A new breakthrough using alumina particles for sandblasting dental implants is considered in the journal Materials.
Study: Benefits of Residual Aluminum Oxide for Sand Blasting Titanium Dental Implants: Osseointegration and Bactericidal Effects. Image Credit: astarot/Shutterstock.com
Sandblasting, also known as grit blasting, is a popular surface treatment strategy for establishing the adequate roughness of titanium dental implants in regard to physiological reactions.
For this reason, alumina particles (Al2O3) have been most popularly used, followed by an acid etching procedure. The abrasive forecast creates a macroroughness with some very sharp peaks and valleys, as well as the acid treatment round for the configuration, and induces a micro-roughness inside the macroroughness.
It is well understood that acid therapy by itself does not create the right roughness for physiological osseointegration. The primary treatment for obtaining a favorable titanium outer layer is sandblasting.
Abrasive Implants
Many various kinds of abrasive particles have already been used, however the particles have to be harder than titanium in order to achieve roughness, which means that materials like titanium oxides and calcium phosphates, amongst many others, cannot be applied successfully because they do not produce the desired roughness.
 Essential implants by Klockner used in the research. Image Credit: Gil, J., et al, Materials
Essential implants by Klockner used in the research. Image Credit: Gil, J., et al, Materials
Many companies use alumina as one of the most popular abrasives, but most implants are handled with all these particles because they provide outstanding osseointegration outcomes and therefore have no foreign body responses or allergic consequences.
Nevertheless, not only the abrasive's existence but also the forecast variables, including the range from the projection gun to the titanium surface, the forecast pressure, the absorption time, the projection diameter, and so on, have an effect. In addition, those certain alumina variables, such as particulate size or shape, will affect roughness.
The roughness produced by sandblasting is determined by the size, nature of the abrasives, projection pressure, and length from the gun to the titanium surface. A roughness of 1 to 3 micrometers is assumed to be an effective surface for osseointegration. Powerful and quick osseointegration is regarded as a critical determinant of titanium implant placement.
Sand Blasting Advantage
Consequently, sandblasting causes compressive stress on the exterior, which increases mechanical characteristics, particularly fatigue resistance. The projection of abrasives at high pressure causes an increase in the compressive stresses on the surface.
This compression inhibits crack nucleation by fatigue on the surface, with crack nucleation on the matrix occurring approximately 10 m from the surface. This fact increases with the number of cycles required to nucleate the crack, that is generated by mechanical cycles, resulting in significant advancement in fatigue life and providing the dental implant with excellent long-term mechanical characteristics.
Osseointegration Parameters
Chemical composition, water sorption, surface energy, and zeta potential are all important parameters that influence the rate and quality of osseointegration. The surface characteristics are increased by sandblasting. As a result, these implants have exhibited more hydrophilic behavior patterns.
When the outer surface of the sandblasting implantable devices was compared to the dispersive or polar elements of surface energy, there was a general trend in the polar element decreasing whenever the specimens were treated with sandblasting. Because of the negatively charged concentration on the exterior, the polar element is important because it can enable the biosorption of human osteoblast proteins or peptides.
The cleanliness of titanium dental implants is an essential criterion for bone tissue regeneration, and contamination may prevent osseointegration. This component has not been thoroughly researched in the literature, and conflicting opinions can be discovered.
