A paper recently published in the journal Energies reviewed the application of digital technologies in the renewable energy sector.

Study: Digitalization in the Renewable Energy Sector— New Market Players. Image Credit: Yellow duck/Shutterstock.com
Background
Digital technologies will play a key role in the emerging new economy (NEE) in upcoming years. These technologies can facilitate the collection, management, and analysis of substantial amounts of data more efficiently. Thus, digital technologies can promote the development of digital business models in the energy sector.
Electricity generation from renewable sources has gained considerable attention to meet the energy requirements amidst the effects of climate change and the energy crisis due to the outbreak of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic and sanctions on the supply of fossil fuels from Russia. However, renewable energy also has certain drawbacks.
For instance, ensuring supply stability and proper energy storage are the major issues in the fastest-growing wind and solar energy industries. These problems can be addressed by the digitalization of renewable power generation and the implementation of digital business models in the renewable energy sector.
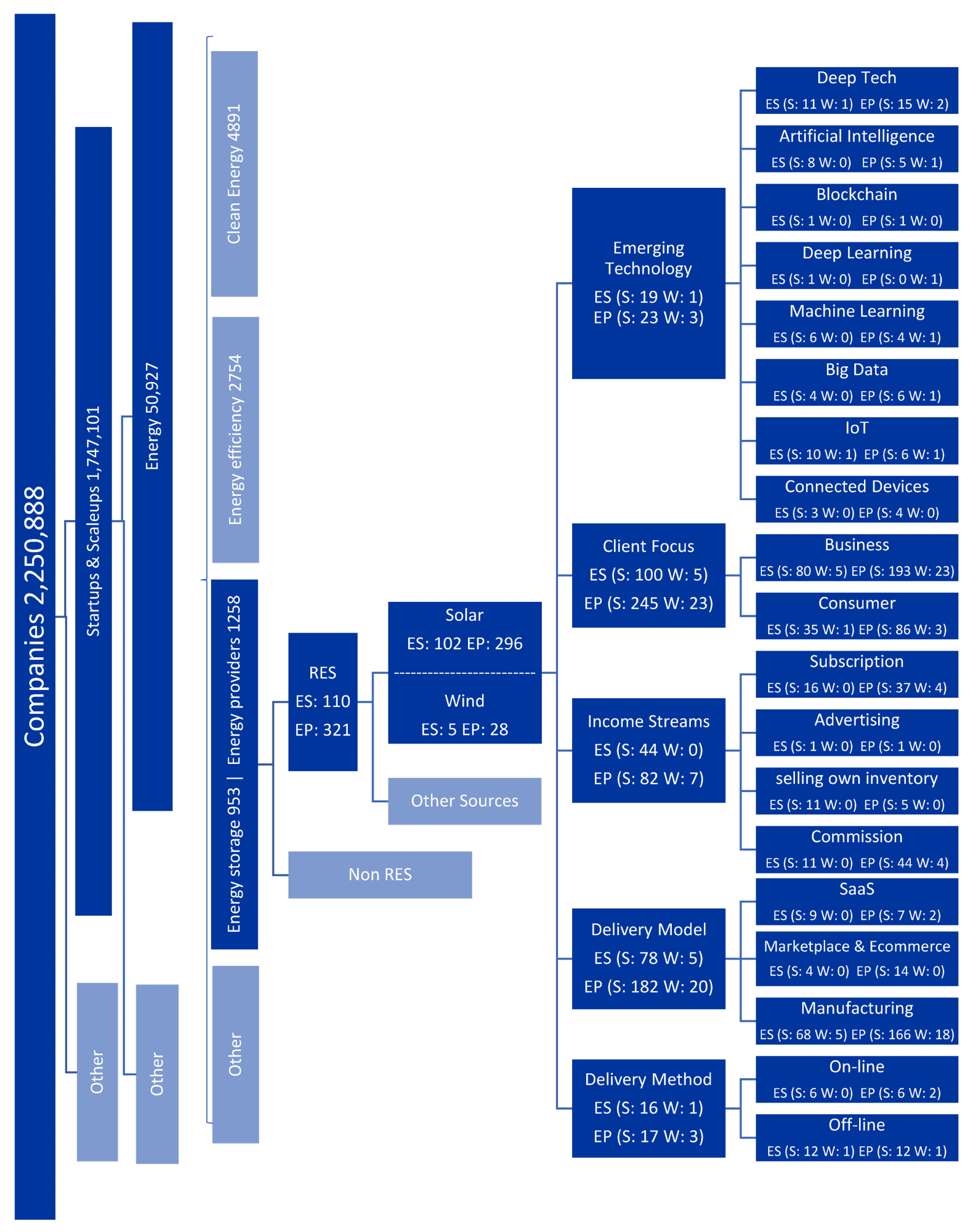
Data collection and selection model. ES—Energy storage, EP—energy providers, W—Wind, S—Solar. Image Credit: Pakulska, T et al., Energies
The Study
In this study, researchers identified and reviewed a framework of business models within a number of wind and solar energy startups operating in the energy supply and storage industries in the renewable energy sector. A research algorithm was employed to identify and classify the startup business models using R software based on the secondary data.
