The study of plasma-liquid interactions has advanced significantly in recent years, owing primarily to the different applications of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP). The latest research published in the journal Materials seeks to investigate the major findings on the alteration of saline water characteristics by CAP supplies using PRISMA.
Study: Plasma–Saline Water Interaction: A Systematic Review. Image Credit: tsyklon/Shutterstock.com
Importance of Liquid-Plasma Interaction Studies
Although studies of plasma-liquid coupling commenced more than a century ago using high-energy pulsing devices or high-voltage confinement, significant growth in this study was not seen until the beginning of this century. This is mostly due to the wide range of applications for cold atmospheric plasma (CAP), such as those in liquid media.
Because of its significance in fields such as nanoparticle (NP) production, environmental cleanup, sterilizing, agribusiness, ecology, pharmacy, and food, the liquid-CAP interaction is receiving more attention.
These and other uses are made possible by the plasma's creation of UV radiation, shock waves, and active radicals.
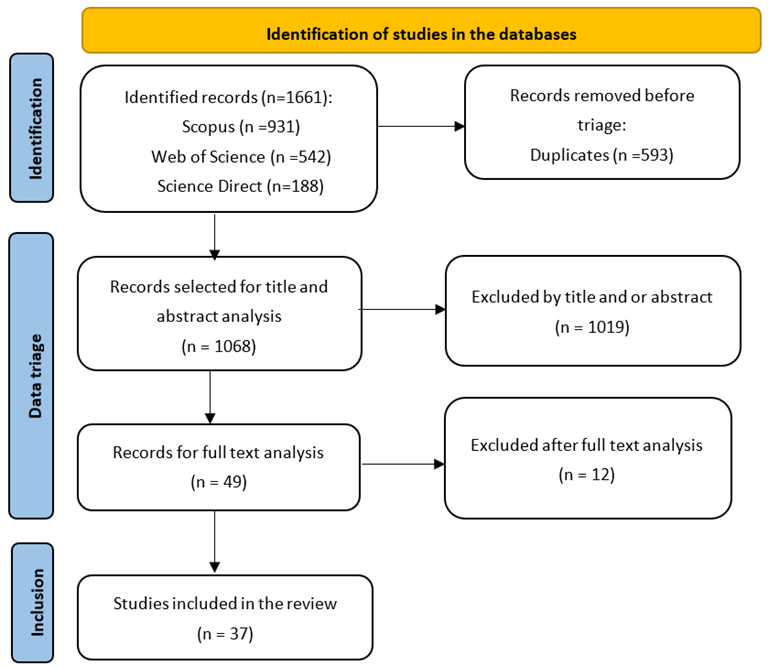
Selection flowchart of studies to be reviewed. Image Credit: Melo TFd et al., Materials
What Happens When Plasma and Saline Water Interact?
When plasma comes into contact with the surface of salt water, the oxidizing agents engage with the solubilized particles and generate extra physicochemical alterations, one of which is the rapid and selective crystallization of salts.
The impacts of plasma-saline water interaction have been described for sterilization and sanitation; distillation, crystallization, and precipitation of salts; catalysis of oxidation process; contaminant cleanup; and alternate supplies of nitrites/nitrates.
Significance of Energy Distribution in Plasma Species
Another critical factor to address is the pattern of energy dispensation among plasma species. A CAP involves the kinetic energy value of electrons (Te) much more significantly than the kinetic energy of the other species (Tg).
When the electronics temperature approaches the temperature of the other plasma species, it matches localized thermal equilibrium (LTE), which is referred to as hot atmospheric plasma (HAP). While impacts regulate plasma transformations and chemical changes in HAP, radioactive processes govern these occurrences in CAP.
Methods of Plasma System Generation
The vast majority of plasma systems depart from localized equilibria. What distinguishes them is primarily the method of stimulation of the power generators employed. In general, they can be generated in three different ways.
The first type of emission is a pulsed corona release, which occurs when high voltage bursts are delivered between a narrow conductive wire and a plane.
The second type of discharge is the dielectric barrier discharge (DBD), which occurs when a voltage is placed between two electrodes isolated by dielectric materials. Finally, an ionized jet is used, which involves applying a high-frequency voltage between two coaxial electrodes through which a gas substrate flows at a rapid pace.
