The MM 500 control is a high-energy laboratory ball mill that is designed to carry out wet, dry and cryogenic grinding with a frequency of up to 30 Hz. It is the first commercial mixer mill that enables monitoring and controlling of the temperature of a grinding process.
The temperature area spans a range from −100 °C to 100 °C. For the highest flexibility, the mill can be used with several thermal fluids, allowing the use of various tempering devices for heating or cooling.
If liquid nitrogen is selected for cooling, the mill has to be fitted with the extension device — cryoPad (optionally available). The advanced cryoPad technology enables choosing and controlling a certain cooling temperature ranging from −100 °C to 0 °C for the grinding process.
Mixer Mill MM 500 control - Introduction #RETSCH #mixermill #laboratoryinstruments
Product Video. Video Credit: RETSCH GmbH
Advantages Through Design
- Dry, cryogenic and wet grinding with up to 30 Hz for high energy grinding
- Patented hermetically closed fluid system guarantees safe operation of thermal fluids
- Ergonomic jar clamping, user-friendly parameter setting via touch display, and low noise level
- Rapid and easy sample processing with two screw lock jars of up to 125 mL each
- A broad range of accessories are available, such as heavy-metal-free grinding jars (also for cryogenic grinding) and ventilation lids

Image Credit: RETSCH GmbH
Temperature Monitoring and Control
- Non-stop temperature monitoring during the grinding process
- High flexibility in terms of selecting a tempering device for temperature regulation (LN2 supply, chiller, cryostat, etc.)
- Heating and cooling ranging from −100 °C to 100 °C
- Operation can be performed with liquid nitrogen or other thermal fluid
- Low-temperature grinding can be done without LN2

Image Credit: RETSCH GmbH
CryoPad
- Extension device cryoPad is necessary to work with LN2
- The technology enables selecting and maintaining a certain cooling temperature in the range between −100 °C and 0 °C when using LN2
- Regulates the flow of LN2 via the thermal plate
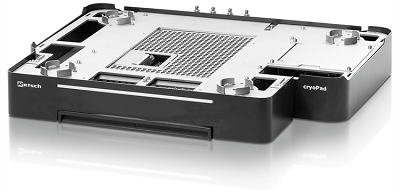
Image Credit: RETSCH GmbH
Temperature Regulation Based on Thermal Plates
The heating and cooling of the sample material are attained with the patented concept of thermal plates, making sample cooling with, for example, dry ice or open liquid nitrogen baths, outdated.
During tempering, the grinding jars are just positioned on top of the thermal plates. When the grinding jars touch the thermal plates, heat is efficiently transferred from or to the jars through the tempering device.
The patented hermetically sealed fluid design enables operating the mill with various thermal fluids, guaranteeing simple and safe temperature regulation and necessitating only limited effort from the user. Based on the operational installation, the temperature of the thermal plates can be fixed from −100 °C to +100 °C.
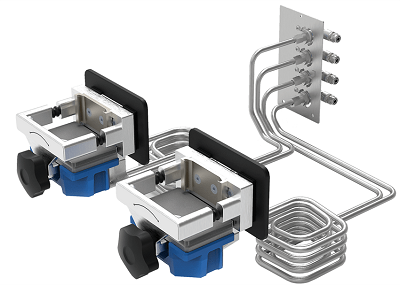
Image Credit: RETSCH GmbH
Configurations
To regulate the temperature of a grinding process, the mill has to be attached to an external tempering device. Fundamentally, there are two choices:
1. Temperature Regulation with Liquid Nitrogen
The mill is run with liquid nitrogen and attached to a nitrogen tank. In this arrangement, the mill must be extended with the extension device cryoPad (optionally available). The cryoPad’s patented PID (proportional–integral–derivative) system controls the flow of liquid nitrogen together with the temperature of the thermal plates.
In this arrangement, it is possible to choose and maintain the temperature of the thermal plates at a certain value. The preferred temperature can be changed via the touch display and can be selected within a range from −100 °C to 0 °C, in 10 steps.
Setup 1: Extension device cryoPad and LN2 tank for working with liquid nitrogen.
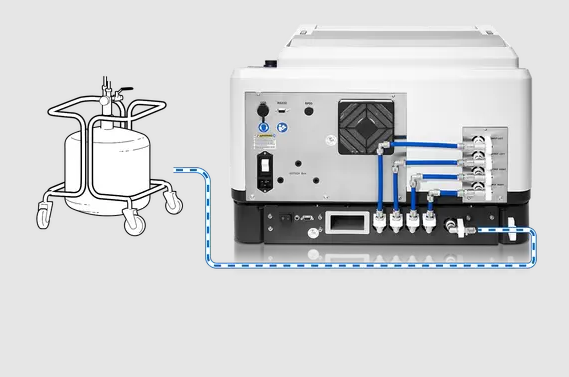
Image Credit: RETSCH GmbH
2. Cooling or Heating with a Liquid Thermal Fluid
In this arrangement, the mill can be attached to a chiller, a cryostat or the water tap. The external tempering device controls the corresponding thermal fluid to a definite temperature and the thermal fluid conveys this temperature to the thermal plates.
When the grinding process takes place, a substantial amount of heat may form within the jar, and the temperature of the thermal plates could be manipulated. To recap, the actual temperature of the thermal plates relies on the temperature of the thermal fluid and on grinding parameters, like jar volume, time, frequency and size of grinding balls.
For the highest control of the grinding process, the real temperature of the thermal plates is constantly checked in the touch display.
Setup 2: Operation with an external tempering device; for example, chiller, water tap or thermostat.
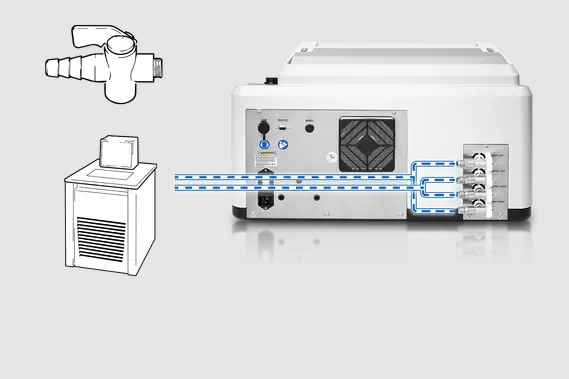
Image Credit: RETSCH GmbH
Application Examples
The temperature control of the MM 500 control is particularly engineered for processing the sample materials that are temperature-sensitive. Heating or cooling may have various objectives.
Cooling can be used for example:
- Embrittlement
- Mechanochemistry
- Preserving temperature-sensitive analytes (such as volatile substances or pharmaceutical and food ingredients)
- Wet grinding below room temperature
Some applications are enhanced if the sample material is heated up during the process. Examples for heating include:
- Intensifying mechanochemical reactions
- Paste making (in the food sector)
The necessary temperatures and the operational setup are conditional on the specific application.
Mixer Mill MM 500 control - Application Video #RETSCH #mixermill #laboratoryinstruments
Video Credit: RETSCH GmbH
videoanimation mixer mill function 480x360
Video Credit: RETSCH GmbH