Molybdates are well known as catalysts in selective oxidation of hydrocarbons. In terms of scale, the most frequent application is the usage as a precursor for catalysts in the hydrodesulfurization of refined petroleum products and natural gas.
RuS₂ is generally used for the latter application, but additionally, Co-Mo containing compounds present excellent activity. Conversely, NiMoO₄ is known to display a good selectivity in oxidation reactions of hydrocarbons. The catalytic activity of such materials is greatly dependent on particle size and the ratio to the support material.
Frequently, Al₂O₃ is used as a support material for these types of materials, which frequently appear as a combination of amorphous and crystalline fractions. The most used method to ascertain both the crystallite size of nanoparticles and the quantitative composition of solid mixtures is X-ray diffraction (XRD). In XRD, the peak width of reflections is related directly to the size of the scattering domain through Scherrer’s equation.
As such, the determination of the crystallite size (CS) is possible by determining the width of reflection in the diffraction pattern. Conversely, crystalline and amorphous contents can be quantified with good accuracy by sophisticated whole pattern fitting (WPF, Rietveld method) in one joint refinement.
Instrument
The Thermo Scientific™ ARL™ EQUINOX 100 X-ray Diffractometer uses a custom-designed Co (15 W) micro-focus tube with mirror optics for high flux, which has no need for external water chilling. The ARL EQUINOX 100 XRD offers very fast data collection times due to its distinctive curved position sensitive detector (CPS) that measures all diffraction peaks concurrently. As such, it is ideal for both the measurement of transmission and reflection in (Figure 1).

Figure 1. ARL EQUINOX 100 X-ray diffractometer. Image Credit: Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers
Experimental
NiMoO₄ and CoMoO₄ powders were measured for 45 min in reflection mode for XRD measurements. Employing MDI JADE 2010 (WPF), quantitative phase analysis and crystallite size determination (Scherrer’s equation) was carried out.
Results
Qualitative phase analysis shows that γ-Al₂O₃ and a significant amount of amorphous phase (most likely Al₂O₃) is present in both samples. The Al₂O₃ is used as a support for the actual β-CoMoO₄ (Figure 2) and β-NiMoO₄ phases (Figure 3). Quantitative analysis (WPF) of all crystalline and amorphous phases show substantial quantities of active Molybdate catalysts (c.f. Table 1) with crystallite size of 10 nm for both Molybdates.
Table 1. Results from WPF quantification. Source: Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers
| Phase |
Sample 1
(in wgt %) |
Sample 2
(in wgt. %) |
| CoMoO4 |
3.5 |
- |
| NiMoO4 |
- |
6.3 |
| γ-Al2O3 |
59.0 |
61.6 |
| Al2O3 (amorph.) |
37.5 |
32.1 |
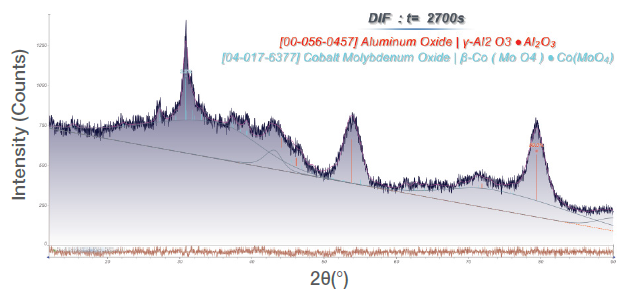
Figure 2. WPF of a CoMoO₄ sample. Image Credit: Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers
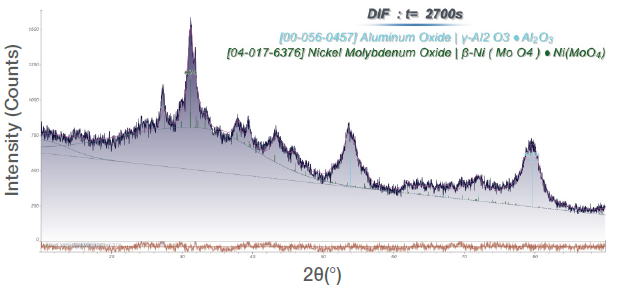
Figure 3. WPF of a NiMoO₄ sample. Image Credit: Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers
Conclusion
In conjunction with the MDI JADE 2010 software suite, the benchtop ARL EQUINOX 100 XRD is a useful solution to simply ascertain crystallite sizes and phase composition of Molybdate type catalysts. Both crystalline and amorphous phase being refined jointly is an intelligent and simple way to ascertain all values appropriate for characterizing the quality of such catalysts. The crystallite size of the active nanoparticles (10 nm) is in a standard range for such applications.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Dr Simon Welzmiller from Thermo Fisher Scientific.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers.
For more information on this source, please visit Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers.