In a recent study published in the journal Materials, researchers from China studied the acid rain erosion durability of different asphalt mixtures.

Study: Study on the Durability of Acid Rain Erosion-Resistant Asphalt Mixtures. Image Credit: Oceloti/Shutterstock.com
Asphalt Mixtures
Rapid growth in the world economy has resulted in the high consumption of fossil fuels such as coal and oil. In the combustion process, these fossil fuels produce a large amount of nitrogen and sulfur oxides that increase the acidity of the atmosphere, which causes severe acid rain.
The high-grade highways are constructed using asphalt pavement because the material has several advantages over its alternatives. The asphalt pavement frequently shows early damage due to acid rain corrosion. Researchers worldwide have conducted various studies to find ways to improve the long-term durability of asphalt pavement and reduce their acid rain corrosion.
In the present study, the researchers systematically studied the durability of epoxy asphalt mixtures to resist acid rain corrosion. Epoxy asphalt is a thermosetting polymer material made of epoxy resin and asphalt with the curing agent. The properties of epoxy asphalt are high thermal stability, deformation resistance, fatigue resistance, and high bonding ability.
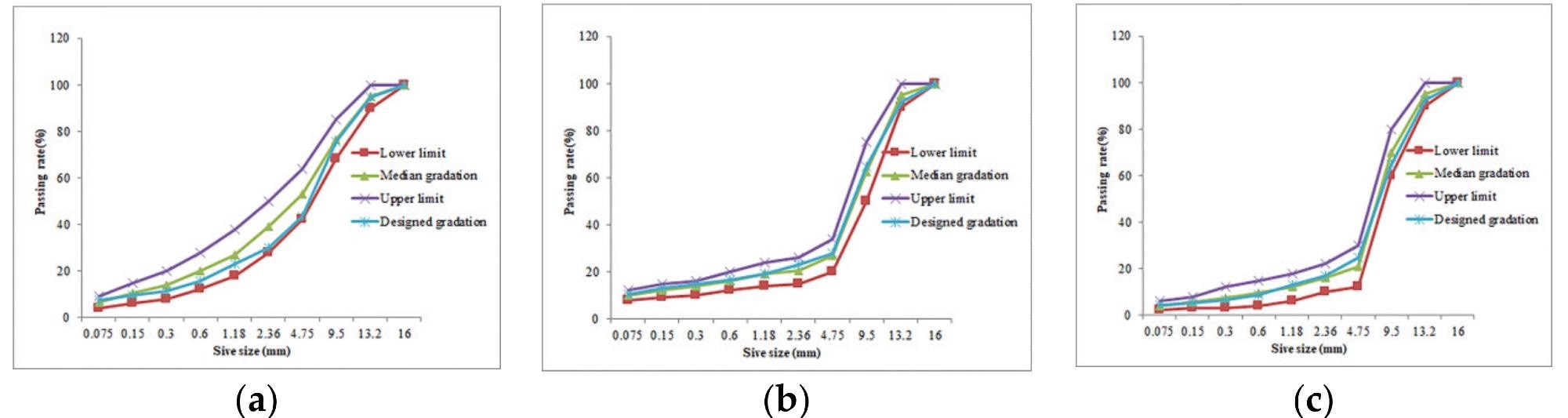
Gradation curve of each asphalt mixture. (a) AC-13, (b) SMA-13 and (c) OGFC-13. Image Credit: Wei, J et al., Materials
Methodology
The researchers selected tafpack-super (TPS), epoxy asphalt, styrene–butadiene–styrene (SBS), and matrix asphalt for binding asphalt. Lignin fiber, reed fiber, waste rubber powder, and modified bamboo fiber were selected as fillers for developing the final epoxy asphalt mixture.
The preparation of the asphalt mixture was completed in four steps. In the first step, waste rubber powder and asphalt were mixed with SBS-modified asphalt, epoxy asphalt, and matrix asphalt to develop modified asphalt. In the second step, the premixing process was completed, during which aggregates and modified bamboo fiber were preheated. The third step was completed by mixing waste rubber powder, modified asphalt, and epoxy resin with epoxy asphalt mixture. The preheated mineral powder was added to the developed mixture during the last step and mixed until the required consistency was reached. Thus, samples of matrix asphalt, epoxy asphalt, and SBS-modified asphalt were prepared by the researchers.
The characterization methods used by the researchers were periodic dry–wet cycle immersion, aging test, low-temperature stability, moisture stability, and fatigue life. To develop actual acid rain composition, a mixture of sulfuric acid and nitric acid at a concentration of 98% was used. All the tests were performed under laboratory conditions to examine the optimized performance of the developed samples.
