Liposomes, composed of lipid bilayers, are often utilized in drug delivery for the encapsulation of the core with therapeutic drugs. Monitoring liposome size and encapsulation is of great importance during the research, formulation, production and quality control of liposomes.
Field flow fractionation (FFF) in conjunction with Multi-Angle Light Scattering (MALS) and Quasi-Elastic Light Scattering (QELS, also known as dynamic light scattering [DLS]) provides an ideal instrument for the characterisation of liposome size and encapsulation.
This article discusses the analytical results of two liposome samples, one empty, and another filled. For this analysis the Eclipse FFF system is used, followed by a DAWN HELEOS (with embedded WyattQELS instrumentation).
The use of Wyatt ISIS FFF simulation software optimizes this FFF method. The hydrodynamic radius, Rh, is directly measured by the online QELS, while the root-mean square radius, Rg, is measured by the HELEOS.
Analysis and Results
The Wyatt QELS detector is placed at roughly 143°, thereby extending the measurement of Rh to up to 300 nm. Elution time is plotted against both R and Rh, as shown in Figure 1. The results from duplicate runs show outstanding reproducibility of the FFF-MALS-QELS technique.
Moreover, Figure 1 reveals that the Rh values are well overlaid for both filled and empty liposomes, implying that the separation relies on hydrodynamic radius as anticipated from an FFF separation. Conversely, Rg values do not overlay for these two liposomes, indicating that these two liposomes possess different degrees of encapsulation.
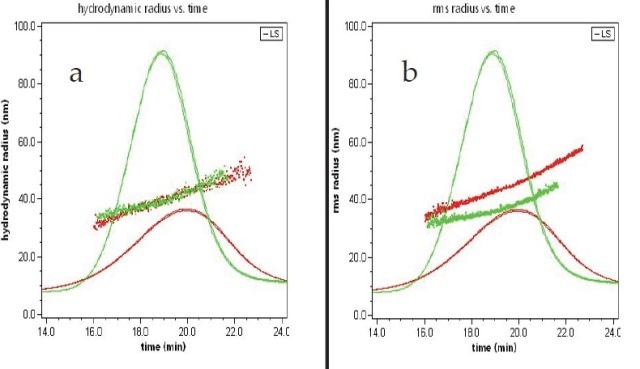
Figure 1. Hydrodynamic radius (a) and root-mean square radius (b) plotted against elution time overlaid with 90° LS signals for empty liposome sample (red) and filled liposome sample (green).
The Rg and Rh values of these two liposomes are then plotted against each other to obtain the internal structure of the liposomes from the slope of plot, as shown in Figure 2. The slope of the empty liposome sample is 1.0, which is in good agreement with a spherical shell structure. On the other hand, the slope of the filled liposome sample is 0.75, which is consistent with a solid sphere structure of uniform density.
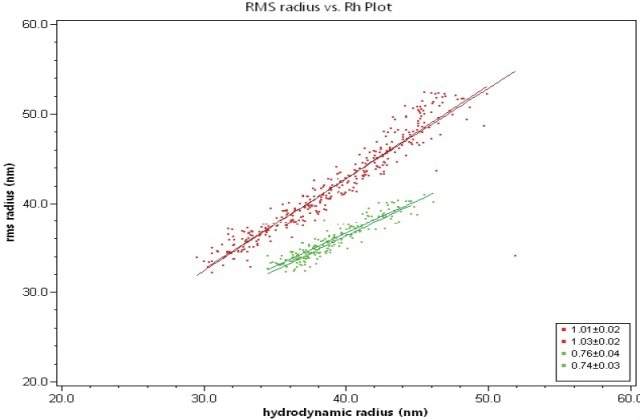
Figure 2. Root-mean square radius, Rg, plotted against hydrodynamic radius, Rh, for empty liposome sample (red) and filled liposome sample (green). The slopes for empty and filled liposomes are 1.0 and 0.75, respectively.
Conclusion
For liposomes or other nanoparticles, FFF-MALS-QELS is an easily adaptable yet robust characterization technique to acquire data on particle size, particle count, size distribution, and structure, all devoid of making assumption about the particles or their composition.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Wyatt Technology.
For more information on this source, please visit Wyatt Technology.