Digital twin (DT) technology is making significant research inroads into several technologies. DT technology has significant potential for another key 21st-century technology: electric vehicles. A paper published in Sustainability has explored the use of digital twins in this important industrial sector.

Study: Overview on Digital Twin for Autonomous Electrical Vehicles Propulsion Drive System. Image Credit: buffaloboy/Shutterstock.com
What are Digital Twins?
Since the concept was developed around 20 years ago, a number of researchers and institutions have defined digital twins and sought to develop effective software systems based upon them. In essence, a digital twin is a replica of a real-world object (its “twin”) and in addition to the physical assets of the twin, a digital twin can be used to replicate processes. By using them in this manner, data can be collected to provide a predictive analysis of performance.
Digital twins can be constructed for physical objects from vehicle and airplane engines to wind farms, buildings, and even entire cities. IoT devices, software analytics tools, machine learning, big data, and AI can be integrated into a digital twin to improve its operation and output. Digital twins are rapidly becoming a key technology in engineering in the 21st century. Digital twins can run any number of simulations on every parameter and process in a physical asset.
A simple way to explain what a digital twin looks like is a wind turbine that has various sensors attached to different working parts and vital areas. The sensors gather data about factors such as wind speed, atmospheric conditions, temperature, energy output, and so forth which are then fed back to a central processing system. This real-world information is then applied to the digital twin.
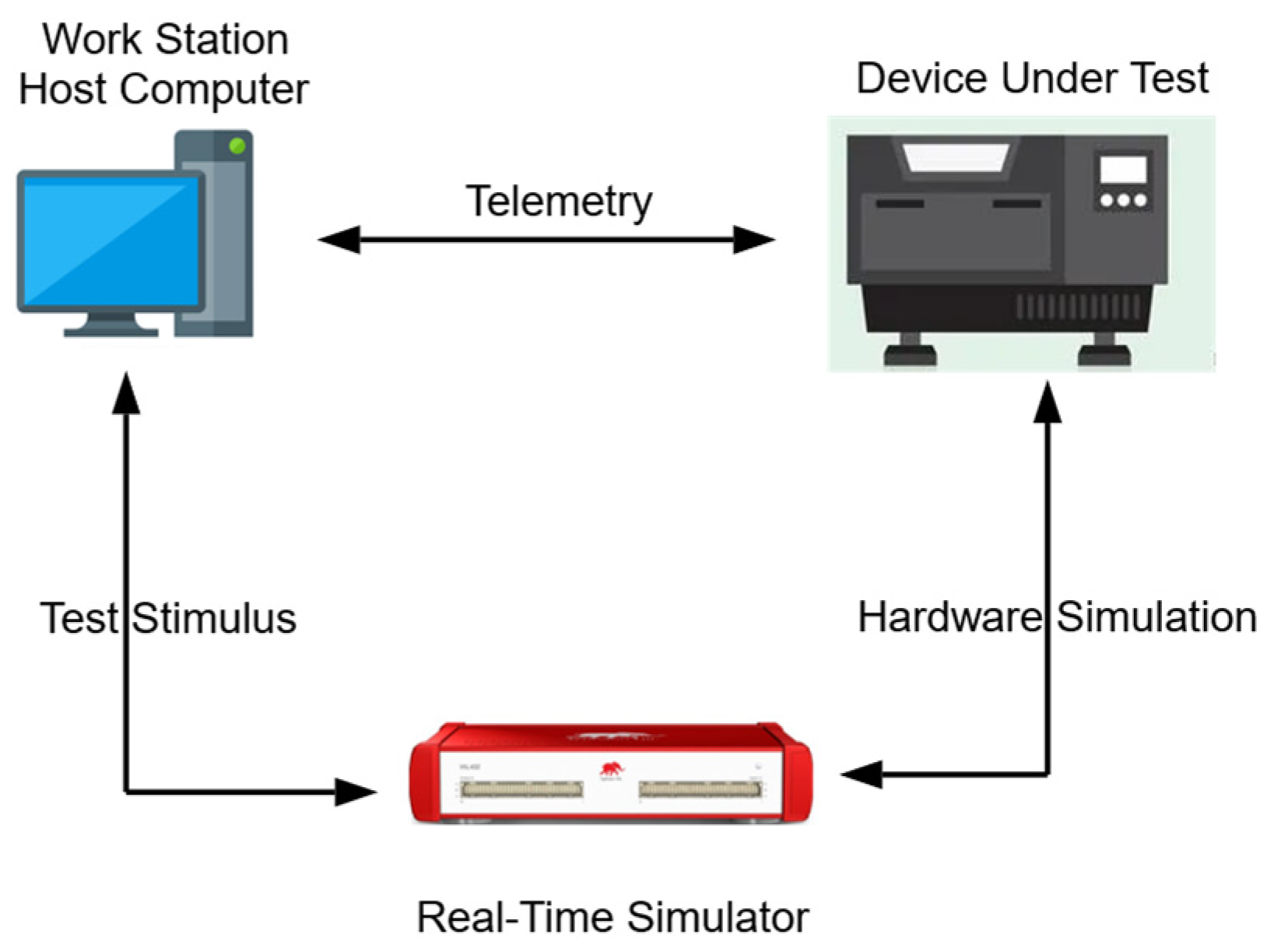
Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) System. Image Credit: Ibrahim, M et al., Sustainability
The data gathered is used to run simulations, analyze performance issues, and provide insights that can help improve the performance of the real-world object. A digital twin can be used to analyze valuable health status and maintenance data throughout the entire lifetime of a physical asset. A key difference between DTs and Hardware-in-the-loop simulations is that the DT is a purely virtual simulation model which is provided with real-life inputs and outputs to determine how well a physical asset is working.
