Renewable energy is a key technology in the 21st Century that is addressing resource shortages and climate change. Now, a new paper in the journal IET Renewable Power Generation has considered the reliability of sustainable energy microgrids which utilize renewable energy technologies.
Study: Reliability evaluation of the renewable energy-based microgrids considering resource variation. Image Credit: petovarga/Shutterstock.com
Utilizing Renewable Energy in Microgrids
Since the Industrial Revolution, accelerating global warming and climate change have led to increasingly severe environmental damage and growing instances of extreme weather events. As our impact as an industrialized society has become more apparent, governments and industries have pledged to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
Renewable energy is a key technological strategy to address and mitigate climate change, replacing environmentally damaging fossil fuels. Solutions such as solar power, wind power, hydropower, and geothermal energy have all been intensively researched in recent decades, with vast improvements made in their power output, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
Renewable energy-based units such as photovoltaic solar cells and wind turbines are finding increasing use in energy grids to supply local loads in microgrids. There are several benefits to this strategy, including reducing the environmental impact of energy use, reducing voltage drops, increasing microgrid reliability, and reducing power losses.
However, there is a key drawback to using these technologies in energy mixes currently, which is associated with the wide variation in renewable power generation in terms of the time of day, local weather patterns, and seasonality. This issue can affect different aspects and elements of microgrids, facilitating intense research to overcome it.
Improving the reliability of renewable energy-based microgrids is key to enhancing the benefits they bring for energy security, supply, and environmental sustainability. Aside from fluctuations in the power supply, random failures in components such as switches, transformers, and circuit breakers can cause interruptions in the power supply to microgrids.
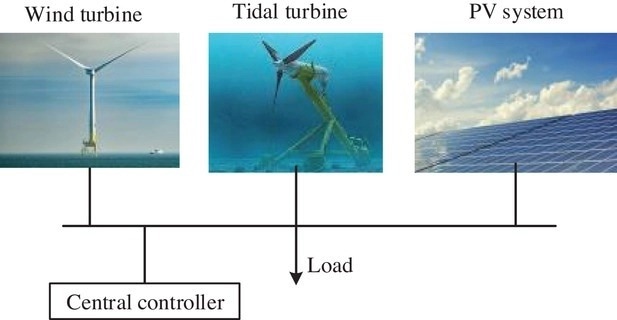
The structure of the renewable energy-based microgrid. Image Credit: Nargeszar, A., et al., IET Renewable Power Generation
The Study
The new paper investigates the reliability of renewable energy-based microgrids and has been conducted by researchers from Iran’s Islamic Azad University. Suitable renewable resource mixtures have been considered, including a photovoltaic system, wind unit, and tidal turbine which are installed in an island or coastal microgrid. The impact of component failure on overall microgrid failure has been studied.
Several papers have been reviewed and analyzed in-depth in the new research. Multiple simulation approaches and algorithms have been employed in past research, such as the Monte Carlo simulation method, Markov Chain model, and fuzzy logic approaches. Whilst the current literature body provides many useful perspectives on renewable energy microgrids, they suffer from some key limitations.
The paper in the journal IET Renewable Power Generation provides a number of innovations that improve on previous research. Firstly, a reliability model of a microgrid which incorporates tidal, wind, and PV components have been developed, with detailed consideration of the impact of all the component’s failure on overall microgrid failure.
Secondly, the paper considers the impact of all renewable resource parameters, such as solar radiation, wind speed, tidal speed, and temperature, on the failure rate of renewable energy microgrid components. For this purpose, the authors have developed different equations such as Arrhenius law, mechanical part contact stress and bending equations, fatigue strength, turbine limit state function, and temperature coefficients of photovoltaic panel power and voltage.
Finally, the paper considers technologies including a double-fed induction generator and a permanent magnet synchronous generator to comprehensively study wind and tidal generator technologies, which have an impact on unit reliability performance in microgrids.
Thus, by considering all relevant parameters and mechanical and electrical components, the research provides a comprehensive study that accurately determines resource-based failure rates in renewable energy microgrids. This improves the determination of system components and overall microgrid reliability.
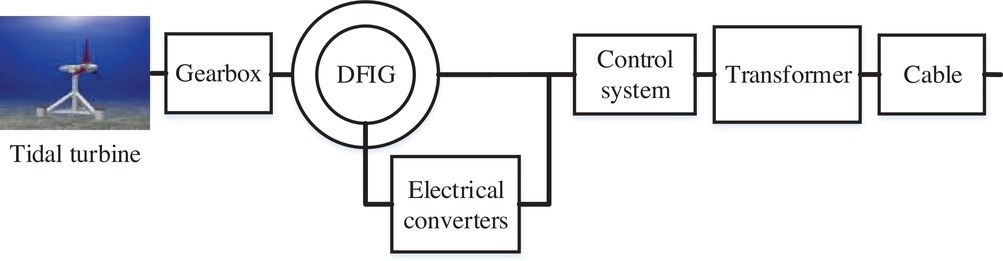
The constitutive components of a typical wind power generation unit. Image Credit: Nargeszar, A., et al., IET Renewable Power Generation
Study Conclusions
The study has revealed the resource-dependent failure effects on renewable energy microgrids, providing important information on the reliability of these components and units for meeting local load demands in energy grids.
Renewable resources display significant variations in energy generation capabilities which can fluctuate according to the time of day, local weather patterns, and seasonality. Wind speed, solar radiation, tidal current speed, and air and water temperature all have an effect on the reliability of renewable energy components. Numerical analysis of component failure rates confirmed this impact and has deduced results that can be employed in microgrid planning and operation.
![The structure of a typical PV system [38]](https://d12oja0ew7x0i8.cloudfront.net/images/news/ImageForNews_60285_16663464329478176.jpg)
The structure of a typical PV system. Image Credit: Nargeszar, A., et al., IET Renewable Power Generation
Mechanical equations determined component failure that arises from fatigue strength reduction at higher water and air temperatures. Temperature rises also affect the failure of electrical components, which was confirmed by Arrhenius law equations. Failure rates in different components are highly variable. The authors applied the Monte Carlo simulation approach to examine this impact.
Future work by the authors will examine the effect of wave period and height on the failure rate of wave converter components, which will improve the assessment of these renewable components' failure rates and reliability for microgrids. Overall, the paper provides an in-depth review of current research and a comprehensive framework for evaluating the reliability of renewable energy systems.
Further Reading
Nargeszar, A., et al. (2022) Reliability evaluation of the renewable energy-based microgrids considering resource variation. IET Renewable Power Generation [online] ietresearch.onlinelibrary.wiley.com. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1049/rpg2.12611
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.