NH3 is the second largest produced chemical in the world, with nearly 80% of the NH3 produced being used in fertilizer synthesis. Meanwhile, NH3 is an important raw material in the production of nitric acid, which can be used in chemical production. Furthermore, because of its high hydrogen capacity, NH3 has the potential to be a carbon-free fuel.
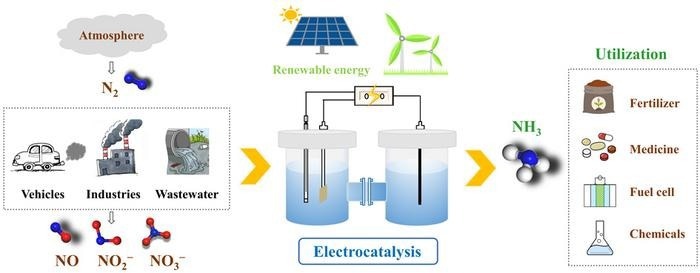
Artificial electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis (which can couple with clean renewable electricity) is recently becoming a research hotspot. Researchers review recent advances in electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis involving electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reaction, nitric oxide reduction reaction, and nitrate/nitrite reduction reaction. The challenges and future perspectives are also proposed in the concluding remarks. Image Credit: Chinese Journal of Catalysis.
As one of the greatest inventions, the Haber-Bosch process enables the large-scale production of value-added NH3. However, it goes against the principle of sustainable development theory due to the high operational costs and negative environmental impacts of the Haber-Bosch process.
Thus, it is vital that we explore new sustainable approaches to produce NH3 and simultaneously realize global environmental sustainability.
The use of N2 gas as the N source in artificial electrocatalytic NH3 synthesis (which can be coupled with clean renewable electricity) has recently become a topic of intereest in this regard.
Even though the electrocatalytic N2 reduction reaction (NRR) is an environmentally friendly and sustainable method of producing ambient NH3, the conversion efficiency of N2 reduction to NH3 is not the best due to the high thermodynamic stability of the N2 molecule.
Fortunately, more active N sources (i.e., NO, NO2−, NO3−) that are also harmful to the environment have been identified as attractive precursors to achieve effective NH3 production, and the development of electrocatalytic NO reduction reactions (NORR) and NO3−/NO2− (NOx−) reduction reactions (NtrRR) is also anticipated to regulate and alleviate the related environmental pollution.
Although there have been many encouraging studies in the area of artificial electrosynthesis of NH3, there are still difficulties in designing and developing active electrocatalysts with high selectivity and stability.
A study team guided by Prof. Xuping Sun from China’s University of Electronic Science and Technology recently introduced three electrochemical NH3 synthesis routes (NRR, NORR, and NtrRR) and then outlined recent advances in electrocatalyst development for ambient NH3 synthesis, primarily using catalytic mechanisms, theoretical advances, and electrochemical performance.
In the concluding remarks, the challenges and future perspectives are also proposed, aiming to provide experience and inspire more critical insights for the electrocatalytic NH3 synthesis reactions.
Journal Reference:
Ouyang, L., et al. (2023). Recent advances in electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis. doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64464-X.