A new paper published in Materials has investigated the microstructure, properties, and influence of processes such as heat treatment on duplex stainless steels to provide information that can help manage the quality of these key industrial materials.

Study: Development of a Methodology for the Quality Management of Duplex Stainless Steels. Image Credit: lbrumf2/Shutterstock.com
Duplex Stainless Steels
The extreme working conditions found in the oil, gas, and chemical industries demand advanced materials that can withstand them and provide reliable performance and durability to avoid critical safety, maintenance, and cost issues.
Conventional structural steels cannot meet these demands, and their use can lead to breakdowns and subsequent safety, financial, and operational issues. To overcome the challenges faced by these industries, duplex stainless steels and various products constructed from them have found increasing application in recent years.
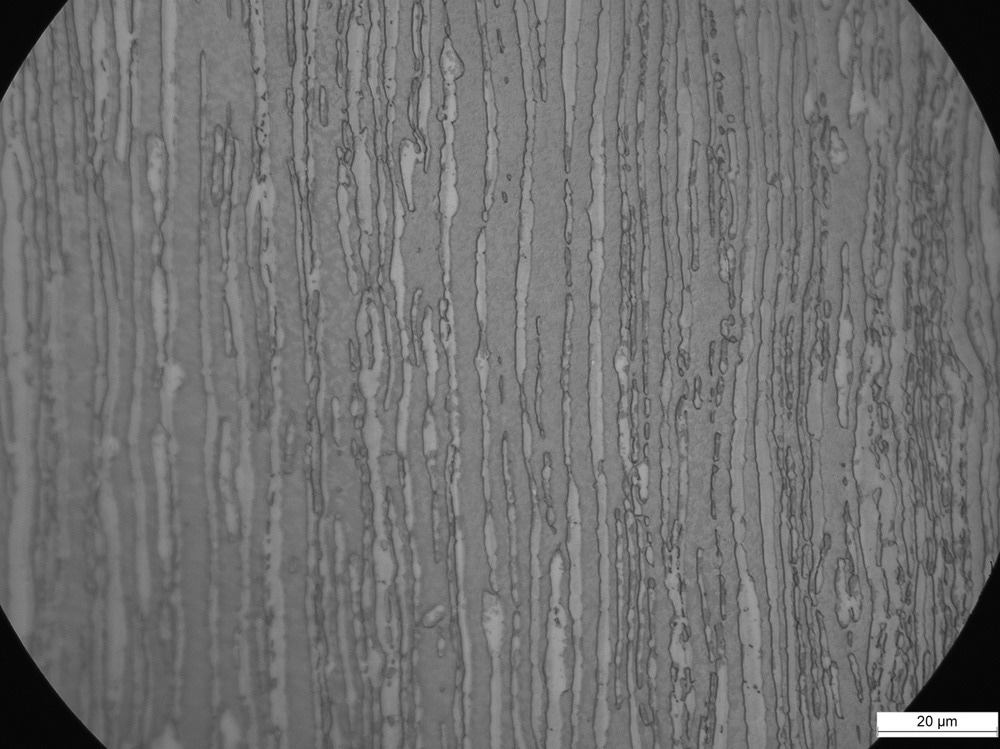
Duplex stainless steels are used in valves, wheels, impellers, and other moving parts of machinery which operate in extreme, aggressive conditions. These advanced steels are classified into various grades according to their pitting resistance equivalent number. The properties of duplex stainless steels rely on their austenite and ferrite ratios and the content of precipitations in secondary phases.
Chromium is used to improve steel’s corrosion resistance, but to retain the austenite-ferrite ratio, nickel must be added, which is expensive. Nitrogen can also be used, but this forms chromium nitrides by reacting with chromium in steel, which is unfavorable.
