Apr 10 2018
Scientists from Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology and Skoltech have demonstrated the high-temperature superconductivity of actinium hydrides and discovered a general principle for calculating the superconductivity of hydrides based on the periodic table alone. The results of their study were published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
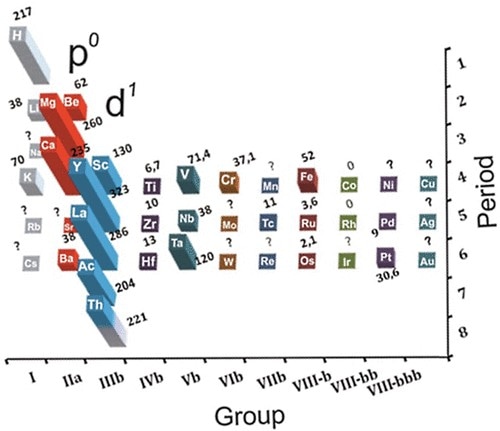 Image credit: Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology/Skoltech
Image credit: Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology/Skoltech
High-temperature superconductivity is a phenomenon of zero electrical resistance in certain materials at temperatures above -196 oC (the temperature of liquid nitrogen) that physicists, chemists and materials scientists worldwide have been intensely researching for decades, as room-temperature superconductors open up vast prospects for the power industry, transport, and other technology-driven sectors.
Currently, the record holder in high-temperature superconductivity is hydrogen sulfide (H3S), which functions as a superconductor at 1.5 million atmospheres and temperatures of down to -70 oC. Such pressure levels can only be attained in a lab environment, not in real life, and the temperature is way below room temperature, so the search continues for new superconductors. Perhaps an even higher-temperature superconductivity can be attained in metal-hydrogen compounds. Yet the link between chemical composition and superconductivity was unclear, leaving scientists to puzzle out by trial and error.
A group of chemists led by Artem R. Oganov, Professor at Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology and Skoltech, discovered that certain elements capable of forming superconducting compounds are arranged in a specific pattern in the periodic table. It was established that high-temperature superconductivity develops in substances containing metal atoms that come close to populating a new electronic subshell.
Metal atoms inside the crystal are assumed to become highly sensitive to the positions of the neighboring atoms, which would result in strong electron-phonon interaction ‒ the underlying effect of conventional superconductivity. Based on this assumption, the scientists supposed that high-temperature superconductivity could occur in actinium hydrides. Their supposition was verified and confirmed: superconductivity was predicted for AcH16 at temperatures of -69-22 oC at 1.5 million atmospheres.
The very idea of a connection between superconductivity and the periodic table was first put forward by Dmitry Semenok, a student at my lab. The principle he discovered is very simple and it is really amazing that no one had hit upon it before.
Professor Artem Oganov