Over at the Department of Organic Chemical Technology and Polymer Materials, Faculty of Chemical Technology and Engineering, West Pomeranian University of Technology in Szczecin, Poland, a team of researchers have been developing a method to produce renewable polymer coatings using bio-renewable oligomers and monomers. The research was published in the journal Materials.
Study: Photocurable Coatings Based on Bio-Renewable Oligomers and Monomers. Image Credit: petrroudny43/Shutterstock.com
Published in the journal Materials, the team discuss how they used two kinds of acrylic bio-renewable components to modify acrylated epoxidized soybean oil (AESO): “The studies showed that it is possible to control the curing process and the properties of cured coatings obtained from renewable photoreactive sources by simply modifying the photoreactive renewable resins without having to reduce biobased carbon content,” explains corresponding author Dr. Paulina Bednarczyk.
This study comes at a time when researchers are working to develop newer, environmentally friendly materials such as renewable polymers as an alternative to synthetic materials. Some of the justifications for this research include tackling long-term problems related to environmental protection, economic aspects, and waste management in the chemical industry.
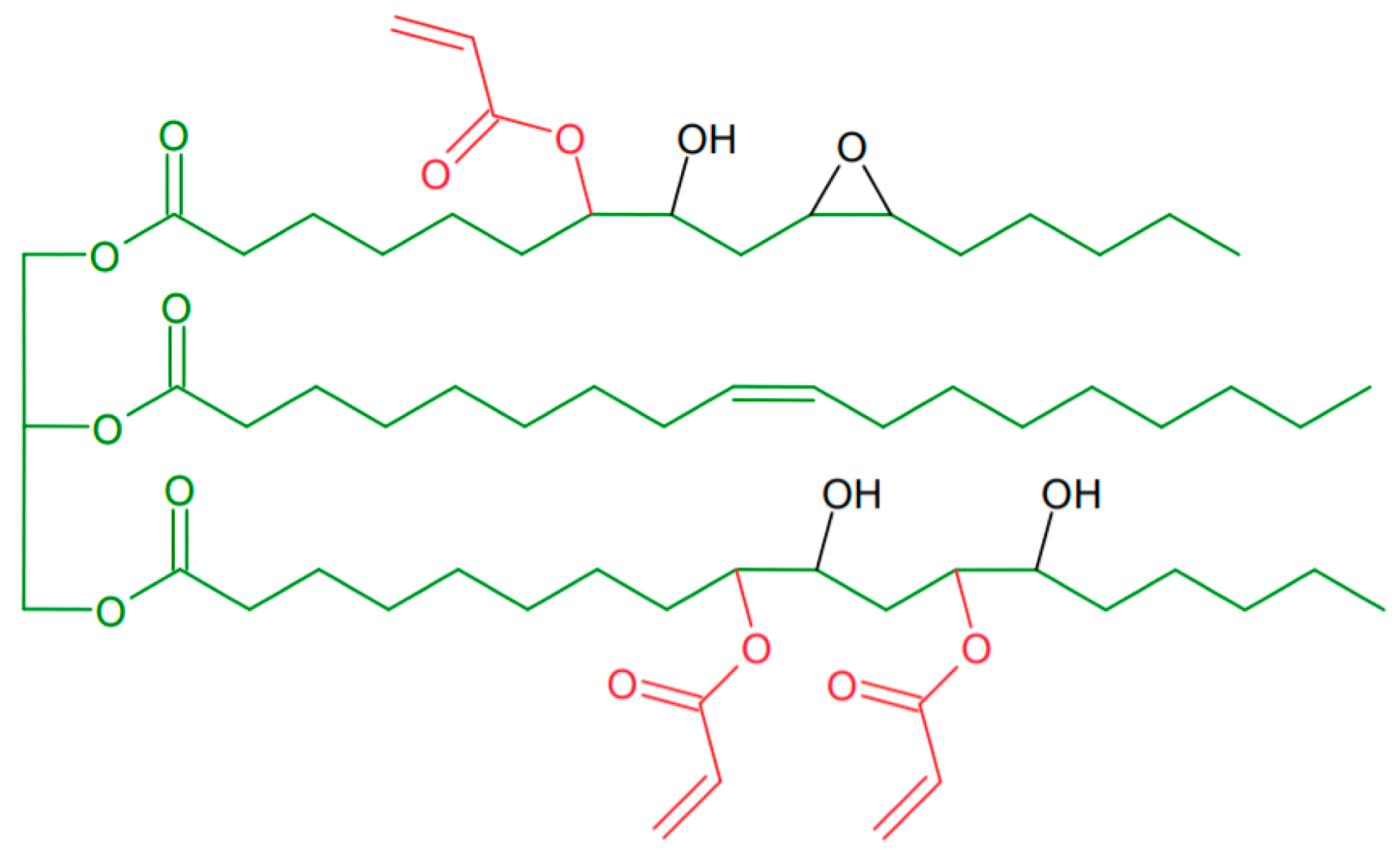
