A novel study published in the journal Materials focuses on a new liquid chitosan-based bio coagulant effectively generated from shrimp shells for cleaning wastewater from a Moroccan fish processing facility.

Study: Novel Liquid Chitosan-Based Biocoagulant for Treatment Optimization of Fish Processing Wastewater from a Moroccan Plant. Image Credit: Sherbak_photo/Shutterstock.com
The restoration of coastal shellfish is a viable approach for bulk marine waste management. A qualitative analysis of these pollutants was performed earlier to assess the treatment efficacy of the proposed bio coagulant.
Importance of Wastewater Effluent Treatment
Because of the many elements included in the pollutants, wastewater effluents from fish processing factories (fish processing wastewater, FPW) create an environmental problem. This industry earns USD 207,407,800.00 in export revenue each year.
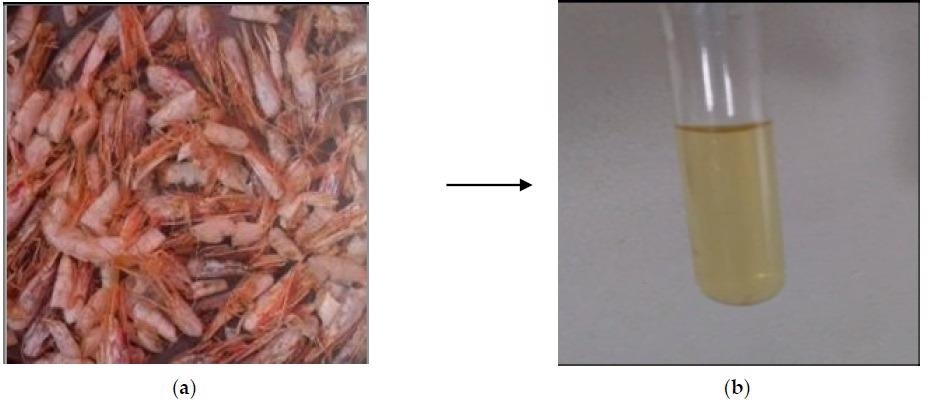

Transformation of shrimp shells to liquid chitosan: (a) dried shrimp exoskeleton; (b) liquid chitosan. Image Credit: Nouj, N., Materials
The seafood processing sector is also responsible for a substantial amount of fish-related waste material, such as bones, skins, scales, fins, and swim bladders, which account for 36% (and maybe up to 60%) of the raw material mass. If a thorough examination is performed, these solid wastes might be potential sources of revenue.
Various Water Treatment Processes
To safeguard the environment, several techniques were used to remediate this effluent. Among the available therapies is coagulation-flocculation, which is the most extensively used method and addresses the need to replace artificial chelating agents with natural ones to protect the environment.
Importance of Chitosan
Chitosan was employed in various investigations and techniques to identify a natural coagulant, including its production from the most prevalent fish by-product: shrimp shells.
Chitosan is the most popular natural coagulant as a biomaterial. Bio-coagulants are primarily used to reduce the need for chemical coagulants. To remediate wastewater, chitosan powder is immersed in acetic acid. Chitosan has been used to treat a variety of effluent from the food sector, including meat, dairy products, bagasse, and egg, as well as numerous turbid natural streams.
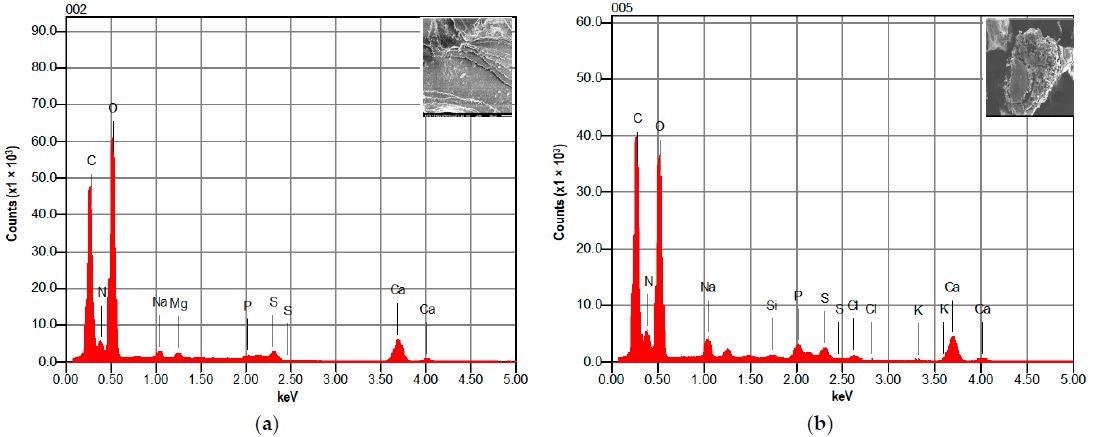
EDX spectrum of raw shrimp shell: (a) for 10 μm SEM image and (b): for 50 μm SEM image. Image Credit: Nouj, N., Materials
It demonstrates a clearance rate of between 70% and 90% for suspended particulate solids content (TSS) and between 83 and 84 percent for biological oxygen demand (BOD) (BOD5).