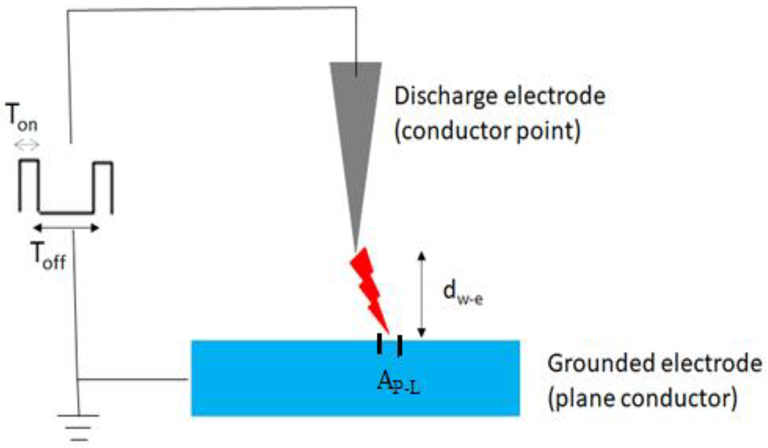
Schematic configuration of a corona discharge. Image Credit: Melo TFd et al., Materials
Factors Affecting Plasma Interaction
It follows that processing variables such as intensity, polarity, frequency of the electric field, pulse duration, activation time, effective region of contact, atmospheric composition, and water salinity content all influence the outcomes of plasma contact.
Identifying how these characteristics influence the plasma-salt water connection and how to connect them is a difficult challenge, but it is required when comparing the various processes.
Applications
As per the research, due to the creation of ozone, a powerful oxidant that can destroy harmful compounds, one of the primary applications of plasma in the environmental arena is the cleansing of industrial effluents.
Because of plasma's extraordinary potential in medicinal applications, a new and distinct medical discipline known as "plasma medicine" or "plasma biomedicine" has emerged. Processing with saline (0.9 percent NaCl) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), for example, is frequent in plasma healthcare treatments, especially for disinfection.
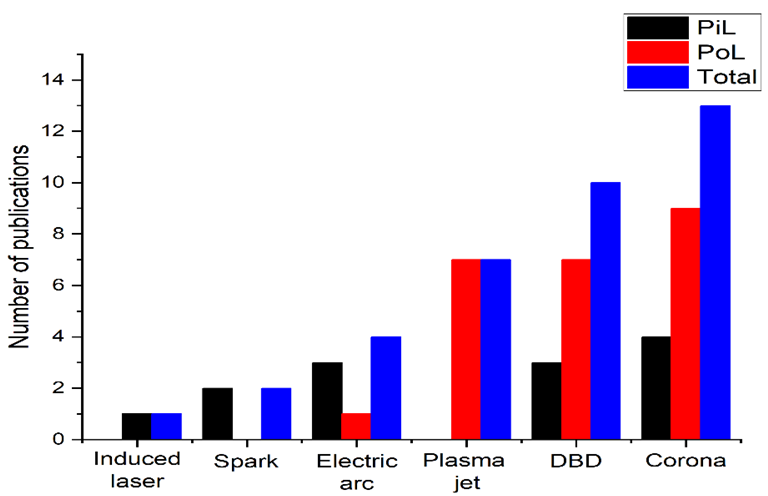
Plasma generation methods for saline-based water treatment, where PiL refers to the configuration in which the plasma is immersed in the liquid, and PoL to those configurations where the plasma is applied to the surface of the saline liquid. Image Credit: Melo TFd et al., Materials
Research Findings
The plasma-saline water contact exhibits the same behavior pattern as the low conductivity plasma-liquid interaction, with pH decreasing over time. The intensity of the discharge is supplied to a tiny AP-L in the corona discharge arrangement, creating localized acidification that is then spread to homogenize the solution.
Because the interaction with the plasma changes the ionic makeup of saline water, there is an improvement in conductance as a result of the concentration of reactive species in the liquid. Surface disturbances generated by electrostatic discharge can be supported by the development of crystalline salts in solutions with a high salt concentration, such as saltwater and brines.
In summary, the interface between the cold atmospheric plasma and this kind of mixture promises to be a potential arena for technological innovations, whether in purification and salt recovery or enhancing liquid characteristics.
Further Reading
Melo TFd et al. (2022). Plasma–Saline Water Interaction: A Systematic Review. Materials. 15(14). 4854. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/15/14/4854
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.