Penn State University research team has developed a new system that employs magnetism for the purification of hybrid nanoparticles, which are structures comprising two or more types of nanomaterials that can be viewed only through an electron microscope.
According to Mary Beth Williams and Raymond Schaak, who led the research team, the novel method will not only eliminates impurities from hybrid nanoparticles, it will also assist scientists to differentiate between hybrid nanoparticles that look similar under the microscopic view but have dissimilar magnetism.
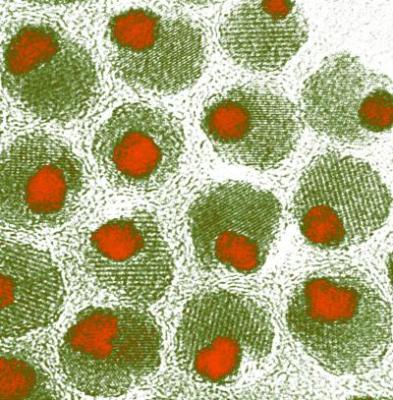 Nano-olives made up of an iron oxide olive with an iron and platinum pimento. Credit: The Schaak/Williams research groups, Department of Chemistry, Penn State University
Nano-olives made up of an iron oxide olive with an iron and platinum pimento. Credit: The Schaak/Williams research groups, Department of Chemistry, Penn State University
The innovative mechanism has the potential to enhance electronic information-storage devices, medical-imaging technologies, drug-targeting technologies and drug-delivery systems. According to Schaak, the presence of impurities can alter the qualities of a sample, for instance, the sample may become toxic due to the presence of impurities.
Williams stated that the novel process utilizes magnetic fields to reduce the flow speed of nanoparticles via small glass tubes known as capillaries. The researchers utilized a magnet to drag magnetic particles against the tube wall and with the reduction of the magnetic field, the particles flowed out of the tube, said Williams . Particle volume increases proportionately with magnetism, thus mild and progressive modifications in the magnetic field allow the researchers to gradually separate and differentiate the nanoparticles based on even small structural and magnetic differences, she added.
Williams further said that the nanoparticles’ magnetism varies with their shape, hence particles having various shapes bind to the capillary wall when various magnetic fields are employed, which in turn helps the researchers to differentiate the various nanoparticles present in the mixture, she added. The new method finds applications in the fields of diagnostics and medicine.