Limitations of Chitosan
Because of its high heat and chemical resistance, chitosan has been extensively employed in the production of active biodegradable films. Despite its many advantages and unique qualities, chitosan sheets have significant drawbacks, such as weak insulation to water vapor and gas, as well as inadequate mechanical and thermal properties, which limit their usage in a variety of applications.
Research Methods
Specimens of waste effluent were gathered at a fish production plant in the Anza industrial district of Agadir, Morocco.
To optimize the FPW treatments utilizing the bio coagulation process, the experimental study model took the following three elements into account as input variables: coagulant percentage (X1), starting pH (X2), and temperature (X3).
The elemental content of the substance was determined by observing various mixes of raw shrimp shells.
Research Findings
It was found that the dried biomaterial was not uniform. A dense network is produced, which is characterized by rather robust C-O-NH hydrogen bonds. These chains maintain a spacing of roughly 0.47 nm.
The existence of peaks indicative of (OH) hydroxyl groups and (NH) primary amines was verified by IR.
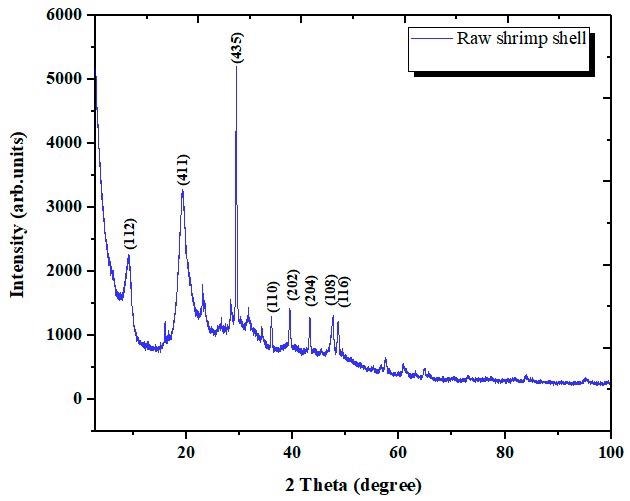
XRD spectrum of raw shrimp shell. Image Credit: Nouj, N., Materials
The bulk of the peaks in the calcite analyzed by X-ray diffraction resembled the peaks in the uncooked shrimp shells. The material's nature was disclosed by the mean peak of the scattering. The fact that this biomaterial demonstrated high compatibility suggests the existence of calcite in the specimen examined.
Significance of Coagulant Dosage
The coagulant dosage is an essential coagulation parameter. The optimal dose influences the sustainability and economic performance of the coagulants.
A lower or higher dose than the optimal may result in inadequate aggregation and a reduction in impact owing to charge stabilization, and will not increase efficiency anymore.
In terms of turbidity, a 3 to 9 mL dose functioned well at alkaline pH (pH = 10). Chitosan was discovered to be pH sensitive and requires near alkaline pH settings for efficient turbidity and BOD5 elimination. A pH of 10 was discovered to be optimal for chitosan effectiveness in FPW.
For fish processing effluent, liquid chitosan has a strong cleaning potential. There was no notable change in turbidity between the three coagulants, however liquid chitosan and commercial chitosan exhibited a considerable reduction in the BOD5 measure.
In short, The acquired findings demonstrated a good agreement between the experimental values and the values estimated by the estimation techniques, which was scientifically confirmed by an extra confirmation run.
References
Nouj, N., Hafid, N., Alem, N. E., & Crestescu, I. (2021). Novel Liquid Chitosan-Based Biocoagulant for Treatment Optimization of Fish Processing Wastewater from a Moroccan Plant. MDPI Materials. https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/14/23/7133
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.