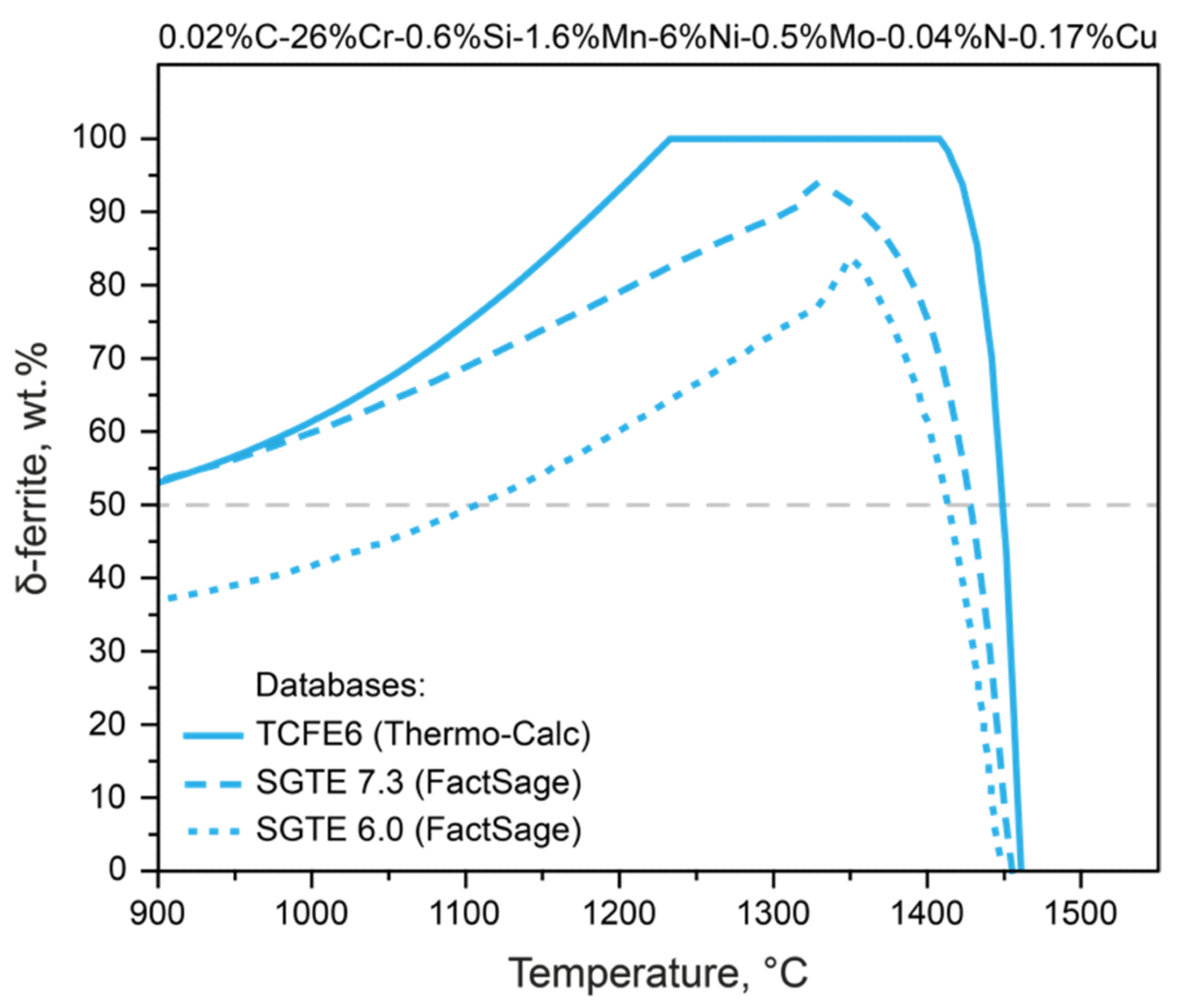
Thermodynamic modeling of δ-ferrite formation in Steel 3, performed using three thermodynamic databases. Image Credit: Federov, A., et al., Materials
Selecting the Optimal Duplex Stainless Steel
Optimizing the composition of duplex stainless steels is essential for ensuring their reliability and durability. Producing a composition with an equal ferrite-austenite ratio at the cast product’s heat treatment temperature whilst ensuring minimal temperature at the start of chromium nitride and σ phase formation is a key technical challenge.
The metallurgical history of the steel must also be considered when selecting a material with optimal properties and product performance capabilities. Sulfur and oxygen, which are harmful impurities that can cause the formation of non-metallic inclusions, reduce corrosion resistance in these materials, making them unsuitable for use in extreme working environments.
Steel melting and oxidization play a crucial role in the formation of non-metallic inclusions, with pitting commonly occurring at the interface between the steel matrix and the inclusions. Complex inclusions can occur during the manufacture of duplex stainless steels containing elements such as iron, manganese, and aluminum, and current studies are inconclusive on the effects of complex non-metallic inclusions.
Clarification of the role of metallurgical technologies and their link with corrosion effects, such as pitting caused by non-metallic inclusions, is crucial for optimizing the manufacture of reliable duplex stainless steels.
Thermodynamic modeling is traditionally used to clarify these issues, but this method is challenging in highly alloyed systems, with problems such as the selection of appropriate thermodynamic databases and predicting final material properties whilst considering the steel’s metallurgical history.
