The latest study published in the journal Materials focuses on a novel class of nano-adsorbent zinc-silver nanostructures embellished with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (Zn-Ag MWCNT).

Study: Water Treatment from MB Using Zn-Ag MWCNT Synthesized by Double Arc Discharge. Image Credit: niruti Puttharaksa/Shutterstock.com
The nanostructures were conveniently produced utilizing a completely redesigned spinning cylindrical electrode in a double arc discharge.
Importance of Water Treatment
The rapid increment in the global population is the main source for the depletion of clean drinking water day by day. More than 2.2 billion people worldwide rely on contaminated drinking water. Wastewater treatment is one of the most important uses, particularly in countries with scarce water supplies.
Various research organizations proposed addressing poisonous dye removal from water with various strategies including organic sources, physical treatment technologies, and chemical procedures. Because of its accessibility, the adsorption technique is a widely used application.
Scientists have started to utilize nanoparticles for water treatment.
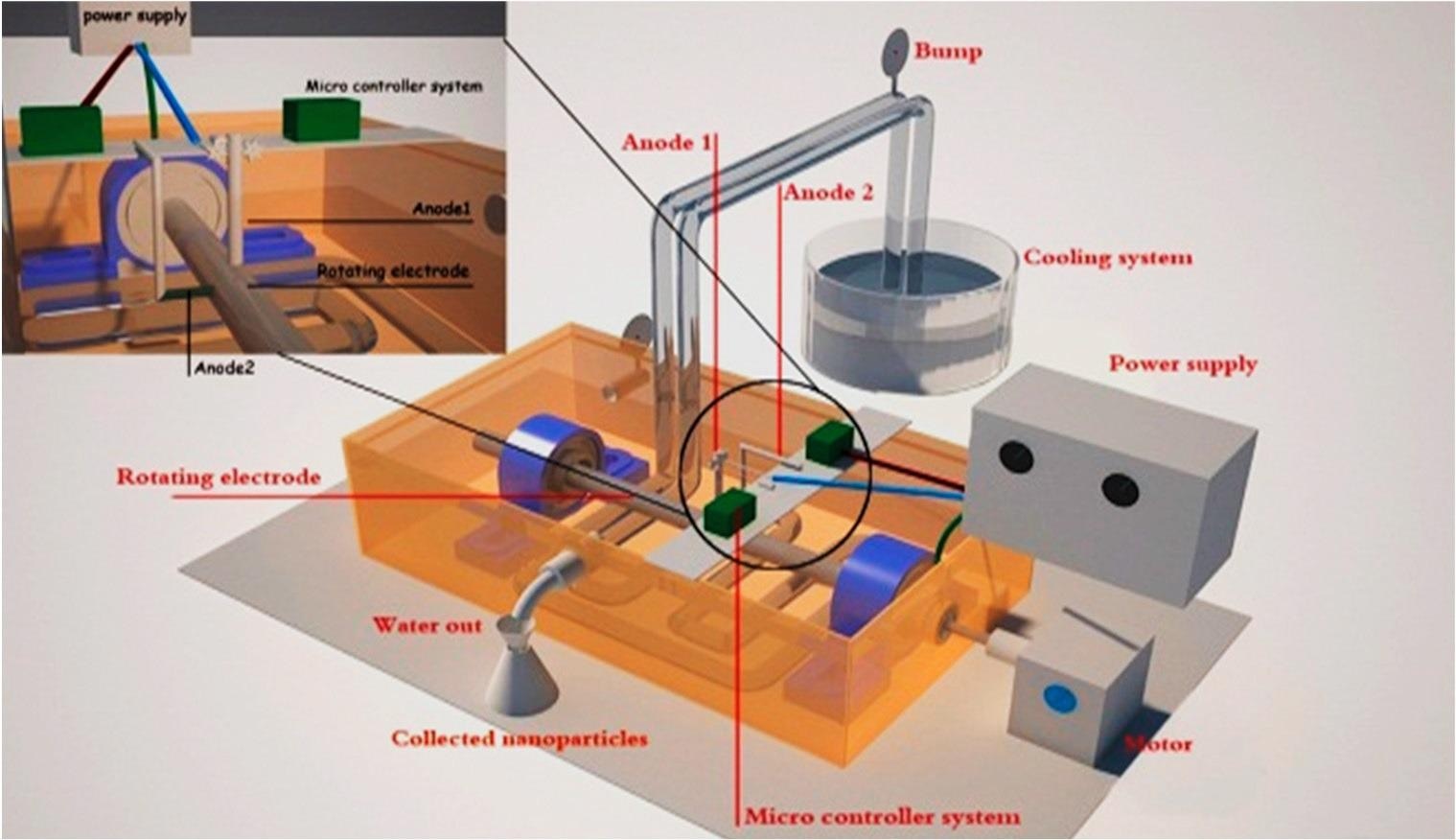
Figure 1. Electric arc discharge system.
Importance of Silver Nanoparticles and Carbon Nanotubes
Silver nanoparticles are very important due to their advantageous characteristics. Because of morphology and size-dependent plasmonic interaction, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have a more noticeable enzymatic mobility in the domain of waste removal from water. The AgNPs in the products were revealed to operate as an e-transport connection between the nano-adsorbent and the MB.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) coated with metallic elements, such as snaps, can boost performance via the charge mediation process. Carbon nanotubes are recognized as one of the most promising adsorbents for wastewater purification due to their excellent adsorption effectiveness for synthetic dyes.
MWCNTs (Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes) were found to be useful in removing MB from aqueous media. It has been claimed that MWCNTs have a higher adsorption capacity for MB removal than CNTs.
