Scientists from the US have presented research into the use of hydrogen blended with natural gas as a bridging energy to achieve long-term carbon neutrality. This strategy could potentially help meet net-zero targets whilst still ensuring energy security in the short term. Their review study has appeared in the journal Energies.

Study: Hydrogen Blending in Gas Pipeline Networks—A Review. Image Credit: petrmalinak/Shutterstock.com
The Role of Hydrogen in Climate Change Strategies
Climate change is one of the main existential threats facing humanity in the 20th century. Carbon dioxide and methane are two of the most damaging greenhouse gas emissions, responsible for the alarming rise in global temperatures since the Industrial Revolution and subsequent environmental damage. Phasing out fossil fuels in favor of low-carbon renewable energy sources and fuels is a key strategy for meeting zero-carbon emissions targets.
Hydrogen has been widely explored in recent decades as an alternative fuel and energy source. Aside from near-zero greenhouse gas emissions, hydrogen is a highly efficient energy carrier, is abundant, and eminently renewable, overcoming both emissions and supply issues. Hydrogen can be easily produced using water splitting methods and, depending on its source, is incredibly clean. The most ideal source of hydrogen is renewable energy, and if produced in this manner, is termed “green hydrogen.”
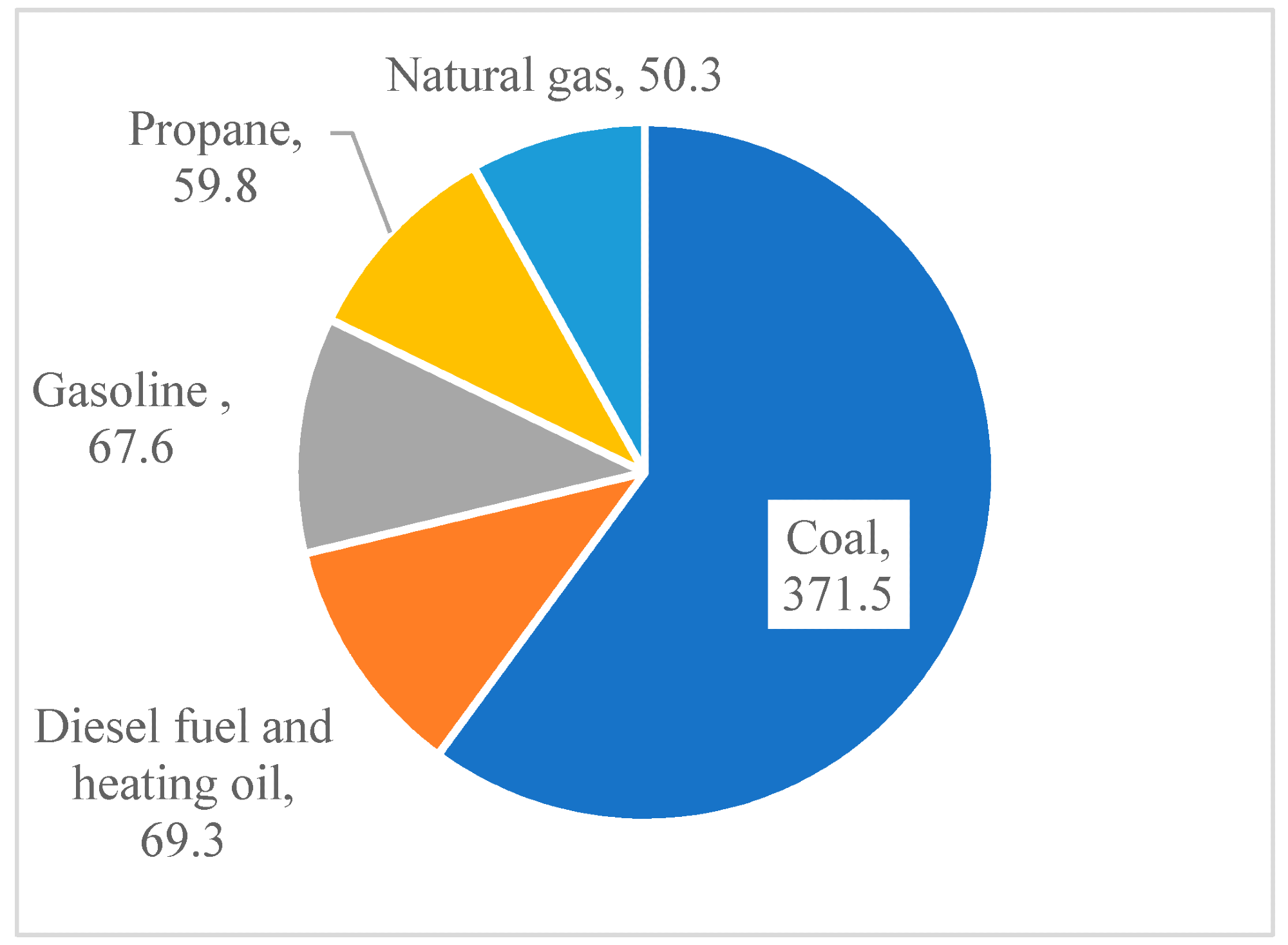
kg of CO2 emitted per million kJ of energy for various fuels in 2020. Image Credit: Mahajan, D et al., Energies
Another advantage of hydrogen is that existing storage and transportation infrastructure can easily handle liquid hydrogen without the need for major alterations. A key resource that, whilst still producing 50.3 kg of CO2 per million KJ of energy, produces less carbon dioxide than gasoline and coal is natural gas. More energy-rich than other hydrocarbons, natural gas has applications in industry as a fuel and for electricity generation.
