A proper design of the drilling fluid is a critical component during drilling operations. For HTHP and ultra-HTHP drilling applications, oil-based drilling fluids are typically preferred. Due to its high toxicity and high cost, the use of oil-based drilling fluid has been banned by rigorous environmental protection rules.
As a result of the need to safeguard the environment, the use of water-based drilling fluid has increased. The use of harmful chemical additives in traditional water-based systems has resulted from a focus on economics and performance in drilling activities, as well as the marginalization of environmental care.
There is a need to research and develop new ecologically friendly additives that will contribute to the same level of control of drilling fluid properties while having a lower environmental impact. As a result, several studies have been undertaken and continue to be conducted on the use of food waste and other biodegradable materials as additives.
Researchers have begun to conduct laboratory tests to see if food waste items may be utilized as additives in water-based drilling fluids to improve the composition and qualities of drilling fluids in recent years. It's also worth noting that drilling operations generate a large amount of drilling fluid waste, which must be appropriately treated and disposed of both during and after the drilling process.
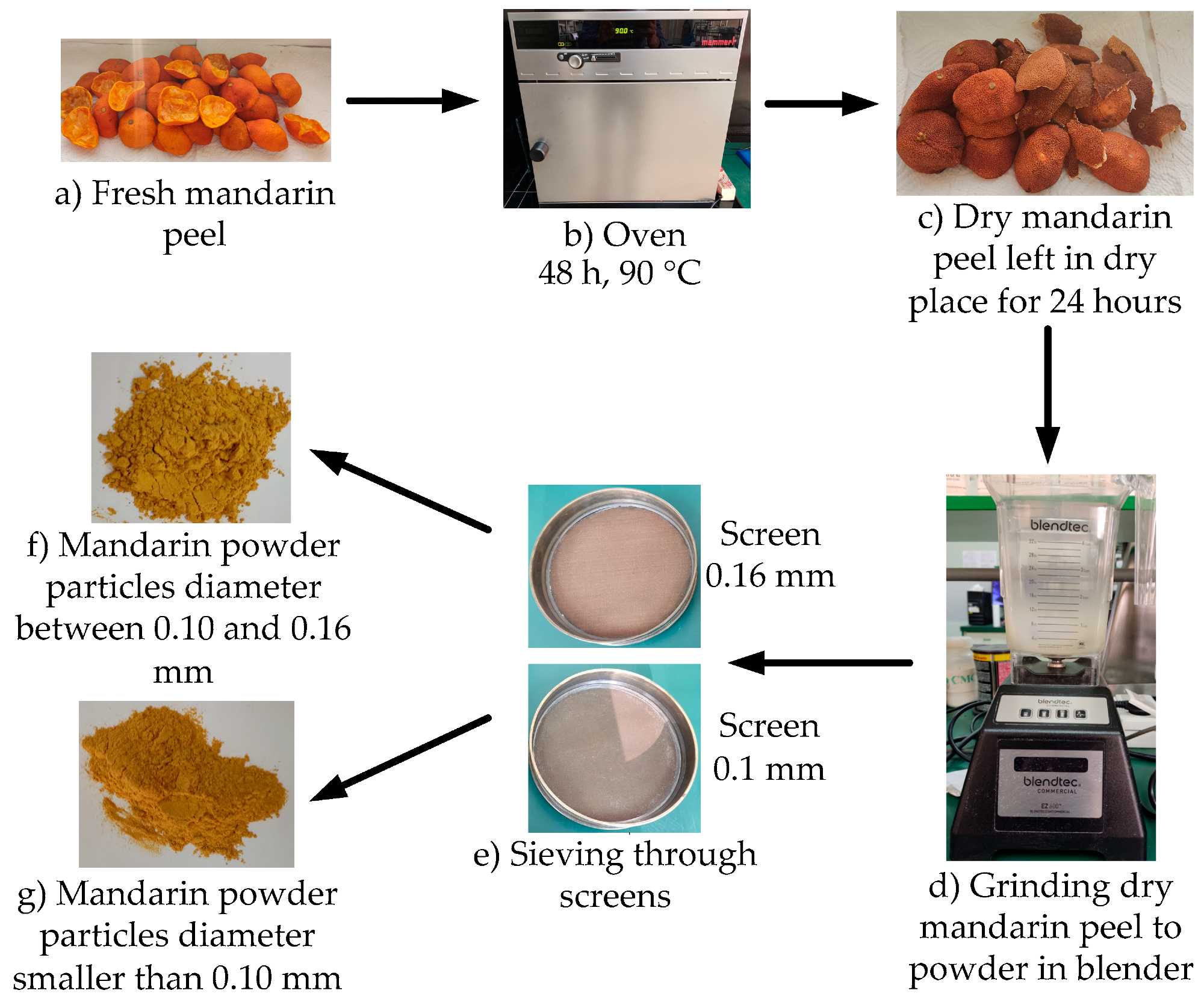
The entire process of preparing waste mandarin peel powder from waste collection. Image Credit: Medved, I et al., Energies