Theoretical structure of epoxidized soybean oil acrylate (AESO). Image Credit: Bednarczyk, P et al., Materials
Renewable Materials Candidates
Demand is currently on the rise for the replacement of petroleum-based polymeric materials due to two major factors: the aforementioned growing concern for the environment and forecasts of a shortage of crude oil resources.
Polymers derived from renewable raw materials are already finding use in packaging, bio-medical and hygiene products, cosmetics, electronics, agriculture, other consumer goods, and they are now being trialed in optical 3D printing.
Bednarczyk says, “Natural resources such as vegetable oils, fatty acids, or lactic acids have been found to be particularly widely attractive for scientists because they can be molecular-engineered into renewable polymers in a way similar to many petroleum chemicals.”
Vegetable oils have been identified as a good candidate as a renewable resource as they are abundant, relatively cheap, and can be easily modified due to an extensive number of highly reactive sites. Soybean oil in particular is regarded as an optimal choice due to its abundance and low cost.
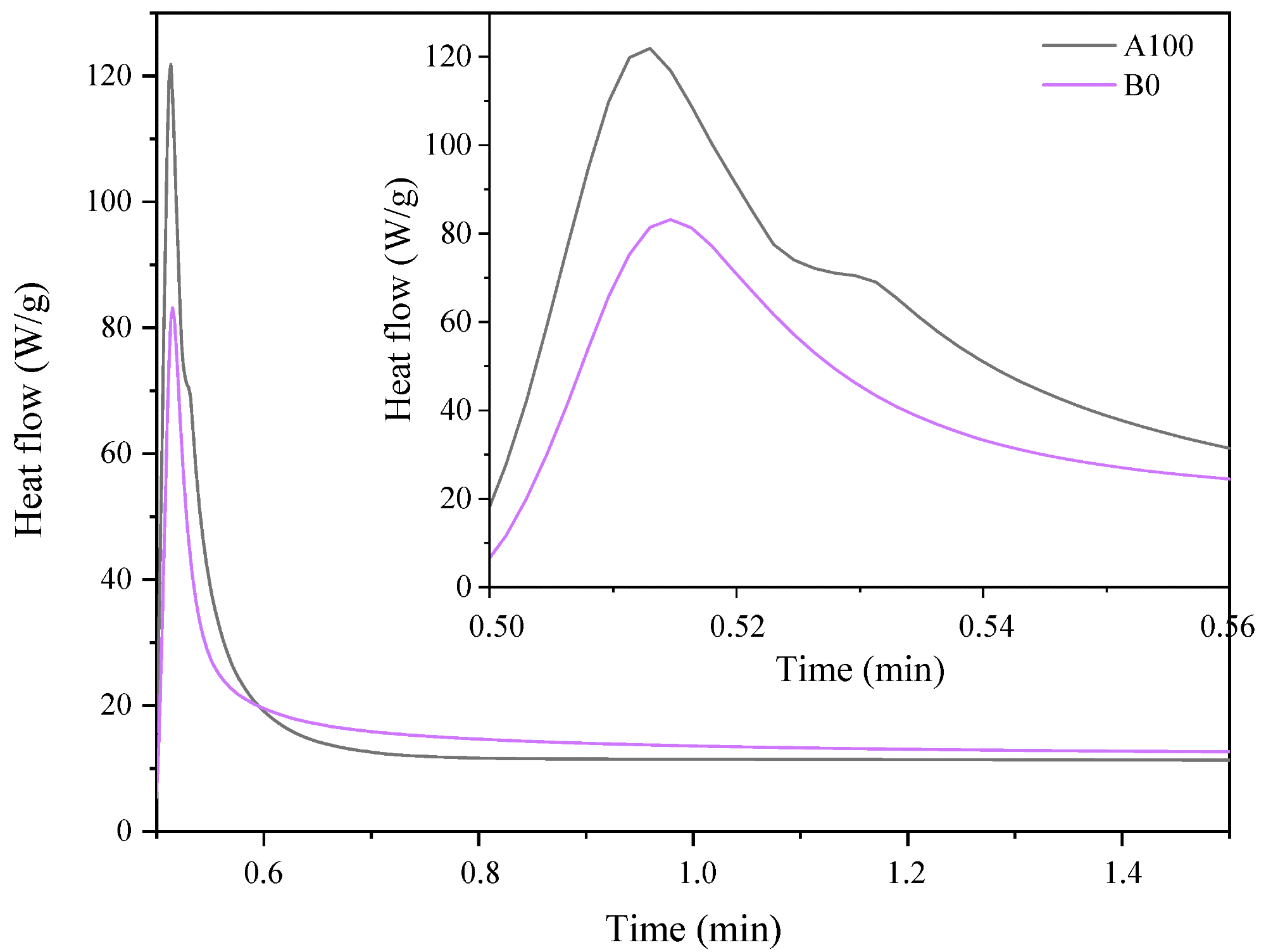
Photo-DSC exotherms for the photopolymerization of AESO composition (A100) and bio-based diacrylate oligomer composition (B0). Image Credit: Bednarczyk, P et al., Materials
Modifying Soybean Oil
While soybeans and soybean oil are primarily used in the food industry and through a process known as polymerization the soy-bean oils can form viscous fluids or weak rubbery films. These films are too weak to provide utility as coating films but with the appropriate modification with functional molecules, they can be used for film-forming applications.
The researchers used renewable oligomers or (math)acrylate monomers in order to modify the AESO to boost the reactivity and reduce the viscosity of the photoreactive system for the purpose of generating renewable and viable alternatives to petroleum-based polymeric materials with perfect film-forming properties.
Additionally, the researchers also discuss how they were able to control the curing process, therefore, allowing them to also control the properties of cured coatings from renewable photoreactive sources by a simple modification of the photoreactive renewable resins without reducing any of the biobased carbon content.
Therefore, the method proves itself as being “green” through a combination of bi-renewable materials and green UV-curable technologies. “Due to the presence of increasingly strict environmental regulations, which are particularly relevant to the chemical industry, this combination provides a “green + green” solution,” states Bednarczyk.