Observations
Implications of Innovative Business Models for the Energy Industry
The introduction of the Internet facilitated the dynamic growth of digital business and the transformation of standard resource-based business models to business models based on ecosystem and network effects. Digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, big data analytics, cloud-based services and applications, Internet of Everything (IoE), and Internet of Things (IoT), were the major drivers of growth in the digital economy.
Typically, digital technologies were considered as digital tools enabling fundamental changes in the enterprise operations or value delivered to customers. Digital technologies allowed the creation of innovative business-to-customer (B2C) and business-to-business (B2B) models and other new customer-centric models.
In the energy industry, innovative business models expanded their orientation on services by combining dedicated digital solutions, with several products at their core being turned into complex systems. These systems combine connectivity, software, microprocessors, data storage, sensors, and equipment in different ways, leading to the rising number of digital energy products in the energy industry that can be availed online in the form of information and data.
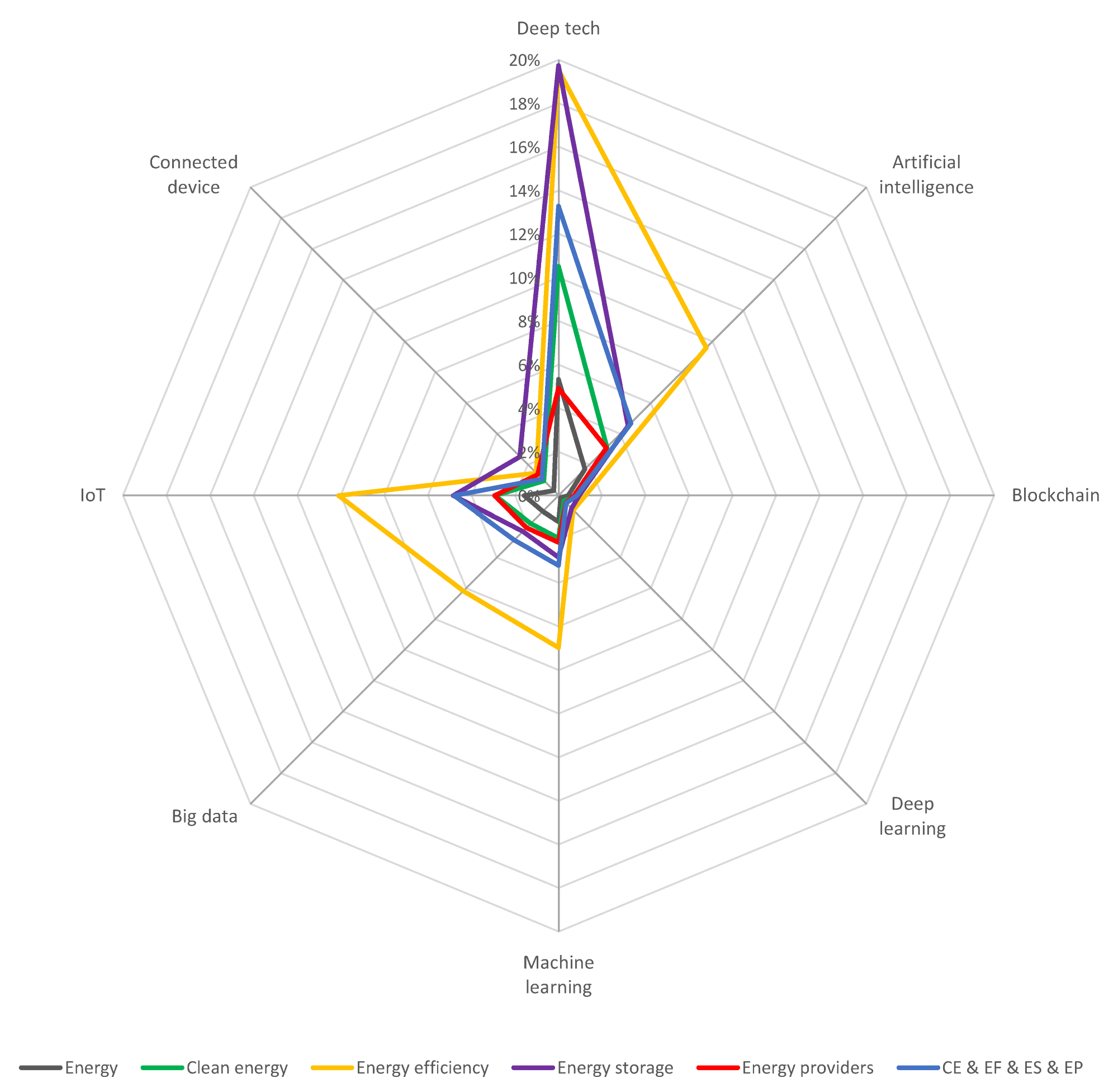
Technologies in power industry startups by energy sub-industry. Image Credit: Pakulska, T et al., Energies
Role of Digitalization to Alleviate Renewable Energy Challenges
The entry of big technology players in the renewable energy industry significantly contributed to the growth of renewable power generation. These players purchase renewable energy for their subsidiaries located in different parts of the world.
For instance, information and communication technology companies accounted for a leading share of global corporate renewable energy procurements in the past few years. However, the transition to renewable energy created new challenges and increased the cost of electricity.
For instance, the number of devices connected to the renewable energy grid increased substantially with the rising electricity generation from renewable sources. Among the digital technologies, the application of IoT witnessed the highest growth primarily driven by new technology standards such as 5G.
Additionally, the challenge to increase supply stability has grown significantly for the sub-industries of the wind and solar industry. The most common issues faced by the solar and wind energy industry were related to greater predictability and independence from weather factors, integration with existing energy systems, and energy storage from renewable sources.