About the Study
In this study, the authors discussed the influence of the particle size of mandarin peel powder on the drilling fluid's qualities. Mandarin peel was employed in the form of a dry powder with particle sizes smaller than 0.1 mm and between 0.1 mm and 0.16 mm. Four different amounts of mandarin peel powder (0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2% by volume of water) were introduced to a water-based drilling fluid.
The team demonstrated a novel detailed technique for preparing mandarin peel powder through drying, grinding, and sieving. The effect of particle size (lower than 0.1 mm, and between 0.1 and 0.16 mm) on the rheological and filtration characteristics was tested through API as well as PPT filtration tests such as high-temperature and high-pressure filtration tests.
The researchers investigated the effects of adding mandarin peel powder to a bentonite-based drilling fluid on its rheology and filtration qualities. The usage of mandarin peel powder as an addition to optimizing drilling fluid qualities without causing environmental issues was discussed. Nine different drilling fluids were created and tested in the lab to see how the addition of mandarin peel powder affected the rheological and filtration properties of bentonite-based drilling fluids. Filtration and rheological parameters, as well as gel strength, were assessed for all nine drilling fluids after they were prepared.
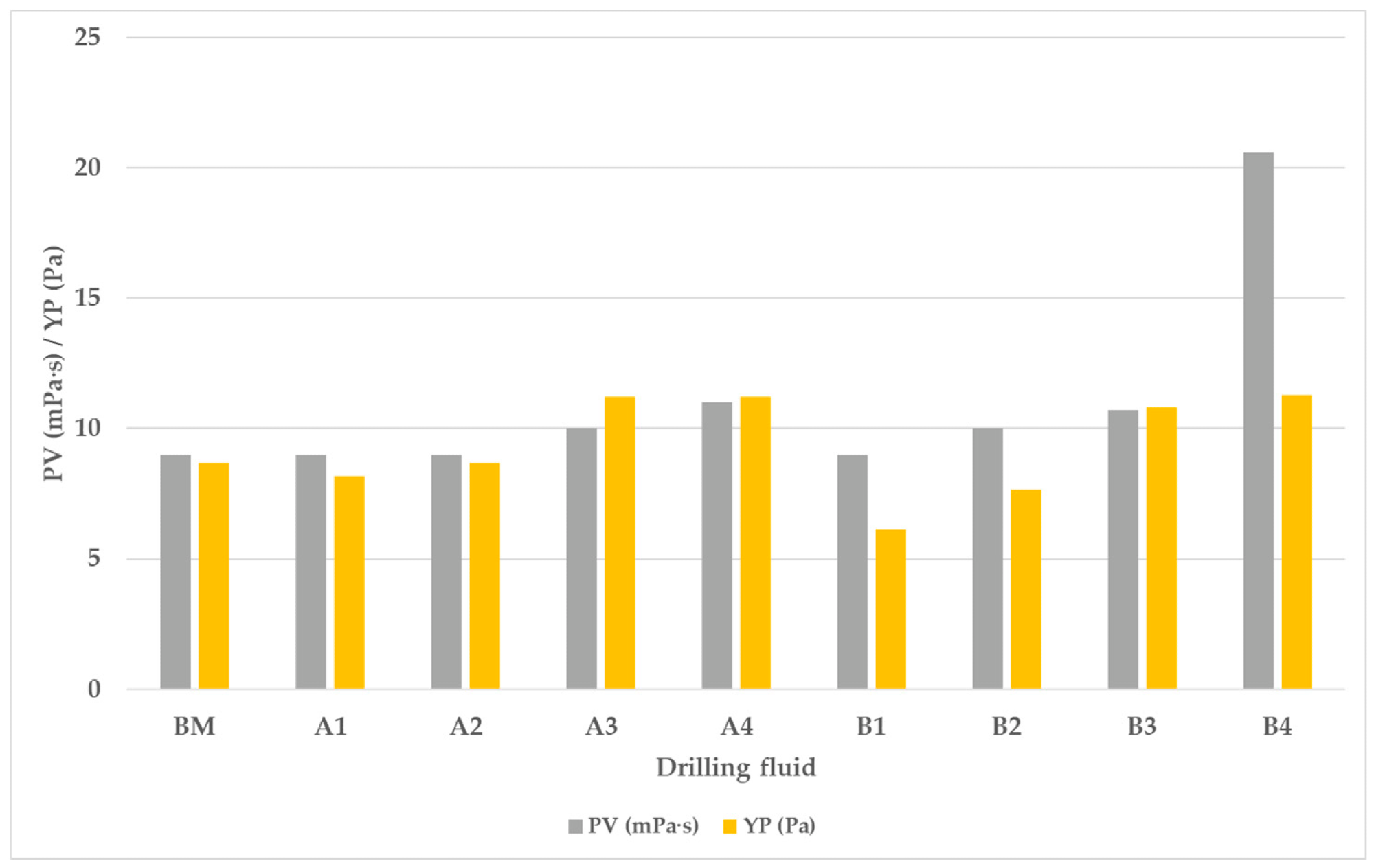
Plastic viscosity (PV) and yield point (YP) of all tested drilling fluids. Image Credit: Medved, I et al., Energies