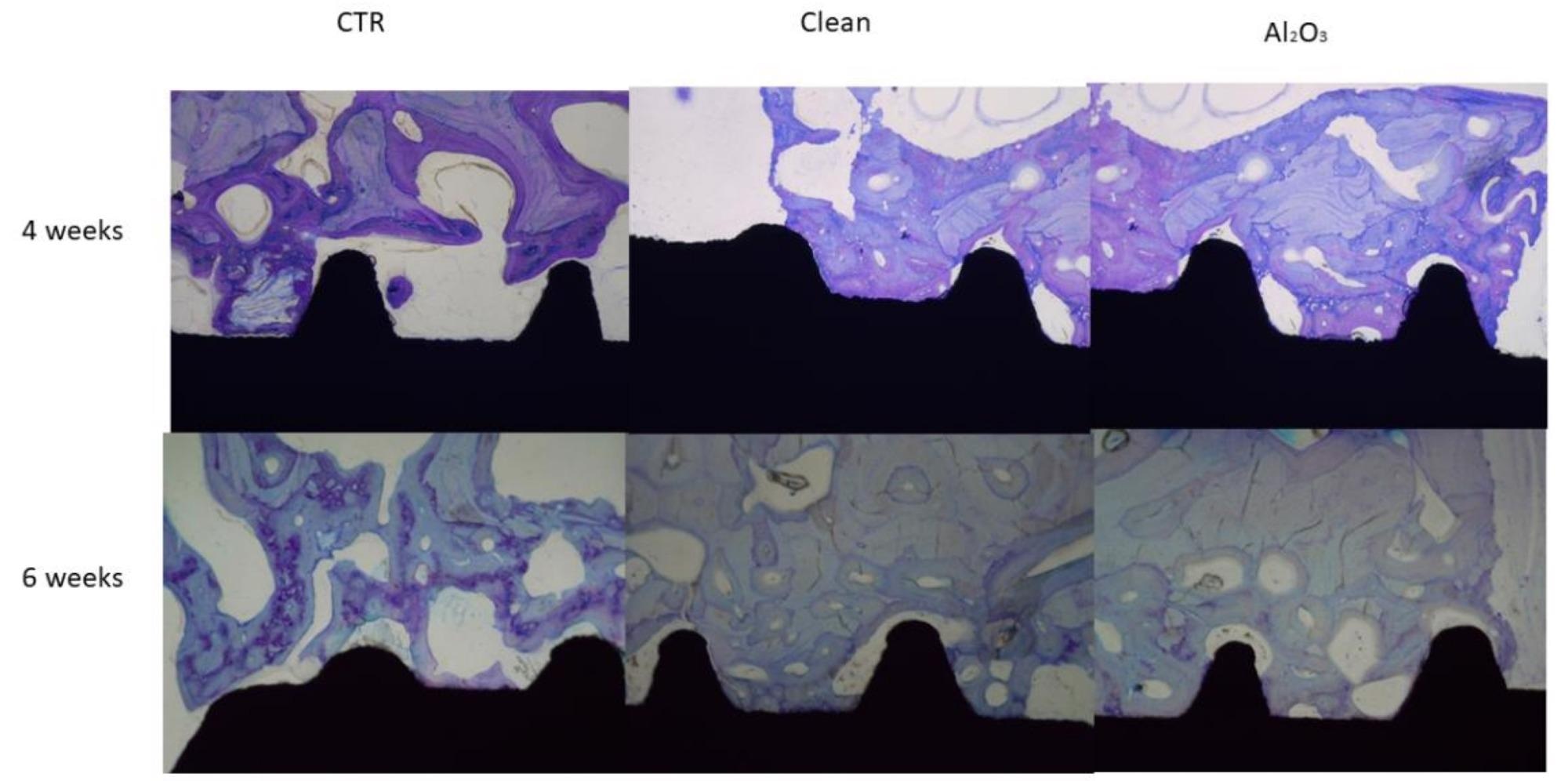
Histologies of the dental implants after 4 and 6 weeks of implantation for the three surfaces studied. Image Credit: Gil, J., et al, Materials
Research Results
The influence of alumina particles upon that titanium surface was shown at high resolutions. It demonstrated 3D roughness using an interferometric microscope, as well as the occurrence of aluminum using X-ray microanalysis.
As previously stated in other opinion pieces, the residue left alumina particles increase osteoblastic adherence, proliferation, and divergence because of their negative charge, which creates selective protein binding, particularly of fibronectin, which promotes the osteoblastic flow of migrants to the surface.
These findings, as well as the widespread clinical use of titanium shot-blasted implant placement with Al2O3, refute the myth that debris can impair osseointegration. According to the research findings, dental implants made of alumina have a significant quantity of bone in both situations. The bone is mature and very well-formed, which is remarkable.
Limitations and Further Findings
According to the findings, the residue alumina enhances osseointegration in titanium with the same roughness.Consequently, X-ray energy-dispersive microanalysis has a sensitivity of 0.8 percent, and more sensitive methods could be used to measure the percentage of byproducts more precisely.
Furthermore, while this microbial study focuses on adhesion, biofilm investigations are necessary to reach the conclusion of the bactericidal ability of the exterior with residual alumina in a more rigorous manner. More research with different bacterial species is required to determine the method of the potential bactericidal impact.
Reference
Gil, J., et al. (2021). Benefits of Residual Aluminum Oxide for Sand Blasting Titanium Dental Implants: Osseointegration and Bactericidal Effects. Materials 2022, 15(1), 178; Published: 27 December 2021. https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/15/1/178
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.