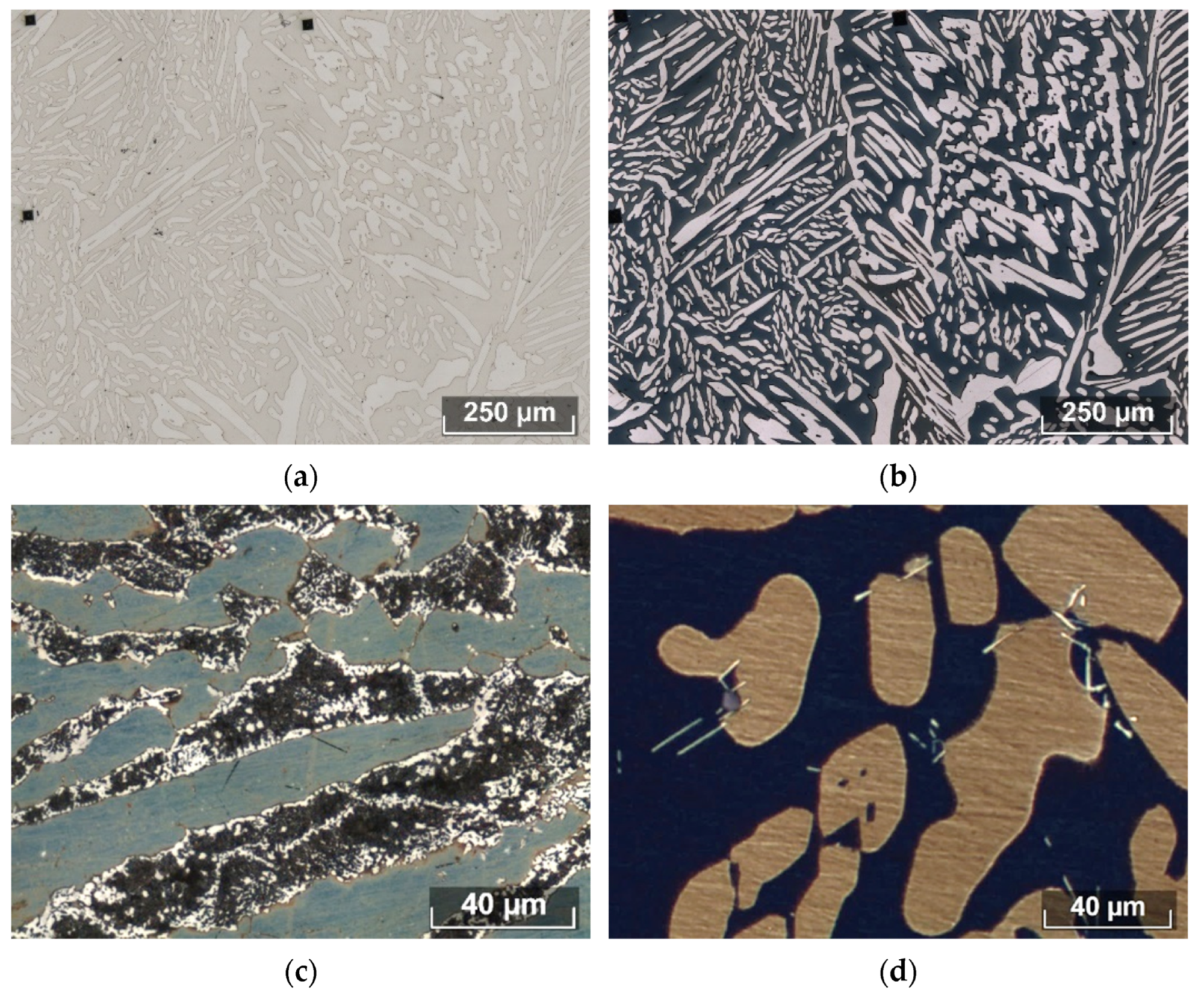
Microstructure of studied steels after electrolytic etching using NaOH (a) and chemical etching using Beraha etchant (b) in Steel 3. The Beraha etchant allows identification of the σ phase in Steel 7 (c) and Laves phases in Steel 8 (d). Image Credit: Federov, A., et al., Materials
The Paper
The new paper has developed a unified methodology to improve the quality control of duplex stainless steel. Different grade steels produced at both laboratory and industrial scales have been investigated in the study. Heat treatment and corrosion property effects on the microstructure of final products were evaluated in depth in the paper.
A thermodynamic database was chosen by the authors which describe phase formation processes in duplex stainless steels. Additionally, the team developed a technique for quantifying the material’s microstructure. The influence of the material’s structural state on the quality of consumer products was revealed.
Study Findings
Some important conclusions were drawn in the paper which are applicable to the field of quality control of duplex stainless steels. One of the main findings was that various deoxidation technologies can produce non-metallic inclusions that are either possess deleterious corrosion activities or are relatively safe. Optimizing these technologies can improve the quality of duplex stainless steel.