There are several types of digital twins which are classified according to the level of product magnification, and they differ according to their area of application. The different types of digital twins are component twins/part twins, asset twins, system/unit twins, and process twins. Digital twins are favorable for engineering applications as they are low-cost and low-risk.
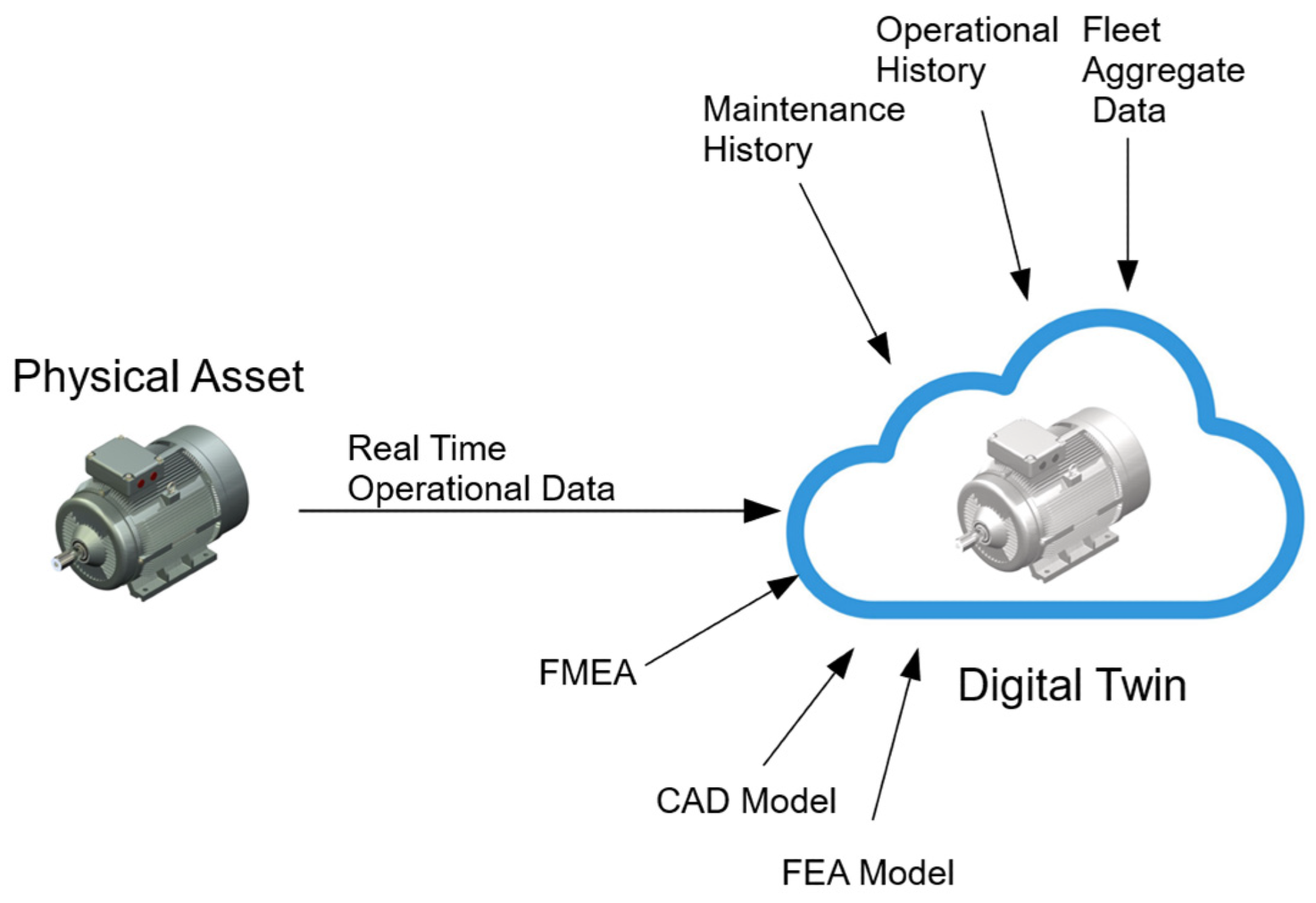
Digital Twin (DT) system. Image Credit: Ibrahim, M et al., Sustainability
Electric Vehicles and How DT Benefits the Technology
The growth in electric vehicle development has been promoted by the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions in the automotive industry. Digital twins have been extensively explored in fields such as biomedical research and the aerospace industry, and due to their potential, they are being increasingly employed in the research and development of electric vehicles. Like any technology, electric vehicles have parts that must be monitored for performance issues and to provide operational improvements.