Observations
The API filtration was lowered by up to 42%, the PPT filtration was greatly reduced by up to 61.54%, and the rheological parameters were increased but remained within acceptable limits when the mandarin peel powder content was increased. The ideal concentration of mandarin peel powder by volume of water was determined to be up to 1.5%.
It was discovered that drilling fluids containing substantial amounts of mandarin peel powder resulted in the greatest reduction in filtrate volume by 2%. Meanwhile, B4 drilling fluid, which had bigger particles ranging in size from 0.1 to 0.16 mm, had the highest percentage of 44%.
Plastic viscosity increased somewhat when the content of mandarin peel powder increased to 1.5%. PV significantly increased to 129% in drilling fluids containing larger mandarin particles of sizes between 0.1 and 0.16 mm after the mandarin peel powder concentration was raised to 2%. The addition of 2% mandarin peel powder having particle sizes between 0.1 and 0.16 mm enhanced pressure loss by 10.5% in turbulent flow, whereas the effect was minimal in other circumstances.
With A4 and B4 drilling fluids, PPT filtration decreased by 61.54% and 57.69%, respectively. Spurt loss was reduced by 75% and 37.5%, respectively, by using A4 and B4. Rheological characteristics improved when mandarin peel powder having particle sizes between 0.1 and 0.16 mm was added. PV and 10-s gel strength values considerably increased at a concentration of 2%, which resulted in higher pressure loss.
