The brightness of X-rays’ sources has increased over the past few years, chiefly because the beam quality of the photon beam has improved, as has the energy resolution and the number of photons.
One method of consuming a high number of photons is resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS), which is specific to the element, the site and the orbital, as well as responsive to the chemical composition of the surroundings. It has thus been increasingly used to investigate many samples, including soft matter.
Experimental Setup
For the current setup, a spectrometer with energy dispersive capability was used. It has an X-ray optical element, namely, a varied line spacing (VLS) grating, whose role is to focus the incident fluorescence on a direct X-ray 2D detector, which was in this case an Andor iKon-L CCD camera with back lighting.
Advantages
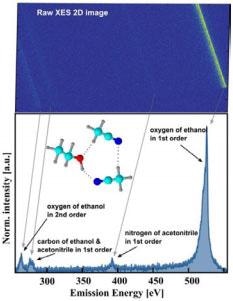
Figure 1. The emission signal from three different elements (carbon, nitrogen and oxygen) are recorded at one detector position.
The Andor iKON-L CCD camera has a resolution of 2048 x 2048 pixels with a 13.5 micron pixel size. It has excellent spatial resolution which is necessary for the spectrometer to offer high-caliber energy resolution of spectral signatures as a whole. Moreover, it is designed for intuitive function as well as possessing an efficient air cooling system to bring the temperature as low as -70 °C, which favors a high ratio of signal to noise. Its large chip size means it can cover a wide energy curve.
The increased size of the Andor iKon-L camera also allows the VLS grating characteristics to be taken full advantage of by the detector, leading to detection of energy of a large range. Figure 1 shows the range to be about 300 eV, that is, including the emission spectra of three separate elements (carbon, nitrogen and oxygen in this particular experiment), without sacrificing energy resolution. This enables efficient experimentation, yielding more data on the electronic structure of the elements tested.
References and Further Reading
- Z. Yin, H. B. Peters, U. Hahn, M. Agåker, A. Hage, R. Reininger, F. Siewert, J. Nordgren, J. Viefhaus, and S. Techert, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86, 093109 (2015).
- Z. Yin, H.-B. Peters, U. Hahn, J. Gonschior, D. Mierwaldt, I. Rajkovic, J. Viefhaus, C. Jooss, and S. Techert, J. Synchrotron Radiat. 24, 302 (2017).

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Andor Technology Ltd.
For more information on this source, please visit Andor Technology Ltd.