The extensive natural gas infrastructure that already exists has the potential to be repurposed for hydrogen storage and transportation, which will help realize the aims of the carbon-neutral economy.
Using Natural Gas Infrastructure for Hydrogen: Current Challenges
Repurposing natural gas infrastructure, whilst presenting the most technologically mature strategy for realizing a hydrogen-based economy, faces several key technical challenges. Natural gas and hydrogen differ significantly in their properties, which means that it is not a simple case of just replacing natural gas with hydrogen in these systems.
Realizing a large-scale conversion of current infrastructure into a hydrogen-carrier system requires a comprehensive examination of factors such as production methods, storage, and transportation, and finding sufficient end-use applications for hydrogen. One solution is to progressively increase the proportion of hydrogen in hydrogen/methane blends over time to 100%, but this is a challenging endeavor for engineers and researchers. To successfully overcome the challenges, a coordinated, cross-functional approach must be taken.
The Study
The main aim of the new paper is to examine state-of-the-art knowledge and progress in research into the hydrogen economy, considering production, transportation of hydrogen blends, and commercial uses.
Properties and benefits of hydrogen/methane blends have been discussed by the authors in-depth, and an emphasis has been placed on safety concerns surrounding the use of methane/hydrogen blends. Density, viscosity, energy densities, and phase interactions are all causes of concern. Issues with pressure and leakage, pipeline stresses, and long-term hydrogen embrittlement are common with long-term hydrogen storage and transport and must be fully understood. These issues are being addressed by current projects.
The study has summarized current projects in different parts of the world. Demonstration projects including THyGA, HyDeploy, HyBlend, and THyGA are currently being supported by governments to elucidate a cost-effective pathway for achieving carbon reduction goals by 2050. Lessons learned from research into hydrogen blends and demonstration projects will help to realize the development of safer, more efficient, and compatible hydrogen fuel infrastructure.
A major impact on blended gas transport cost dynamics is caused by pressure reduction in blends. Increased energy is needed to transport blends to domestic and commercial users compared to natural gas alone. This increased cost can be mitigated by modifying flow rates and pressures. Techno-economic studies can play a key role in providing relevant information to address these issues.
![(a) damaged boiler tube facture; (b) position of facture on the boiler tube [56].](https://www.azom.com/images/news/ImageForNews_59070_16526901326542198.png)
(a) damaged boiler tube facture; (b) position of facture on the boiler tube. Image Credit: Mahajan, D et al., Energies
In Summary
Four key challenges have been identified in the review study in Energies. End-use appliances such as heating equipment and burners may need design modifications to cope with increased combustion temperature and flame speeds. Additional compressors will be required to address challenges with lower energy transport and mass flow. The increased risk of leakage and explosion will require new safety standards and codes. Finally, there is an increased risk of long-term embrittlement and corrosion caused by hydrogen storage and transport.
![Influence of hydrogen charging on 1018 steel [61].](https://www.azom.com/images/news/ImageForNews_59070_16526901469544767.png)
Influence of hydrogen charging on 1018 steel. Image Credit: Mahajan, D et al., Energies
Whilst the review only touches upon the subject of hydrogen/methane blends and issues with current infrastructure and how to overcome them, the authors have laid a good foundation for future specific-topic related studies which will help the technology reach maturity.
Further Reading
Mahajan, D et al. (2022) Hydrogen Blending in Gas Pipeline Networks—A Review Energies 15(10) 3583 [online] mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/10/3582
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.