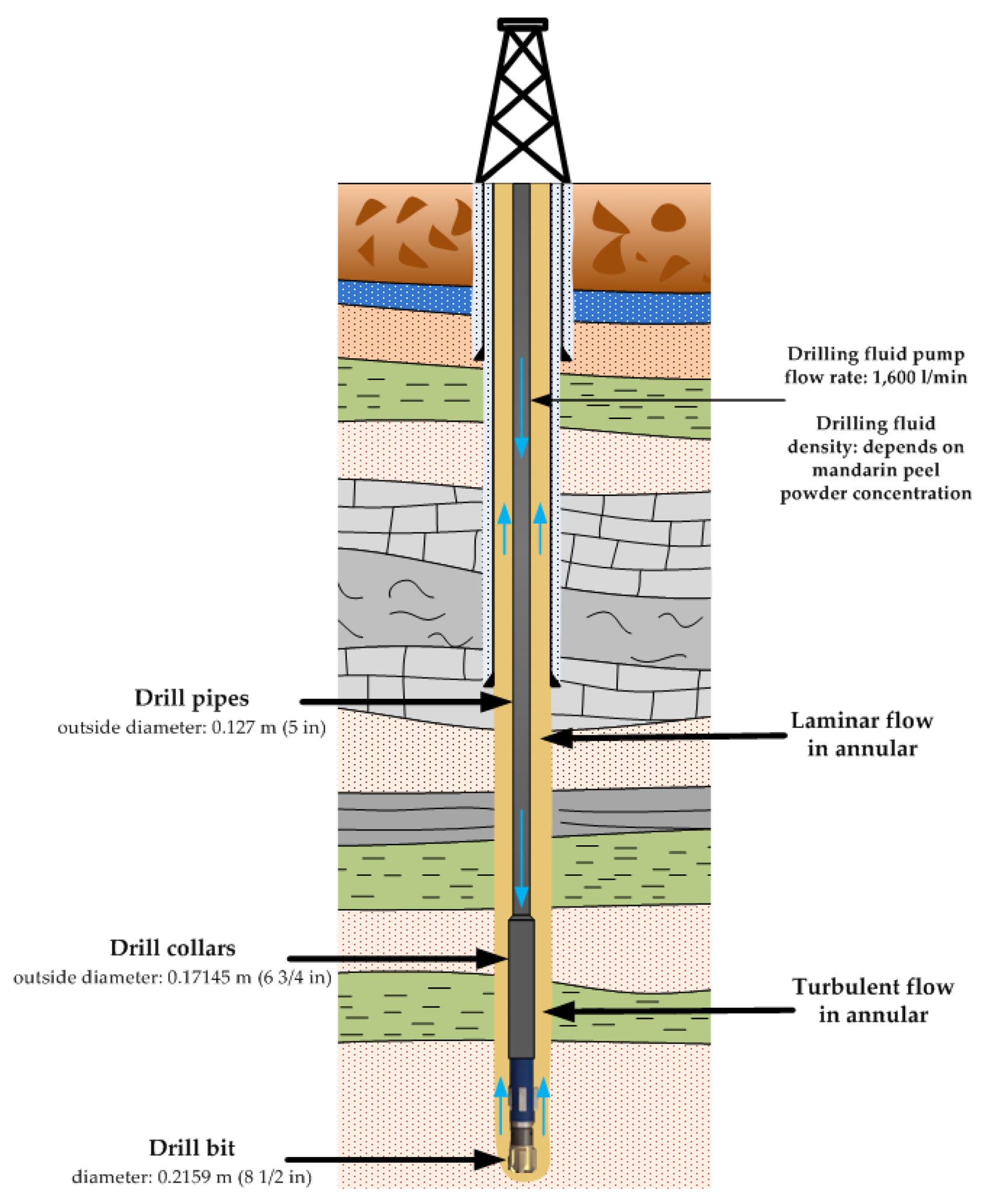
Input data for the calculation of the pressure loss in the annular. Image Credit: Medved, I et al., Energies
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study elucidated that the particle size and concentration of mandarin peel powder had an impact on drilling fluid characteristics. The API filtering diminished as the concentration of mandarin powder increased. When comparing the particle sizes of mandarin peel powder, it was observed that larger particles between 0.1 and 0.16 mm produced slightly better results, although, for field operations, both sizes produced adequate drilling fluid qualities.
The authors determined that a concentration of up to 1.5% by volume of water is best for mandarin peel powder. They emphasized that the findings of this study can be a good starting point for additional research on various types of food waste that can be used as an additive to improve drilling fluid qualities. They also believe that it is a good idea to figure out drilling fluid qualities in more complicated drilling fluid formulations.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.
Source:
Medved, I., Gaurina-Medimurec, N., Mavar, K. N., et al. Waste Mandarin Peel as an Eco-Friendly Water-Based Drilling Fluid Additive. Energies 15(7) 2591 (2022). https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/7/2591