Tools were developed in the study which can control duplex stainless-steel quality at all production stages, from initial melting to final heat treatment. These tools also consider secondary phases during manufacturing. Thermodynamic criteria were developed to help select the reasonable choice of cast duplex stainless steel composition.
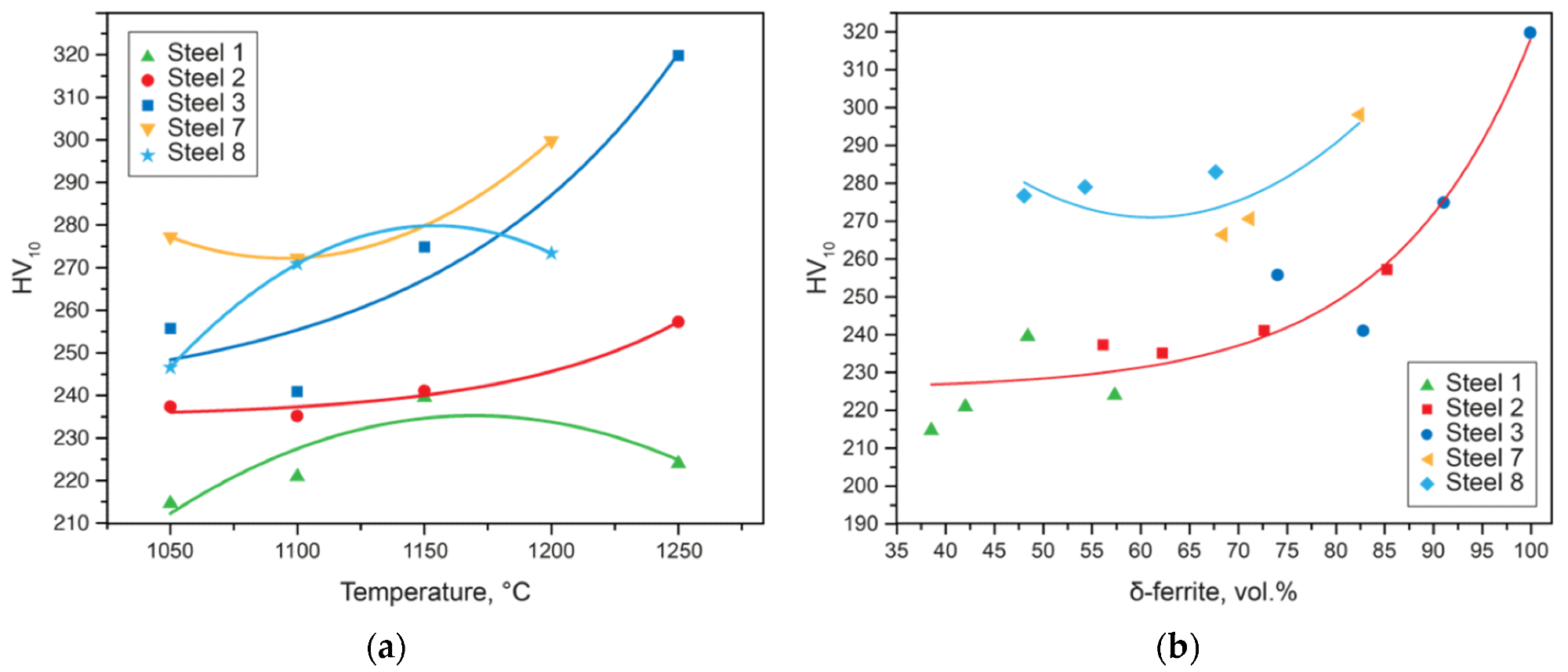
Correlation of hardness (HV) and the quenching temperature (a) and the amount of δ-ferrite in the steel microstructure (b). Image Credit: Federov, A., et al., Materials
The microstructural quantitative assessment technique developed in the research was utilized a Beraha etchant to etch the steel combined with the analysis of austenite, ferrite, and secondary phase precipitation. The technique utilized the ASTM E1245 method.
Al2O3 is an aggressive inclusion that causes enhanced pitting and corrosion; therefore, the authors have recommended that it should not be used as a deoxidizer. Instead, preliminary deoxidization with titanium and modification with REMs should be employed when manufacturing duplex stainless steels. This has the effect of reducing non-metallic inclusion fraction and size, converting them into inert forms.
Overall, the study has provided an innovative approach to quality control of duplex stainless steels that can help enhance the quality of these important industrial materials. By providing a unified methodology to control the properties of products constructed from duplex stainless steels, this research is important for the future development of advanced materials which can resist extreme working conditions.
Reference
Federov, A., et al. (2022) Development of a Methodology for the Quality Management of Duplex Stainless Steels Materials, 15(17) 6008 [online] mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/15/17/6008
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.