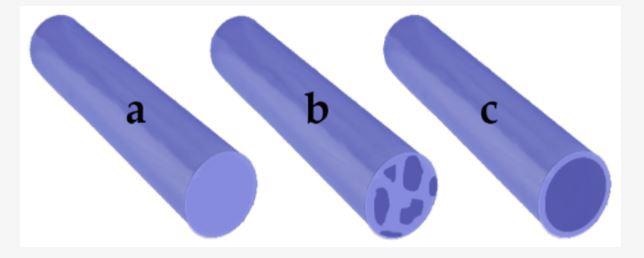
Types of electrospun fiber: (a) simple; (b) blend; (c) core-shell. Image Credit: Hermosilla, J et al., Pharmaceutics
Simple fibers are the most fundamental type consisting of a single material, enabling bioactive compounds to be injected into its lattice due to intrinsic properties. The second major category of blend-type fibers. It is a homogeneous mixture of two or more bioactive materials which are then processed via electrospinning.
These fibers are different from composite fibers, which contain several distinct solution mixtures. Composite fibers are heterogeneous and at least two distinct phases can be observed. The third major category is the core/shell fibers. It consists of a core solution encapsulated by a shell solution.
Natural Materials Used for Electrospun Fibers
Several natural materials are utilized for electrospun fibers. Among them, chitosan is essential. It offers beneficial qualities such as bioactivity, non-toxicity, high availability, ease of customization, great chemical stability, the capacity to form coatings, gels, and nanostructures, and affinity for metals, proteins, and colorants.
Collagen is the major protein in the mammalian body, accounting for around 30% of the overall quantity. It is the primary constituent of the ECM and is essential for improved durability of body tissues as well as physiological modulation of the cell surface; it is frequently employed in biomedicine and pharmacological applications.
Another major and famous material is gelatin. Because of its great biomedical compatibility, ease of biodegradability, and low allergenicity, this polymer is frequently employed in activities linked to the food industry, medical, and cosmetics sectors. Keratin is another substance used for drug delivery systems.
Importance of Synthetic Materials in Electrospun fibers
The major synthetic material is polyethylene glycol (PEG). PEGs, through steric stabilization, lower the propensity of nanoparticles to agglomerate, resulting in compositions with improved durability during preservation and administration.
Polylactic acid is also a major synthetic substance used for this purpose. Although properties like high stiffness and wettability limit its application in some areas, it is frequently employed in biotechnology for its bioactivity and as a therapeutic agent. Apart from these several other polymers are also extensively utilized in the electrospinning fiber sector.
Natural Bioactive Compounds in Electrospun Fibers
These naturally extracted oils etc. have found their way into the electrospinning fiber industry. Olive oil is an essential natural bioactive substance. It has a high concentration of essential vitamins, dienic fatty acids, and other organic minerals.
Its nanofibers are antibacterial. Curcumin is a yellow pigment that is an active component of turmeric. Curcumin possesses antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and anti-infective activities; nevertheless, it is exceedingly unstable in vivo and has limited bioavailability. Several other substances and extracted oils are also helpful in burn treatments, wound healing, and anti-bacterial applications.
In short, the research has mentioned the development of electrospun fibers and their active biomolecules and substances essential for their development. These fibers aid in the treatment of chemical burns and/or disease management in the afflicted region, and are being researched extensively.
References
Hermosilla, J., Navarrete, E. P. & Acevedo, F., 2021. Electrospun Fibers Loaded with Natural Bioactive Compounds as a Biomedical System for Skin Burn Treatment. A Review. Pharmaceutics, 13(12). 2054. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/13/12/2054
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.