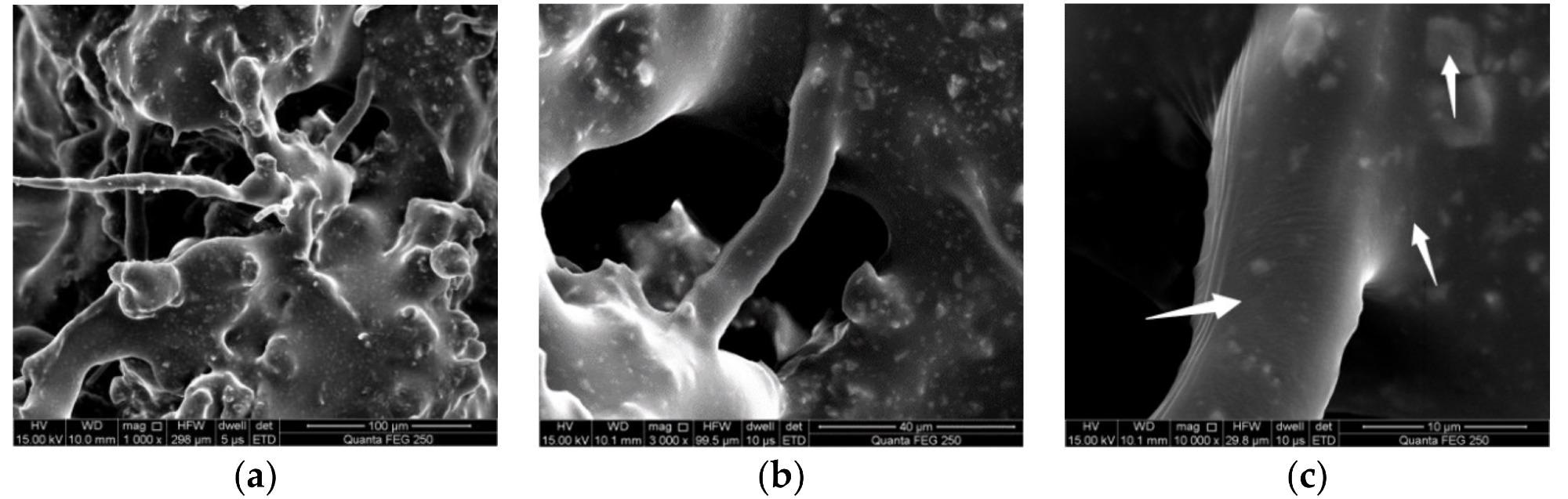
Microstructure of fiber asphalt mastic in asphalt mixture. (a) 1000 times, (b) 3000 times and (c) 10,000 times. Image Credit: Wei, J et al., Materials
Results
The researchers observed that acid rain erosion reduces the adhesion between asphalt-aggregates. It also affects the significant properties of asphalt, such as fatigue and low-temperature performance, which results in accelerated aging of the asphalt mixture. Additionally, the asphalt mixture's properties deteriorate rapidly as the acid concentration and the immersion period increase.
The epoxy asphalt demonstrated improved performance over the matrix asphalt and SBS-modified asphalt. The improved performance was observed in the acid rain erosion resistance test and adhesion with the aggregates. The improved adhesion property of epoxy asphalt resulted from the formation of polar groups and the development of properties such as low shrinkage and high cohesion. The test also demonstrated that it could effectively resist spalling, moisture erosion, and temperature stress cracking.
The epoxy asphalt mixture exhibited the highest acid rain erosion resistance when combined with modified bamboo fiber and waste rubber powder. The improvement in the property resulted from a reduction in the mixture's void ratio. The addition formed a complex spatial network structure that improved the epoxy asphalt mixture's impermeability, durability, and acid rain erosion resistance.
The surface free energy of the matrix asphalt, epoxy asphalt, and SBS-modified asphalt decreased with increased pH value. The test conducted on different gradation mixtures showed that asphalt concrete gradation mixture and stone mastic asphalt had improved durability over the open-graded friction courses type gradation mixture. It was also observed that a high-density asphalt mixture with a wider asphalt film could effectively resist acid rain erosion.
Asphalt mixture durability and acid rain erosion resistance were also affected by the gradation of the asphalt mixture and the asphalt binder. It must be noted that the micro-scale erosion process of acid rain on various asphalt binders and mixtures was not studied by the researchers.
