It can be difficult to create a removable insulation blanket. Aside from the design process, including ensuring that the insulation blanket suits the part appropriately and considering whatever screws, brackets, and other protrusions may be present - the right materials need to be chosen.
How To Install Firwin's Removable Insulation Blankets
Video Credit: Firwin Corporation
Removable Insulation Blanket Construction
Removable insulation blankets can be categorized into three key elements:
- An outer protective cover—also called the cold face—is developed to safeguard and secure the insulation from the environment in which it finds itself.
- The insulation mat, normally 1-inch thick fiberglass, offers real heat containment. Thicknesses differ from ½” to a maximum of 4,” which relies on the quantity of heat reduction the application needs.
- The inner liner—also called the hot face—helps retain the insulation mat and might serve as a barrier to safeguard the insulation mat from fluid seepage.
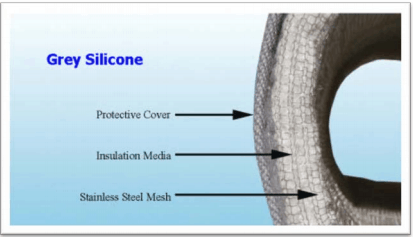
Image Credit: Firwin Corporation
Apart from these three elements, a fastening system is utilized to safeguard the insulation blankets in place. The fastening type employed is highly dependent on the equipment being wrapped, the applications for which it will be utilized, and the setting in which the wrapped equipment functions. A broad range of fastening devices is available with removable insulation blankets. Some of the common fastening methods comprise:

Image Credit: Firwin Corporation
Material and Fastening Options: Typical Engine Exhaust System
Material and fastening options are for example purposes and do not essentially correspond to the indicated component.
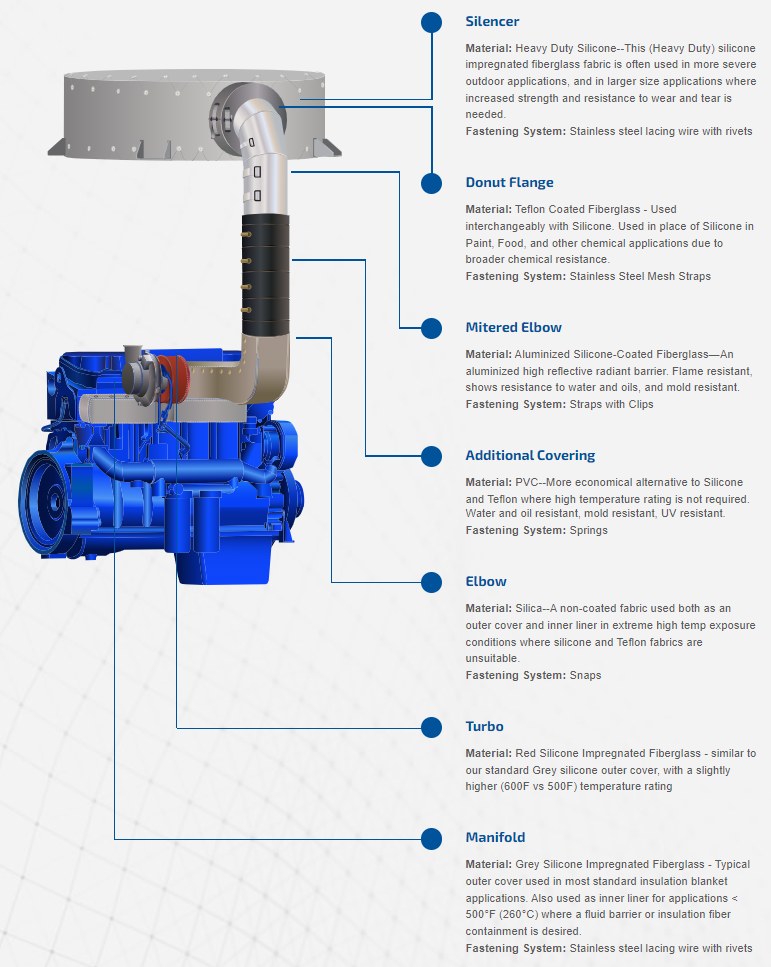
Image Credit: Firwin Corporation
Silencer
Material: Heavy Duty Silicone--The fiberglass fabric is impregnated by this (Heavy Duty) silicone. It is often employed in more extreme outdoor applications, and in greater-size applications, enhanced strength and wear and tear resistance is required.
