Physicists at the Commerce Department's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have taken the first ever two-dimensional pictures of a "frequency comb," providing extra information that enhances the comb's usefulness in optical atomic clocks, secure high-bandwidth communications, real-time chemical analysis, remote sensing, and the ultimate in precision control of atoms and molecules.
The work, described in the Feb. 8 issue of Nature, demonstrates a novel method for separating and identifying thousands of individual colors--or frequencies--of visible light while simultaneously measuring intensity and imaging the results in real time. The pictures transform frequency combs, long imagined as one-dimensional, like hair combs in which individual teeth represent specific frequencies, into twodimensional brushes, in which many rows of bristles represent frequencies.
"This is really the first time we've seen individual elements of the stabilized comb, without interacting it with atoms or probing it with another laser, and it turns out to look more like a brush than a comb," says lead author Scott Diddams. "We now can see all the bristles at once with high precision."
Frequency combs are a measurement tool designed and used at NIST and other laboratories for frequency metrology and optical atomic clocks. By providing a second dimension to the typical output of a frequency comb, the new technique efficiently packs more data into a given area without sacrificing precision, Diddams says. All light waves, or bristles, are displayed simultaneously, with a comb resolution as narrow as any other yet demonstrated, he says.
In the latest experiments reported in Nature, the researchers made a comb using an ultrafast laser that emits a continuous train of very brief, closely spaced pulses of light containing millions of different colors. The laser emits about 1 billion pulses per second, and each pulse lasts just a few quadrillionths of a second, or millionths of a billionth of a second. To demonstrate the imaging technique, the researchers selected a small section of the comb's spectrum (centered around 633 nanometers), which was passed through a filter to flexibly alter the spacing between frequencies, a technique necessary for the experimental set-up that also will be useful in applications.
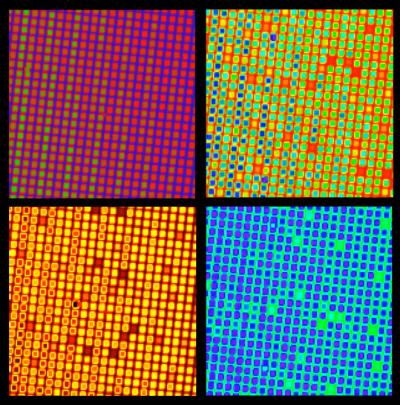
The light was then spatially separated twice, first vertically using a glass plate, and then horizontally with a metal grating. In combination, the two devices directed each wavelength of light in a specific and unique direction. The grid-like output was recorded by a digital camera connected to a computer. The pixels in the resulting images represent many different individual colors of light as well as the intensity of each signal. Thousands of different frequencies are shown in a single image in a pattern that repeats vertically as successive pulses of light are processed. Unique sections of demonstration images contain about 2,200 different frequencies.
The scientists demonstrated an application by making images with and without passing the laser light through iodine vapor, which absorbs some of the frequencies (bristles of the brush) in characteristic patterns, producing a unique "fingerprint" of the iodine molecules. They also altered the pulse repetition rate of the laser to scan a wide range of optical frequencies, a technique that fully maps the absorption features of the molecules at video rates.
The new technique will enable scientists to measure and manipulate optical frequencies in a massively parallel manner, Diddams says. The frequency brush could enable more precise control of individual frequencies than is currently possible in high-bandwidth communications, making it possible to reliably pack more channels with greater security into the same spectrum. The technique also may be useful in optical signal processing--synthesis and control of light as easily as electronic signals are currently manipulated--that could boost the power of surveillance, remote sensing, trace gas detection and high-speed computing systems. And it could enable the "ultimate" in precision control of atoms and molecules, a valuable tool in many areas of science, Diddams says.
http://www.nist.gov