Developing a new car model is a lengthy process, typically taking up to five or six years from design to market launch. Effective design is key to the long-term success of a new vehicle, and digital twins provide a means to virtually model the component and, additionally, the design and development process at all stages.
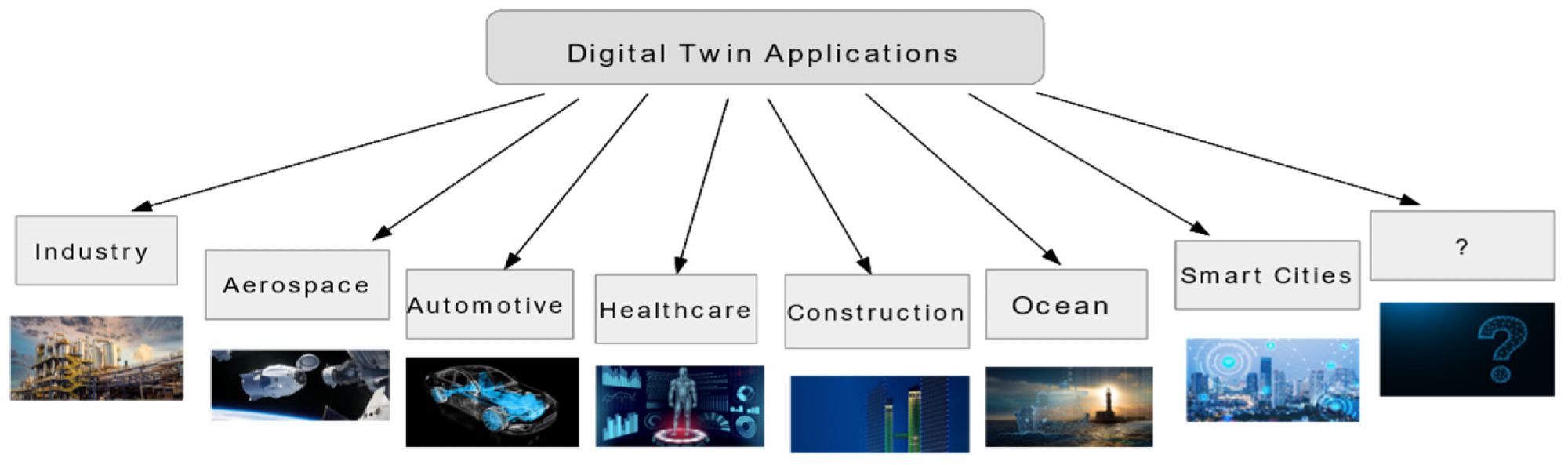
Digital Twin applications map. Image Credit: Ibrahim, M et al., Sustainability
Electric vehicles are still a relatively new technology, but the growth in their global demand has facilitated the urgent need for the design of high-performance parts. It is predicted that they will represent an 80% of the share of the global automotive industry by 2050. One of the critical components that affect their performance is the propulsion drive system, and though this can benefit from digital twin technology, there is a lack of studies concerning EV propulsion systems.
Digital twins are frequently used for applications such as diagnostics, prognostics, system health monitoring, and risk assessment in electric vehicle drive applications. The paper published in Sustainability has provided an overview of the use of DT technology in the propulsion drive systems of electric vehicles.
