A unique self-purifying water treatment system utilizing CoFe quantum dots embedded in graphene nanowires is presented in a pioneering study. Using the internal energy of wastewater, this device effectively eliminates more than 70% of different emergent pollutants from wastewater in less than two hours.
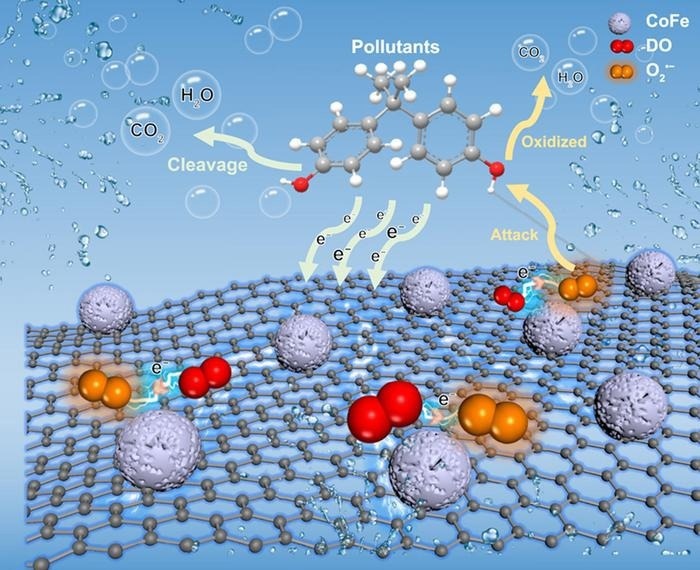 Graphical abstract. Image Credit: Environmental Science and Ecotechnology
Graphical abstract. Image Credit: Environmental Science and Ecotechnology
Public water safety is seriously threatened by emerging contaminants (ECs) in natural water bodies, such as synthetic dyes, medications, and endocrine disruptors. Despite their relative effectiveness, current wastewater treatment methods are unable to effectively remove these pollutants because of their hydrophobic nature and low concentrations.
A CoFeQds@GN-Nws catalyst system, which specifically utilizes the internal energy found in wastewater, was presented by Guangzhou University researchers in a recent study that was published in Volume 20 of the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology.
Electron-rich and electron-poor micro-regions are present on the catalyst’s surface, which promotes a self-purification process. In addition to oxidizing and cleaving contaminants, this mechanism increases the elimination of pollutants by converting dissolved oxygen into superoxide radicals. Surprisingly, the system achieves almost complete EC removal while running at room temperature and pressure without additional oxidants.
According to the study, CoFe quantum dots play a critical role in producing an uneven electron distribution that drives contaminants’ electron-donation action and activates dissolved oxygen into reactive oxygen species, a novel cleaning method.
The development of the CoFeQds@GN-Nws system marks a paradigm shift in wastewater treatment technologies. By leveraging the internal energy of wastewater and reducing dependence on external resources, this method not only addresses the challenge of ECs removal but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
Lai Lyu, Study Lead Author and Professor, Guangzhou University
The CoFeQds@GN-Nws system offers a technically revolutionary method for water filtration. The CoFeQds@GN-Nws system helps manage water pollution in a way that is more ecologically friendly and sustainable by lowering the resource and energy requirements of water treatment.
This cutting-edge technology supports international initiatives to reduce emissions and achieve carbon neutrality, strengthening the will to find long-term solutions for water security.
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (52350005, 52122009, 52070046, and 51838005), the Guangdong Province's “Pearl River Talent Recruitment Program” (2019ZT08L387), the Basic and Applied Basic Research Project of Guangzhou (202201020163), and the Introduced Innovative Research and Development Team Project provided financial support for this study.
Journal Reference:
Shi, Y., et. al. (2024) Water self-purification via electron donation effect of emerging contaminants arousing oxygen activation over ordered carbon-enhanced CoFe quantum dots. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology. doi:10.1016/j.ese.2023.100356