Writing in the journal Scientific Reports, a team of researchers from the Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences in Poland have investigated eggshells and orange peel as organic sorbents to treat wastewater.

Study: The efficiency of removing heavy metal ions from industrial electropolishing wastewater using natural materials. Image Credit: Ekaterina Prokosheva/Shutterstock.com
The Problem with Industrial Wastewater Contamination
Whilst modern industry has undoubtedly improved the quality of life for a significant proportion of the world’s population, the environmental damage industrial activity causes has become more apparent over the past few decades.
One of the key environmental challenges associated with heavy industry is the release of wastewater contaminated with organic and inorganic pollutants, which can cause damage to fragile marine ecosystems and critical health problems for many communities around the world. Many industrial processes use heavy metals, which are one of the most critical wastewater pollutants if released in excessive quantities.
An example of an industry that has a particular problem with metal ion wastewater contamination is the electroplating industry, which deals with the production and processing of metal products. Large amounts of wastewater are produced during electroplating processes, and due to the presence of excessive amounts of metal ions, wastewater must be treated on-site before release.
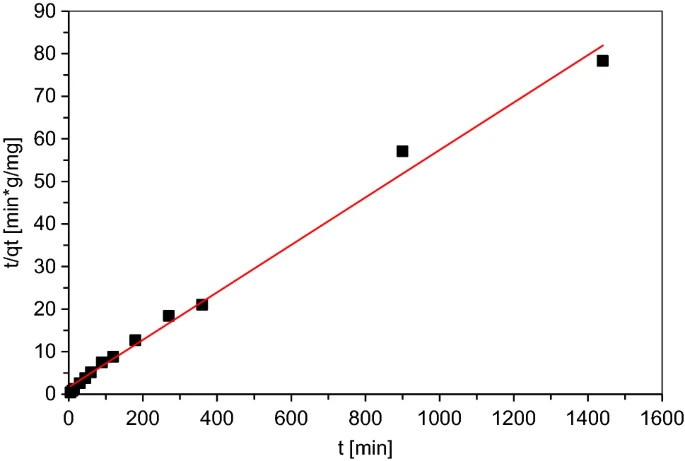
Pseudo-second order kinetic model for Eclipta alba powder. Image Credit: Charazińska, S et al., Scientific Reports
Commonly Used Wastewater Treatment Methods
To ensure the safety of wastewater disposal into the environment, researchers have concentrated on the development of several treatment methods over the space of the past few decades. The most commonly employed wastewater treatment methods include membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, sorption, and ion exchange.
Various methods have different advantages and drawbacks compared to other technologies. In the case of chemical precipitation approaches, which are commonly used in the electroplating industry, advantages include low cost and simplicity, with disadvantages being slow metal precipitation, the generation of sludge, which requires additional treatment, and the long-term environmental impact of sludge disposal.
Sorption methods have emerged as suitable candidates in contemporary research. Sorption is a low-cost process that possesses environmental advantages over methods such as chemical precipitation. It is highly efficient and produces vastly reduced amounts of sludge that would otherwise be problematic to treat and dispose of safely. Moreover, sorption uses fewer reagents than some other treatment methods.
One of the key benefits of sorption processes is the ability to use low-cost organic biomass from the food and agricultural industries, industrial waste materials such as ore and furnace slag, sewage sludge, and household waste as sorbent materials. Attesting to the suitability of these waste streams, there has been a steadily growing body of literature on their use in sorption methods.
Biosorbents from the agricultural industry have received particular attention in recent years, due to the intensification of fertilization in the agricultural sector which causes untoward eutrophication of groundwater and waterways. Utilizing agricultural waste provides a twofold solution to both the problems of the agricultural industry and the needs of the industrial wastewater treatment sector.
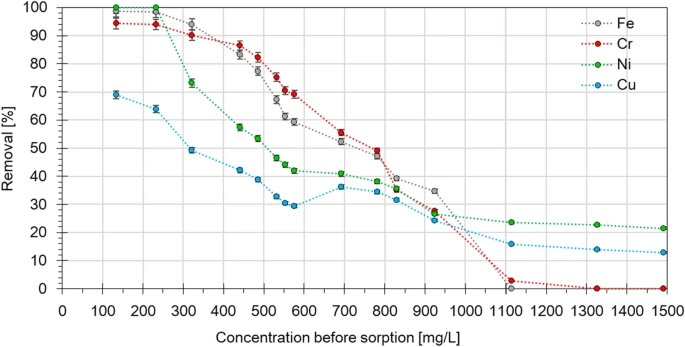
Removal percentage of metal ions from industrial solution at different initial concentrations of Eclipta alba powder. Image Credit: Charazińska, S et al., Scientific Reports
The Study
The study has focused on the employment of agricultural biosorbents for industrial wastewater treatment in the electroplating industry to provide a route toward a low-cost, high-efficiency, and sustainable sorption process for removing metal ions from wastewater runoff. Specifically, the authors have applied biosorbents to wastewater produced by stainless steel electropolishing, a key method in the electroplating industry.
