The need for forming slanted gratings for applications such as combiners for AR headset has seen a recent surge. Ion beam etching technology is one of the best-suited techniques to enable the grating design required for these applications. Ion beam directionality in conjunction with variable incident beam angle via platen angle setting enables profile control and feature shaping during nanopatterning.
Ion beam expertise is critical to delivering the manufacturing tolerance required for these gratings. Oxford Instruments Plasma Technology has developed a technology to allow optical designers to build high-quality gratings for masters. Our solution delivers a large uniform processing area over 200 mm wafers for angles from 0° to 55°. In this paper, we share our experience in tuning the process for excellent shape control.
Process Tuning for Slanted Gratings
Unique ion beam capability allows materials to be etched without rotation, at a fixed platen angle. This technique can be applied to create slanted gratings as well as slanted waveguide facets. Figures 1a and 1b show schematic drawings of before and after the etch process and the actual process set up with platen angle set to 35°. This can be done for shallow or deeply etched gratings; the typical mask is to photoresistor a metal such as Cr or Al. The angle targeted is usually between 35° and 55°.
In ion beam etching, the platen angle defines the angle of incidence of the ions. Further process adjustments are achieved using parameters such as the beam current, the beam voltage, accelerator voltage, and source gas flows. When etching slanted features, critical parameters include the fill factor, the CD variation, and the etching depth. To meet these requirements, the thickness of the mask should be carefully selected as the selectivity can be limited in a physical etch. However, it is not recommended to use an excessively thick mask as the aspect ratio might affect the etch profile quality due to shadowing depending on the platen angle.
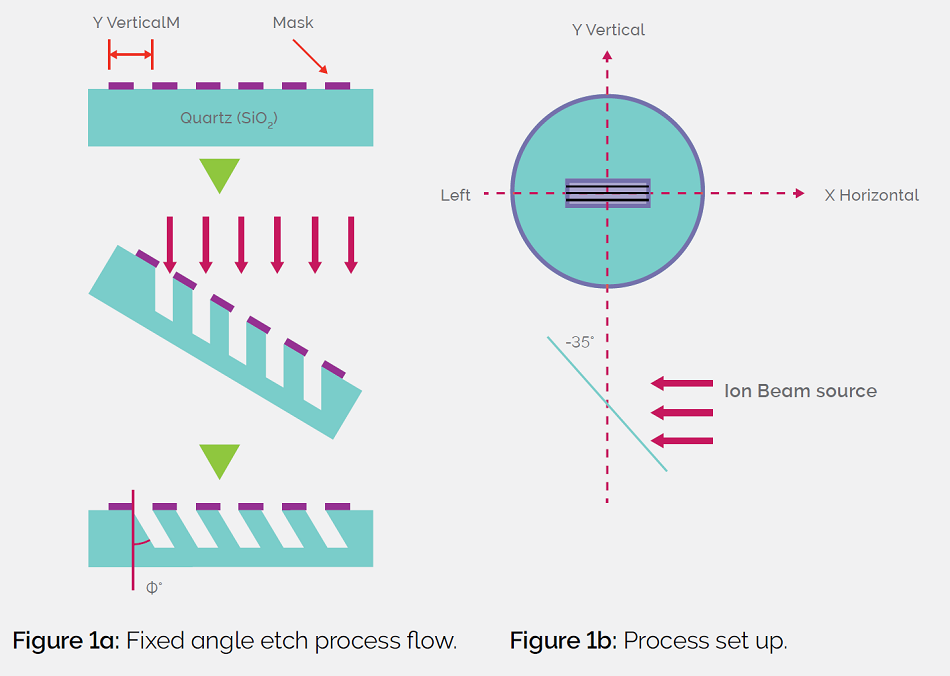 Figure1a: Fixed angle etch process flow. Figure 1b: process set up.
Figure1a: Fixed angle etch process flow. Figure 1b: process set up.
When etching slanted features, it is also critical to have control over sidewall angles and how parallel the sidewalls are. In order to achieve equal depth on either side of the trench, we recommend using a chemical process rather than a purely physical process. Chemical by-products will be removed easily in tight corners naturally created because of the slanted profile. Typically, a mixture of Ar/CHF3 for SiO2 and Ar with SF6 or Cl2 can be used for Si.
The potency of the chemical and physical side of the etch is also tightly linked with the beam current (IB), and beam voltage (VB). The higher the beam current, the more dominant the chemical side will be; whilst the higher the beam voltage, the more dominant the physical side will be.
The beam voltage drives the directionality of the etch whilst the chemical side provides the isotropic and necessary material removal required.

 Want to know more? Click here to read the full article.
Want to know more? Click here to read the full article.
.jpg)
This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Oxford Instruments Plasma Technology.
For more information on this source, please visit Oxford Instruments Plasma Technology.