In a ground-breaking advancement for cardiovascular care, Hiden Analytical Ltd is proud to announce a surface measurement technique for devices critical in the treatment of heart disease. Utilising the most sensitive surface analysis technology, Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS), Hiden Analytical is setting new standards in the safety, efficacy, and innovation of stent technology.
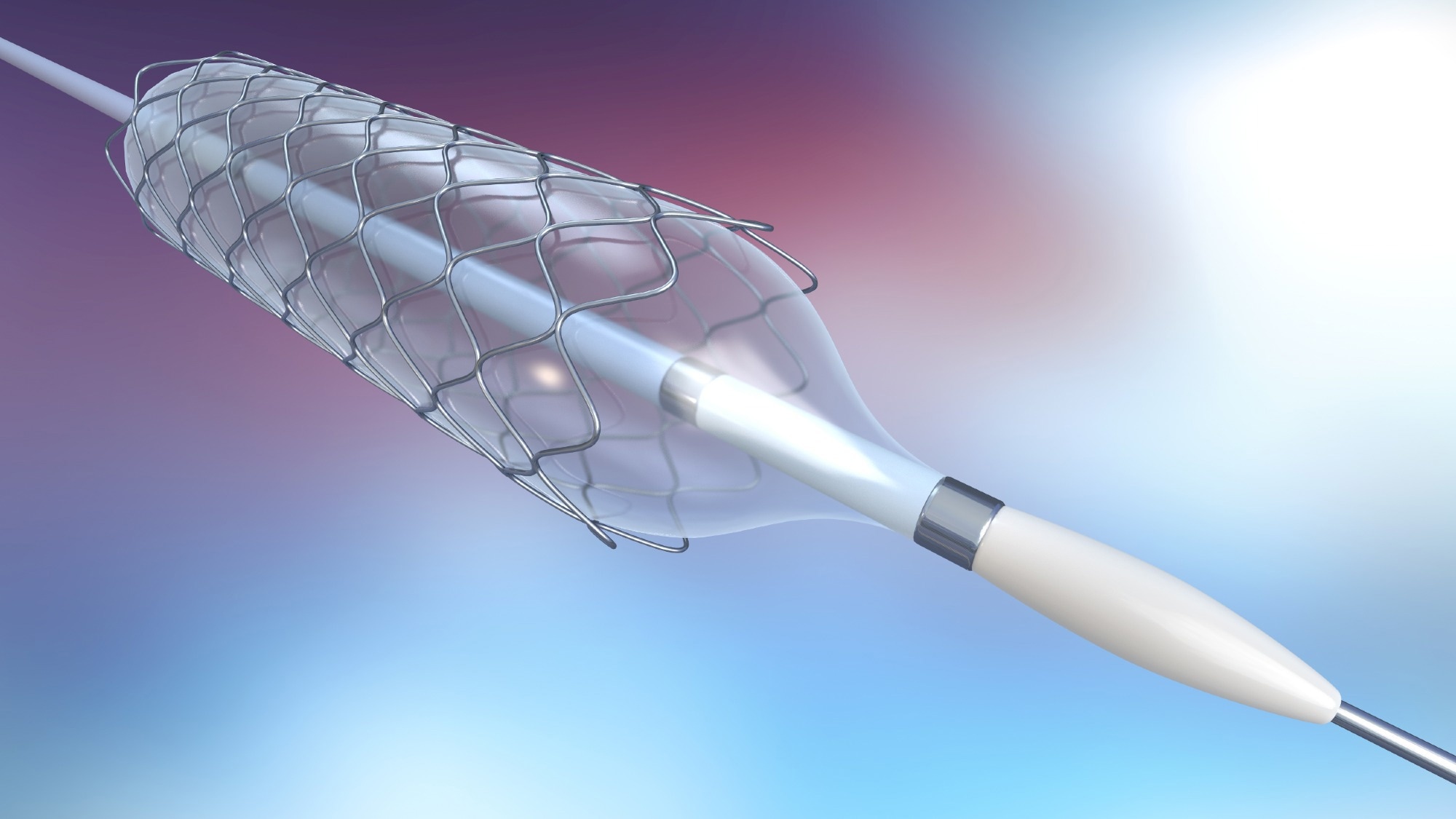
Image Credit: Hiden Analytical Ltd
Surgical stents, wireframe scaffolds typically laser-cut from stainless steel, play a vital role in holding narrowed arteries open, ensuring blood flows unimpeded through the body's vital pathways. The insertion of these stents via a catheter, followed by expansion with a small balloon, is a life-saving procedure for countless patients worldwide. However, the performance and longevity of these stents are highly dependent on their surface condition.
Recognizing the critical nature of the stent's surface, Hiden Analytical leverages SIMS to examine the nanometre-thick protective chromium dioxide layer that naturally forms on the material. This meticulous analysis, using caesium ion bombardment, has revealed how certain disinfecting treatments can leave the stent's surface iron-rich and vulnerable to corrosion—a condition that could lead to stent failure, rejection by the body and tissue damage.
The unparalleled limit of detection (LOD) offered by SIMS—capable of identifying substances at ppm and even ppb levels— and atomic layer depth resolution, sets a new benchmark in medical implant characterisation. This sensitivity, combined with techniques to enhance the analyte volume, allows for an optimization of analysis, balancing lateral and depth resolutions to focus on the most critical aspects of stent performance.
Dr. Graham Cooke remarks, "SIMS provides a rapid and reliable measurement of the near surface chemistry and corrosion behaviour, which is very reassuring in a life-saving medical product."