A new method for synthesizing thiochromenopyrroledione derivatives in blue light is proposed by Hitomi Yutaka, a professor, and Pijush Kanti Roy, a Ph.D. candidate, from the Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Science and Engineering, along with their research team. The catalyst for this new method is titanium dioxide.
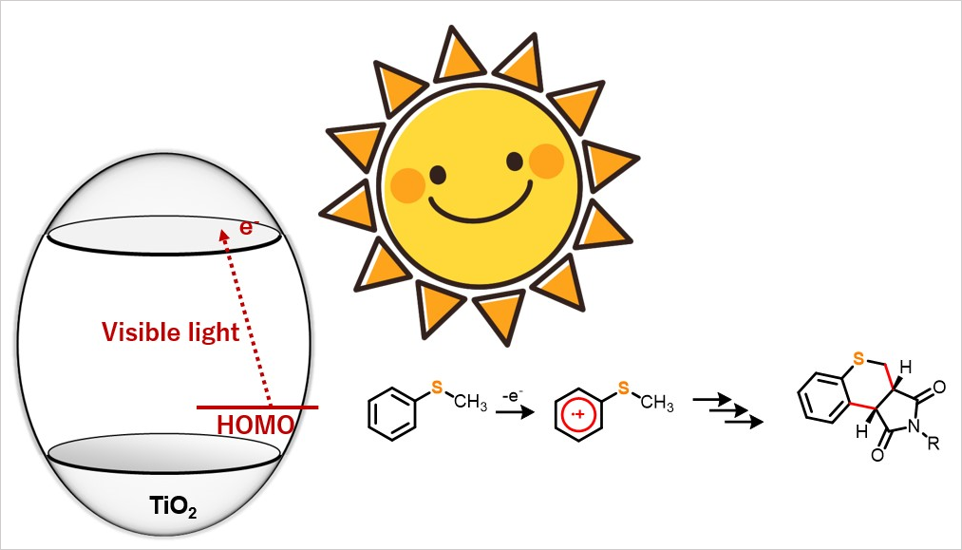
Chemical Synthesis Transformed by Solar Light: An Eco-Friendly and Innovative Approach with Titanium Dioxide. A team of researchers now present an eco-friendly and innovative approach for the blue light-promoted synthesis of heterocyclic thiochromenopyrroledione derivatives catalyzed by titanium dioxide. Image Credit: Professor Yutaka Hitomi from Doshisha University
Although sulfur is a common ingredient in many drugs, thiochromenopyrroledione derivatives are not yet recognized as a main structure in pharmaceuticals, highlighting its potential for medical use.
Recently, the researchers showed that a dual carbon–carbon bond formation reaction was produced when 4-substituted thioanisoles and N-substituted maleimides were exposed to blue light while titanium dioxide was used as a photocatalyst.
The study introduces titanium dioxide as a sustainable catalyst for the production of thiochromenopyrroledione derivatives and promotes novel techniques for organic synthesis.
Journal Reference
Roy, P. K., et. al. (2023) Blue Light-Promoted Synthesis of Thiochromenopyrroledione Derivatives via Titanium Dioxide-Catalyzed Dual Carbon–Carbon Bond Formation with Thioanisole and Maleimide Derivatives. Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis. doi:10.1002/adsc.202301021