Satellite data were used to develop insulation forecasts, while light detection and ranging (LIDAR) and satellite mapping tools enabled more efficient designing of entire wind- and sun-based energy systems. Moreover, the volume of data provided by wind turbines and photovoltaic (PV) systems was increased exponentially with the use of new sensors with a higher level of control, which translated into an enhanced demand for analytical solutions in the wind and solar energy industry.
The issue of energy storage was another major concern for the wind and solar energy sectors. Although the development of battery technology reduced the cost of batteries, they were still notably expensive and large, which necessitated the development of expensive and massive batteries to store wind and solar energy. However, new research demonstrated that massive renewable energy storage can increase carbon dioxide emissions.
Flexible renewable energy storage systems, application of AI algorithms, and more efficient analytical tools for the real-time management of energy systems can resolve the issue of energy storage. Moreover, the energy management digitalization can also lead to lower transmission losses, leading to lower costs.
Startups in the Renewable Energy Industry
The use of digital technologies was not prevalent among renewable energy startups. Connected devices, IoT, big data, machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), blockchain, AI, and deep tech were the digital technologies commonly used by renewable energy startups. A notable share of startups in the renewable energy sectors, including wind and solar energy, used at least one of these digital solutions.
Among the renewable energy startups, startups in the solar energy sector accounted for the largest share, followed by wind energy. Startups relying on at least one of the digital technologies were substantially higher in solar energy compared to startups in wind energy.
Clean energy and energy storage startups in solar energy significantly relied on digital technologies, while the use of these technologies was lower among energy providers. In wind energy, a smaller share of startups uses at least one digital technology.
Deep tech was the most commonly used digital technology in solar energy, followed by IoT and AI. Startups used deep tech to modify existing business models characterized by high environmental impact and significant capital requirements, and develop new solutions. Other digital technologies were utilized in a sporadic manner. Digital technologies played a crucial role in the energy storage sub-industry compared to the energy provider sub-industry.