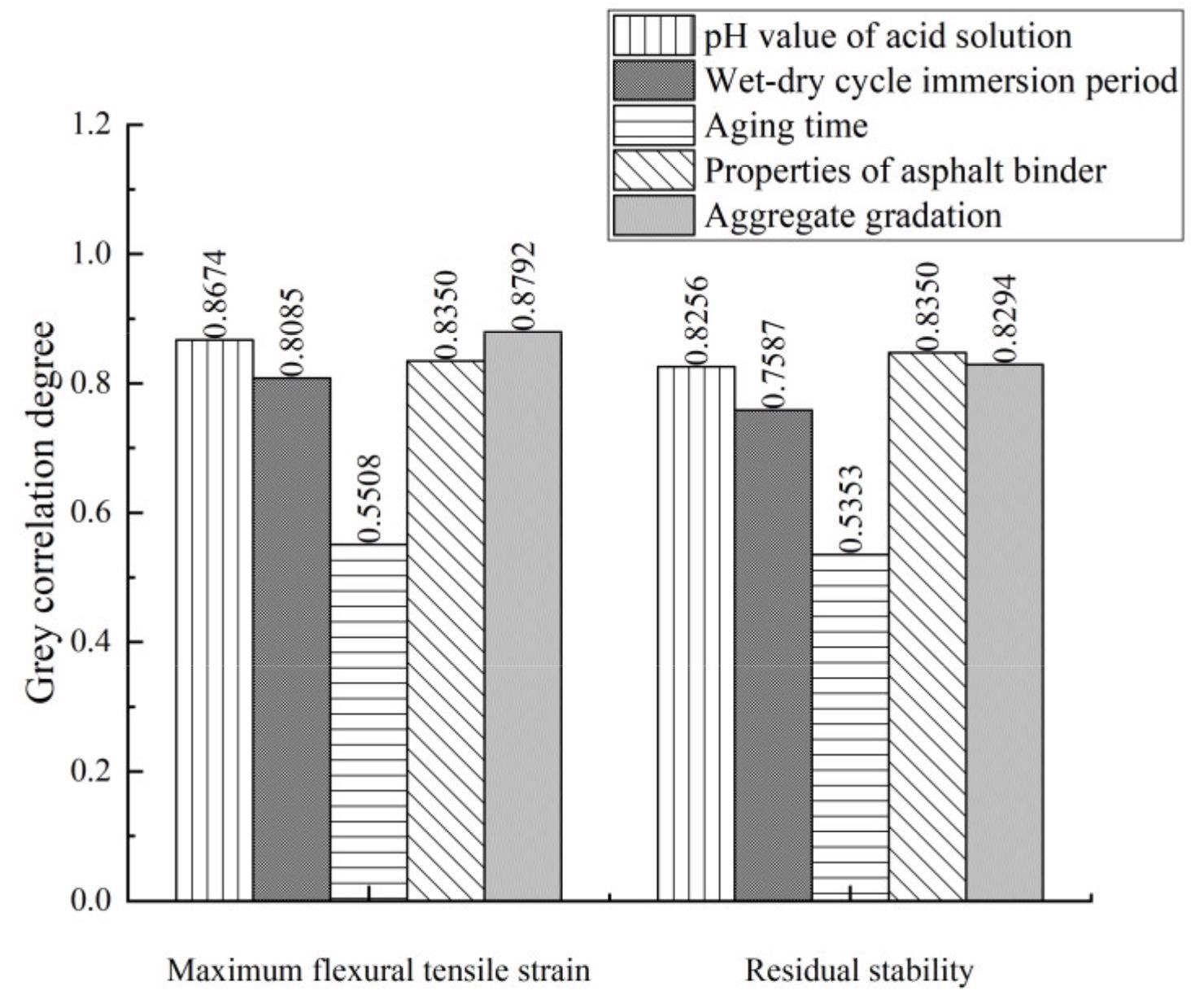
Grey correlation analysis results of influencing factors of aging durability. Image Credit: Wei, J et al., Materials
Conclusions
To summarize, the researchers conducted tests to systematically examine the impact of acid rain erosion on the durability of asphalt mixtures. Their findings show that acid rain erosion reduces the adhesion between asphalt and aggregate, which affects the asphalt mixture's road performance. The mixtures' mechanical properties, adhesion, and durability are also affected by acid rain erosion.
Future studies need to focus on the directional control of acid rain erosion resistance and durability of different asphalt mixtures. The researchers also suggested using a multi-parameter comprehensive assessment study to improve the results achieved and identify new outcomes.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.
Source:
Wei, J.; Chen, Q.; Du, J.; Liu, K.; Jiang, K. Study on the Durability of Acid Rain Erosion-Resistant Asphalt Mixtures. Materials 2022, 15, https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/15/5/1849