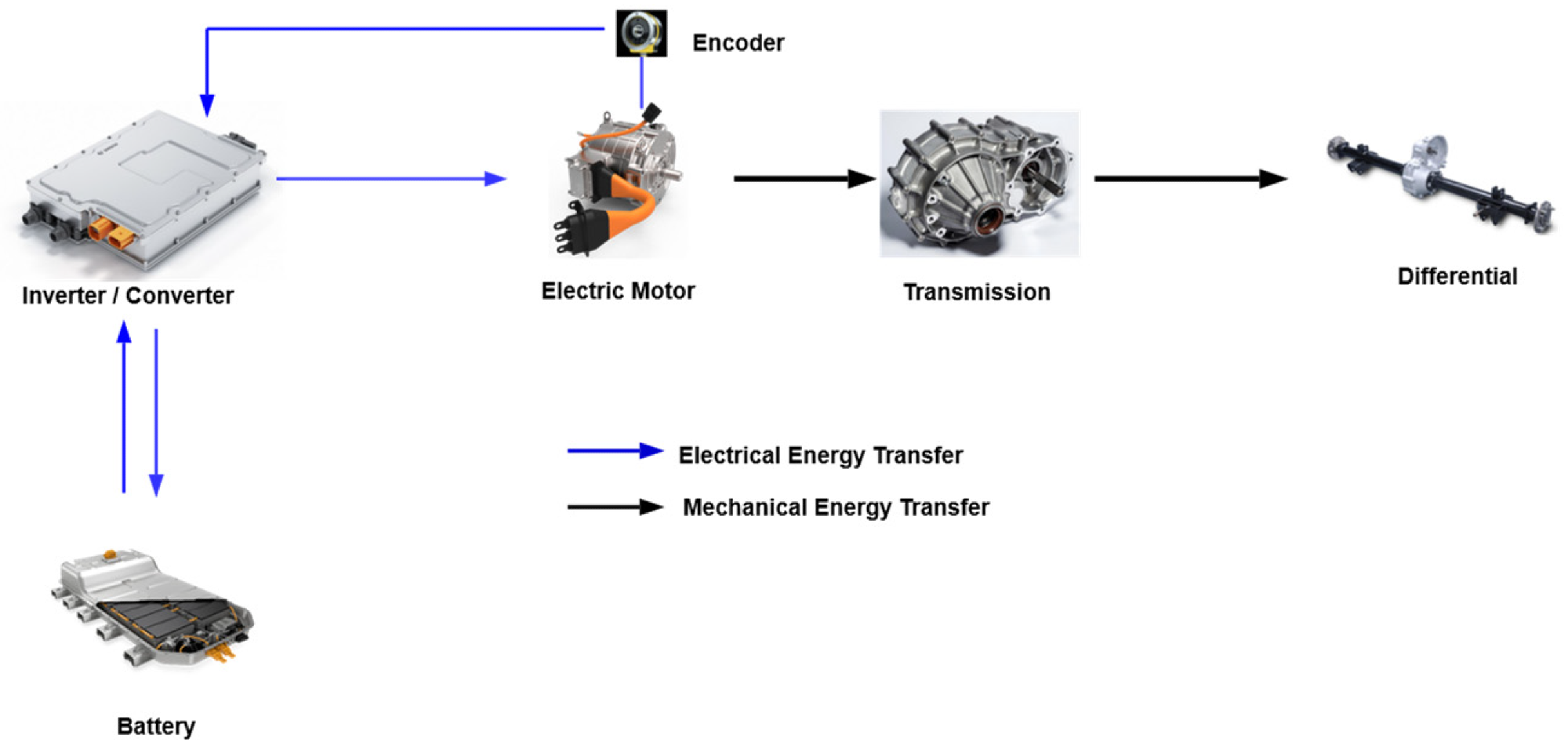
Electrical Vehicle (EV) drive system components. Image Credit: Ibrahim, M et al., Sustainability
The authors have conducted an extensive review of current studies on the use of digital twin technology in this area. Additionally, the authors have provided a comparison between different simulation technologies currently available. Finally, they have identified several routes for technological development that will inform future research directions. In conclusion, the study has found significant potential for digital twin use in electric vehicle design, and as such, the paper serves as a vital resource for this field.
Further Reading
Ibrahim, M et al. (2022) Overview on Digital Twin for Autonomous Electrical Vehicles Propulsion Drive System [online] Sustainability 14(2) 601 | mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/2/601
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.