Fastening System: Stainless steel lacing wire with rivets
Donut Flange
Material: Teflon-Coated Fiberglass. It is used with silicone interchangeably. It can be used in place of Silicone in Food, Paint, and other chemical applications owing to wider chemical resistance.
Fastening System: Stainless Steel Mesh Straps
Mitered Elbow
Material: Aluminized Silicone-Coated Fiberglass. It is a high-reflective radiant barrier that is aluminized. It is also flame-resistant and reveals resistance to oils and water and is mold-resistant.
Fastening System: Straps with Clips
Additional Covering
Material: PVC, which is a more cost-effective substitute to Teflon and Silicone, where a high-temperature rating is not needed. It is oil- and water-resistant, UV-resistant, and mold resistant.
Fastening System: Springs
Elbow
Material: Silica, a non-coated fabric employed as an inner liner and outer cover in very high temp exposure settings where Teflon and silicone fabrics are inappropriate.
Fastening System: Snaps
Turbo
Material: Red Silicone Impregnated Fiberglass. With a somewhat higher (600 F versus 500 F) temperature rating, it is identical to the standard Grey silicone outer cover.
Manifold
Material: Grey Silicone Impregnated Fiberglass is a usual outer cover in most standard insulation blanket applications. It is employed as an inner liner for applications <500 °F (260 °C) where an insulation fiber containment or fluid barrier is desired.
Fastening System: Stainless steel lacing wire with rivets
Material Considerations for Removable Insulation Blankets
The materials employed for the above-mentioned components can differ per the end-user requirements and application. Particular factors that the Firwin design team considers when determining the building of an insulation blanket comprise:
Flame Retardance
Appropriate flame-retardant insulation materials should be employed for applications in which open flames exist.
Mold Resistance
If users’ insulation is going to be frequently exposed to humid or damp surroundings, it is essential to choose materials that are resistant to microbe and mold growth to guarantee the safety and health of the employees and the durability of the blanket.
Color Selection
Most of the materials are available with a range of varied color options. This is something to take into account for aesthetic reasons and organizational, identifying reasons. Varied insulation colors can be employed to aid in differentiating various surfaces to make maintenance more effortless.
Location
Will the insulation be situated outdoors or indoors? If it is outside, then the material’s UV resistance will be an essential consideration.
Exposure to Elements
Will the insulation be subjected to oil, water, chemicals, or harsh substances that may erode the insulation? It is necessary to consider any exposure threats when choosing a material, as not all materials can stand up to these components.
Space Limitations
If the equipment is irregularly shaped or situated in a restrained space, it is essential to source thinner, more flexible insulation blanket material to guarantee the utmost coverage.
Maximum Temperature Range
Some materials tackle lower or higher temperature ranges better, whereas others can tackle a broad array from very low to very high. Understanding what ranges the insulation will be subjected to will be critical in identifying the appropriate material for the application.
Sound Absorption
Besides temperature control, insulation could be employed to minimize the sound produced by loud industrial equipment. Consider the requirement for noise alleviation while selecting the ideal material for the removable insulation blanket.
UV Resistance
Steady exposure to UV radiation, along with sunlight, can destroy some materials. Consider whether the insulation will be subjected to sunlight or other sources of UV radiation while making a decision on the right material.
Durability
Certain applications will subject the insulation blanket to a higher threat of damage via punctures, impact, or tears. For these harsh environments, extremely sturdy and durable insulation materials are available.
Other factors to take into account at the time of material selection might comprise:
- Desired outer surface “touch temperature“
- Desired heat retention inside the system (i.e. desired exhaust temperature)
- Safety and regulatory requirements (i.e. underground mining, marine, UL, OSHA)
- Frequency of insulation removal
Problems to Avoid When Sourcing Removable Insulation Blankets
Video Credit: Firwin Corporation
Applications
Removable insulation blankets are extremely adaptable and can be tailored to fit a range of equipment in a broad array of applications. Frequently, they are employed to insulate exhaust systems, engine components, and industrial machinery. Sectors like on-highway vehicles, power generation, marine and mining advantage from the application of insulation blankets to control engine heat.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Firwin Corporation.
For more information on this source, please visit Firwin Corporation.