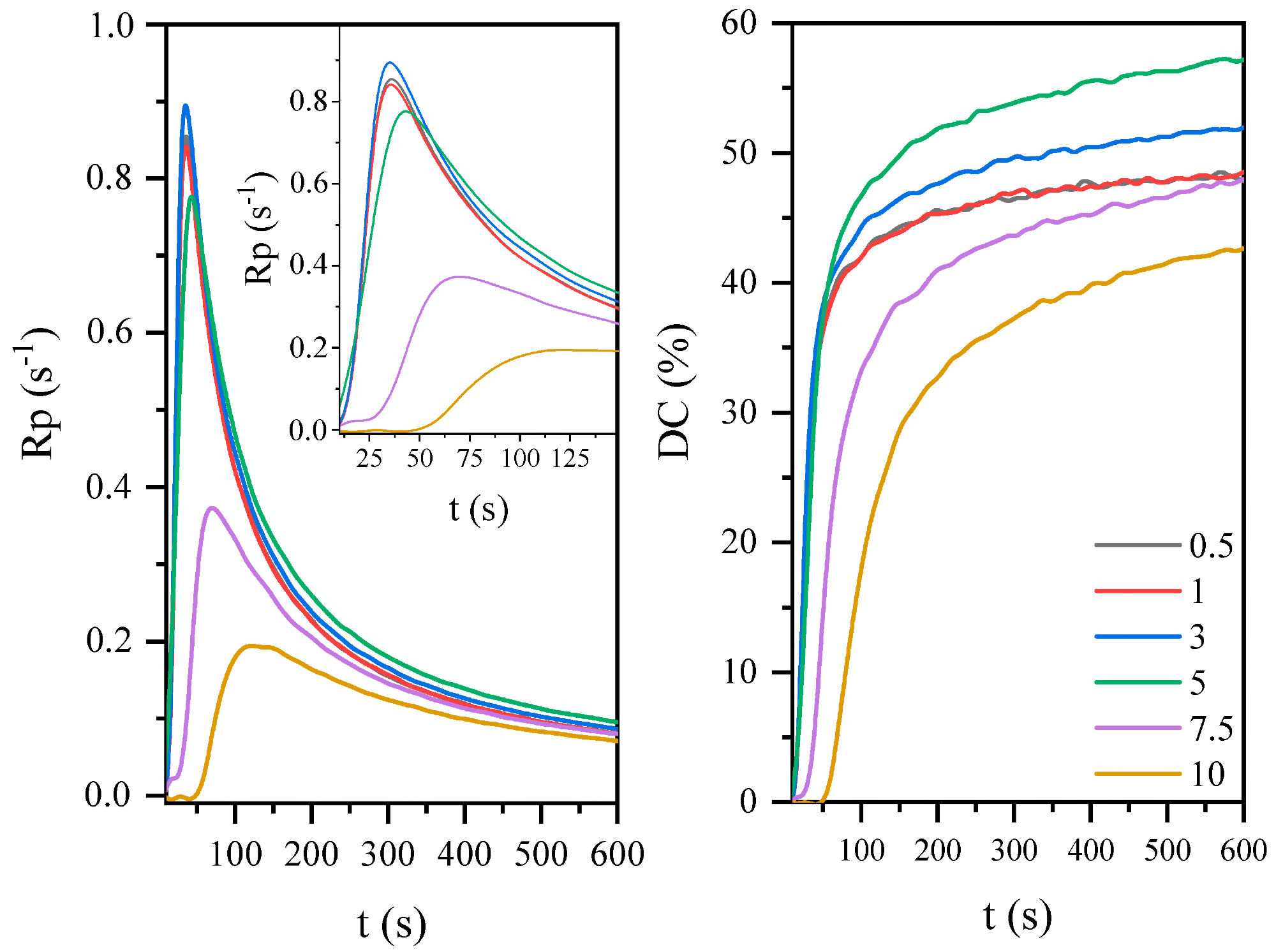
The effect of photoinitiator concentration on the photopolymerization process of coatings based on the AESO. Image Credit: Bednarczyk, P et al., Materials
As a result of the study, the team was able to effectively propose a method utilizing bio-renewable oligomers and monomers to produce renewable polymers that could in effect replace synthetic photoreactive polymers. Potential applications for the coatings could find use in coatings, adhesives, biomedical, and electronic packaging materials.
At a time when the collective consciousness is thinking about the current climate emergency, developing new renewable materials using environmentally friendly “green” methods is an attractive prospect.
The material developed by the team at the West Pomeranian University of Technology can be very promising for the coating industry, especially for the development of advanced bio-based UV-curable materials deriving from soy-bean plants oil and other unsaturated plant oils. Using this method, it would be possible to acquire cured polymer and coating materials in a short amount of time using renewable materials and “green” fabrication methods.
References
Bednarczyk, P.; Nowak, M.; Mozelewska, K.; Czech, Z. Photocurable Coatings Based on Bio-Renewable Oligomers and Monomers. Materials 2021, 14, 7731. https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/14/24/7731
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.