Lithium ion batteries are used in most portable electronic devices, such as mobile phones and laptops, because they are free from memory effects and provide the best energy to weight ratio. For these reasons they are also the most popular battery type in modern electric and hybrid automobiles.
Importance of Quality Control in the Manufacture of Li-Ion Batteries
When producing Li-ion batteries quality control during and after manufacturing is important as small imperfections can have big consequences. There have been several instances in recent years where devices containing imperfect Li-ion batteries have had to be recalled, sometimes in volumes of millions.
These batteries can also be dangerous if contaminated with metal particles; these particles can short circuit the battery resulting in thermal runway and a subsequent explosion.
Identifying Sources of Contamination in the Production Process
AZtecFeature can be used to detect particles in large samples and characterize them according to their composition and size. Information from the characterization can then be cross-referenced to possible sources of contamination from the production process.
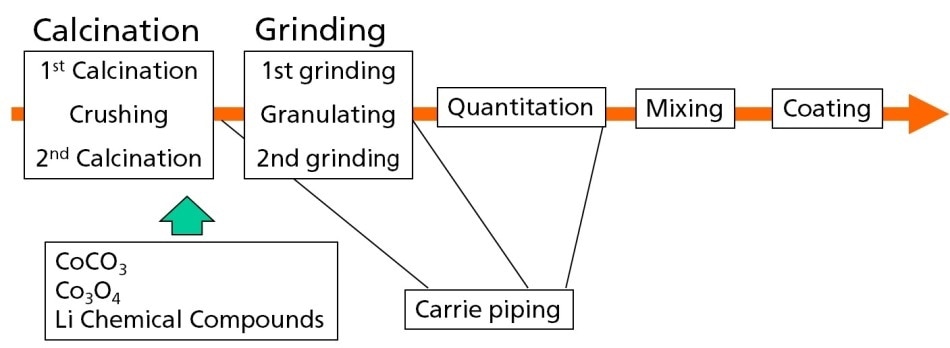
Figure showing a schematic of Li-Ion battery production process.
In this example particles collected from filters in a Li-ion battery manufacturing plant were characterized to determine the level of contamination and the contamination source.
AZtecFeature was able to differentiate between the cobalt oxide particles, used in the battery production, and unwanted Fe, Cr and Ni-containing contaminants. The accurate determination of the particle composition and size allowed the contamination source to be identified as stainless-steel pipes used for components transfer.
In addition, the particle sizing feature was used to determine if particles large enough to cause membrane piercing and catastrophic failure were present.
AZtecFeature for Determining Contamination Levels
Following this proof of concept the Li-ion battery manufacturer now uses AZtecFeature to regularly determine contamination levels in filters and ensure significant contamination does not occur. Running a contamination test to find, analyze and characterize over 900 particles takes only 12 minutes.
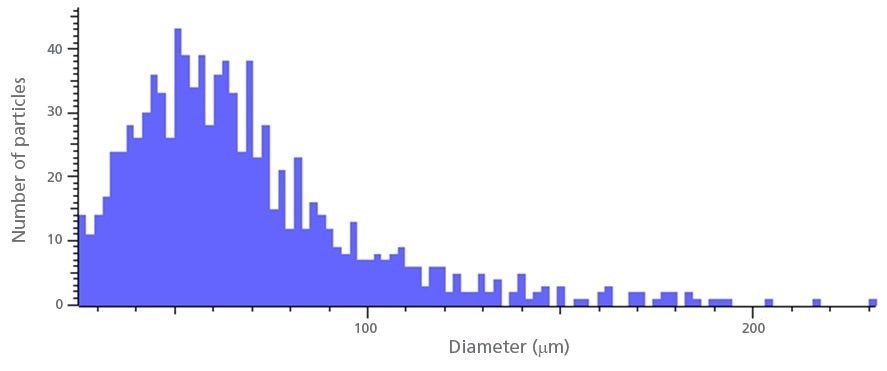
Figure showing the size distribution of contaminant particles.
Table showing three different classes of particles identified by AZtecFeature.
| Class |
Detected Elements |
Number of Particles |
Area of Particles (mm2) |
Percentage Particle Area (%) |
| 1 |
O, Cr, Fe, Ni |
414 |
2.46 |
2.214 |
| 2 |
O, Co |
199 |
0.25 |
0.257 |
| 3 |
O, Fe, Cr, Ni, Co |
193 |
0.80 |
0.717 |
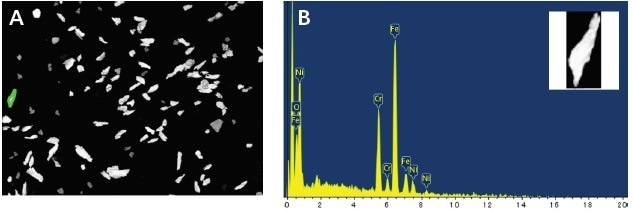
Figure showing (a) a typical field of view with one particle selected and (b) showing the spectrum of that particle.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Oxford Instruments NanoAnalysis.
For more information on this source, please visit Oxford Instruments NanoAnalysis.