The complementary base pairing rules can be used to design and assemble a wide range of complex secondary structures, which can help develop DNA molecular devices with unique functions that significantly contribute to diverse research fields.
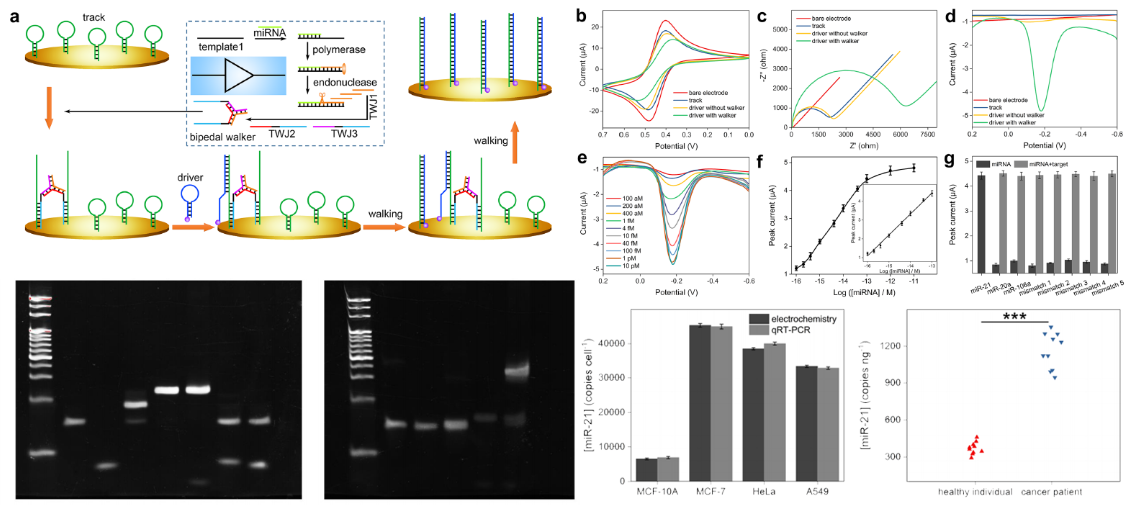 Bipedal DNA walking-based electrochemical detection of miRNA. Image Credit: SIBET.
Bipedal DNA walking-based electrochemical detection of miRNA. Image Credit: SIBET.
The DNA logic gates accept biomolecules (for example, DNA) or other external information as input and characterization results brought about by the variations in DNA structures as output. Post Boolean operation, it is possible to determine the mutual identification and correlation of different inputs.
Furthermore, several cascaded logic circuits or logic gates can be built by using the output of the former logic gate as the input of the latter one. With several combinations and different output modes, logic circuits have wider biomedical application potential.
Peng Miao’s team from the Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently created an innovative bipedal DNA walking nanomachine. The team built a series of DNA logic circuits based on cascade strand displacement amplification. The tools can be employed to explore the link between biological molecules in complex samples.
The research involved the modification of the electrode interface of track DNA probes with the stem-loop structure. Target-triggered strand displacement amplification was introduced into the upstream homogeneous system for generating a huge number of single-stranded sequences.
Then, the three-way DNA junction structure was organized into a bipedal walker. When the stem-loop structured driver strand was present, the bipedal walker moved around the electrode interface to enrich electrochemical signal molecules.
In addition, the researchers used incomplete three-way junction and double-stranded structures to build logic gates AND and OR by cascading strand displacement amplification. Then, NOR, NAND, XOR, and XNOR gates were also developed. The two-input logic circuits showed superior logic operation performance.
The three input AND and OR gates were later constructed with the help of the designed four-way junction and double-stranded structures. The logic circuits created as part of the research can offer fresh ideas for researchers in communication, biomolecule information control, and biological computing, in addition to finding use in ultra-sensitive biomedical sensing.
This study was financially supported by the Science and Technology Cooperation Project between the Chinese and Australian Governments and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Journal Reference:
Miao, P & Tang, Y (2021) Cascade Strand Displacement and Bipedal Walking Based DNA Logic System for miRNA Diagnostics. ACS Central Science. doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.1c00277.