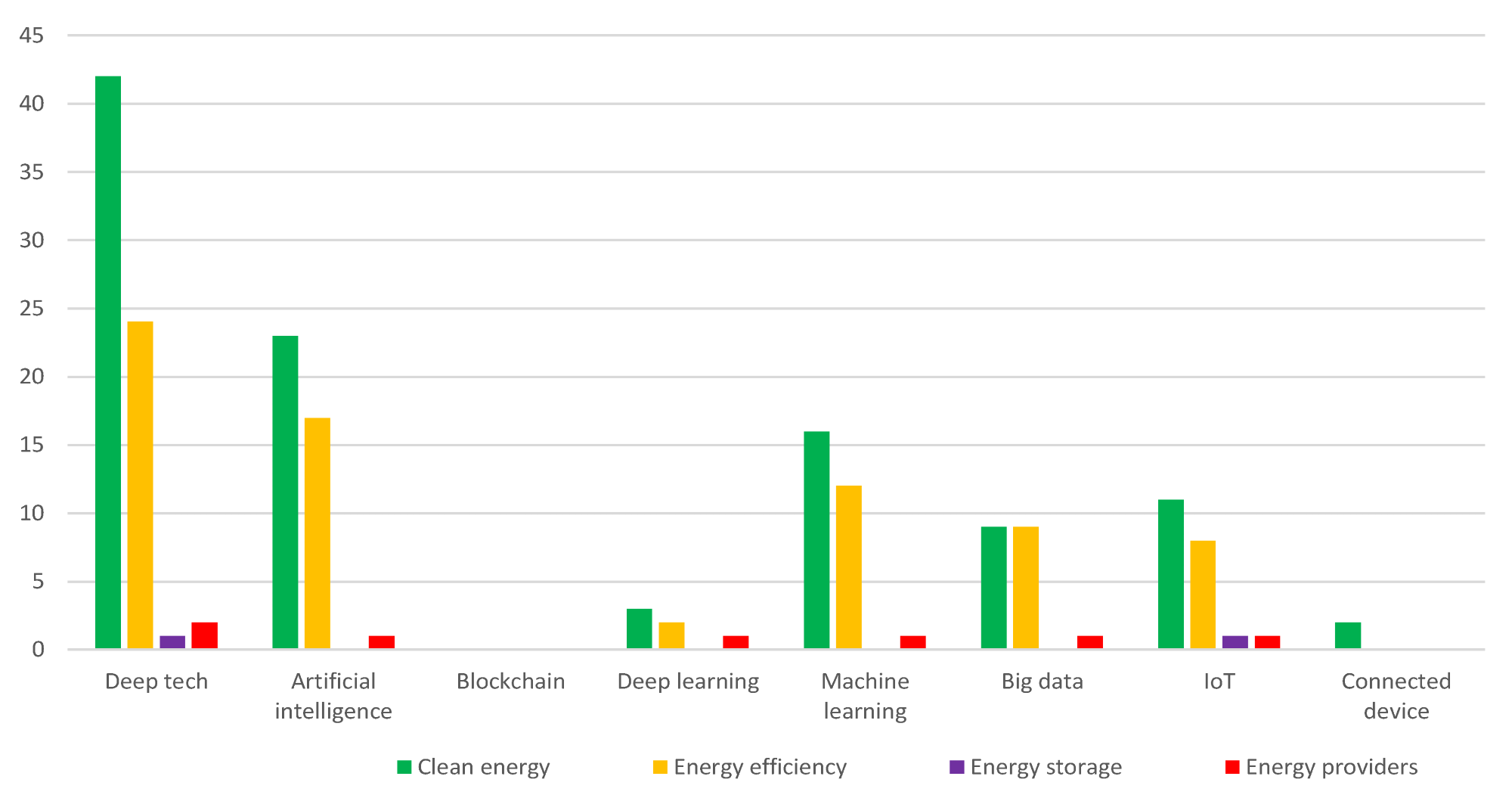
Startups dealing with wind energy by technology and sub-industry in January 2022. Image Credit: Pakulska, T et al., Energies
Conclusion
To summarize, the growing application of digital technologies in renewable energy has led to a dynamic transformation of the sector. However, the pace of these changes is slow due to the limited use of digital tools and certain non-technological factors, such as regulations and politics.
In the future, the environment for business model innovation, specifically for new entrants and startups, must be improved to encourage the development of digital technology-based innovative business models.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.
Source:
Pakulska, T., Poniatowska-Jaksch, M. Digitalization in the Renewable Energy Sector— New Market Players. Energies 2022. https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/13/4714