Considering the applicability, effectiveness, and availability of natural biosorbents for acidic wastewater, the authors selected two widely produced agricultural waste materials for preliminary studies, orange peel and chicken eggshells, along with algae and plant material from Eclipta alba.
One of the key contributions of the research paper is demonstrating the effectiveness of using biosorbents for highly acidic wastewater treatment whilst retaining high heavy metal ion removal efficiency. Currently, this is a key challenge in wastewater contaminant remediation research.
The authors have noted that, whilst several studies have investigated using biosorbents, studies on real wastewater are still lacking. Therefore, real industrial effluent was used to evaluate the sorption efficiency of the organic biosorbents investigated in the research.
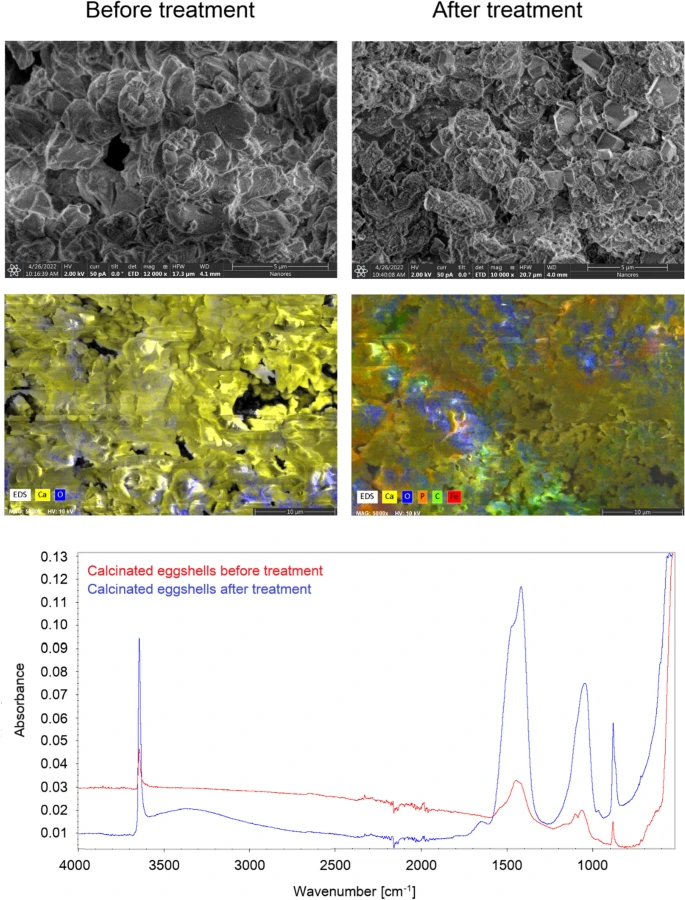
FT-IR spectra and SEM with EDS images of calcinated eggshells before and after sorption. Image Credit: Charazińska, S et al., Scientific Reports
Study Findings and Conclusions
The authors undertook a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of the biosorbents. The results of their experimental observations and analytical approaches confirmed the efficaciousness of using organic materials for heavy metal ion removal from real-world industrial wastewater.
Orange peel and algae were found to be insufficient for wastewater treatment due to factors such as the absorption of vast amounts of solution, which made separation from wastewater after treatment problematic. Eclipta alba has a relatively low sorption capacity. Fe and Cr ions were easiest to remove from wastewater, with copper and nickel harder to remove.
However, calcinated and dried eggshell, when used as a biosorbent for heavy metal ion removal from wastewater, demonstrated extremely high removal efficiency. Virtually 100% of Fe(III) ions were removed, with a removal efficiency of Cr(III) ions exceeding 90%. Ni(II) and Cu(II) removal were high as well. With removal efficiency in excess of 90% for metal ion removal, dried or calcinated eggshells are a good candidate for sorbent materials and wastewater remediation processes.
Overall, the study has provided a comprehensive preliminary investigation of a number of natural biosorbents and their action in real wastewater, which provides a route toward low-cost, high-efficiency, and environmentally friendly wastewater contaminant removal strategies.
Further Reading
Charazińska, S., Burszta-Adamiak, E., & Lochyński, P (2022) The efficiency of removing heavy metal ions from industrial electropolishing wastewater using natural materials Scientific Reports [online] nature.com. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-22466-9
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.