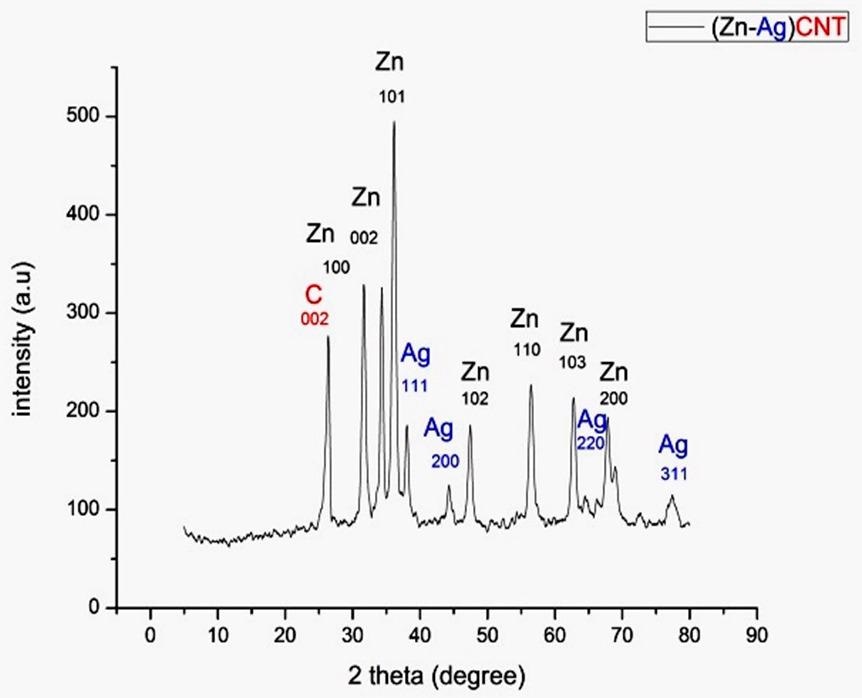
Figure 2. Shows the XRD patterns of Zn-Ag MWCNT.
Limitations of Carbon Nanotubes
Although CNTs offer a package of advantages, several limitations are present which much be addressed. Contaminants, irregularities in shape and topology, large interfacial area, substantial hydrophobicity characteristics, low solubility, and the tendency of CNTs to bundle together are all barriers to their immense utilization in various industries.
Since CNTs are a relatively new discovery, many facets are yet to be critically researched. Certain limitations during the research include the financial constraints, as they are costly to synthesize and the need for high energy sources for emissions.
Research Findings
In the innovative research, a double arc discharge unit was built to regulate one electrode, which is linked at 70 volts and a current route of 15 amps through it first. The glow discharge approach has several advantages, including a straightforward design and architecture, the use of non-toxic substances, and the use of low-cost adsorbents with great efficiency.
The initial step was the results of the electroscopic analysis. The TEM image reveals a darkish spherical morphological form of silver around 24 nm and a hexagonal zinc particle with an average diameter of 33 nm that is adorned with a pale MWCNT. All of the test findings indicated a high concentration of zinc peaks, which was attributed to an elevation in zinc % in the produced material.
The adsorption time was estimated to be 25 minutes with almost 65% dye removed. It was discovered that at low concentrations, about 100 percent of the dye was eliminated; however, as the intensity of dye grows, this clearance percentage steadily drops to more than 65 percent.
Additionally, an improvement in the percent removal of MB was seen for a neutral and basic environment within the first 25 minutes of interaction. These positive results were indicative of rapid enhancement of performance.
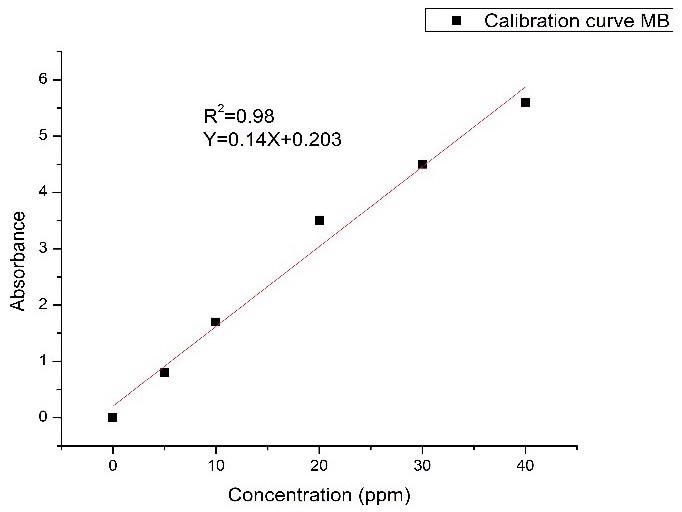
Figure 3. The variation of absorbance versus MB concentration.
Limitations of the Study
During the research, experimental adsorption data for various time intervals at incipient intensities were obtained. Lagergren's formula was one of the most often used numerical equations in the research to depict the adsorption of a substance from the liquid stage.
The results suggest that Pearson's correlation "R" of the adsorbents during the process is minimal, and the substantial difference between the theoretical and quantified adsorption potential (qe) of first-order kinetic models was the proof that this model fails to comprehend the experimental data.
Future Utilization of Silver Nanoparticles
Viruses, parasites, and fungi are all present in living beings. Because of their particular features, silver nanoparticles are seen as a potential leader in the battle against hazardous microbial diseases. The utilization of silver nanoparticles along with consumer electronic gadgets shall be expanded to wastewater treatment and biomedical applications in the near future.
In short, this work presents a unique way of producing pure nanocomposites Zn-Ag MWCNT employing a double arc discharge process and non-traditional rotating electrodes, at a price of less than one American dollar per nanogram produced.
References
Anon., 2021. Water Treatment from MB Using Zn-Ag MWCNT Synthesized by Double Arc Discharge. MDPI Materials. 14. 7205. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/14/23/7205
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.