Writing in the journal Sustainability, scientists from India and the United Arab Emirates have investigated the factors which affect the safe disposal of electronic waste. The new research has implications for improving the sustainability of the electronics industry, helping it realize its circular economy aims.

Study: Factors That Influence the Safe Disposal Behavior of E-Waste by Electronics Consumers. Image Credit: Morten B/Shutterstock.com
Electronics Waste
Waste and pollution from industry is a growing environmental issue. In 2019, over 50 million metric tons of waste were generated by the electronics industry alone. Aside from the obvious environmental issues this causes due to toxic chemicals such as lead and mercury leaching into the environment, the generation of e-waste presents significant economic problems.
Electronic parts contain significant amounts of critical resources. Gold, platinum, lithium, copper, silver, and other highly valuable resources which could otherwise be recovered, recycled, and reused are lost every year. It is estimated that in 2019 alone, $57 billion of these critical resources were wasted. Moreover, the continued exploitation of virgin materials leads to environmental damage and resource depletion.
Future supply bottlenecks can be avoided by the efficient recovery and reuse of critical materials. However, several countries have insufficient recycling infrastructure, and a lack of regulations governing the recovery of electronics waste is exacerbating the issue. In India alone, e-waste is growing at a CAGR of 30%. 3.5 million tons of e-waste were generated in the country in 2019, and only 800,000 tons of e-waste can be managed by the nation’s formal recycling infrastructure.
Most e-waste is handled by the informal recycling sector, which is poorly regulated and lacks sufficiently safe infrastructure. Several richer nations send their waste to developing countries, including significant amounts of e-waste, which causes environmental and social challenges. Increasing consumption of electronic products and technological redundancy are leading to growing amounts of polluting electronic waste materials.
The Study
The new paper has investigated factors that influence electronic waste disposal. Using mobile phones as an example, the authors have explored the behavior and intentions of consumers. The study uses a questionnaire to investigate the research question. The theories which formed the basis of the research question were the theories of planned behavior and reasoned action, which both govern consumer behavior and intentions.
In the research, the authors have developed specific hypotheses with the support of current literature that links the wider research question with the factors under consideration. Factors highlighted in the questionnaire were convenience, awareness, regulators, manufacturer intentions, and subjective norms. A cross-sectional survey was conducted in the Indian market.
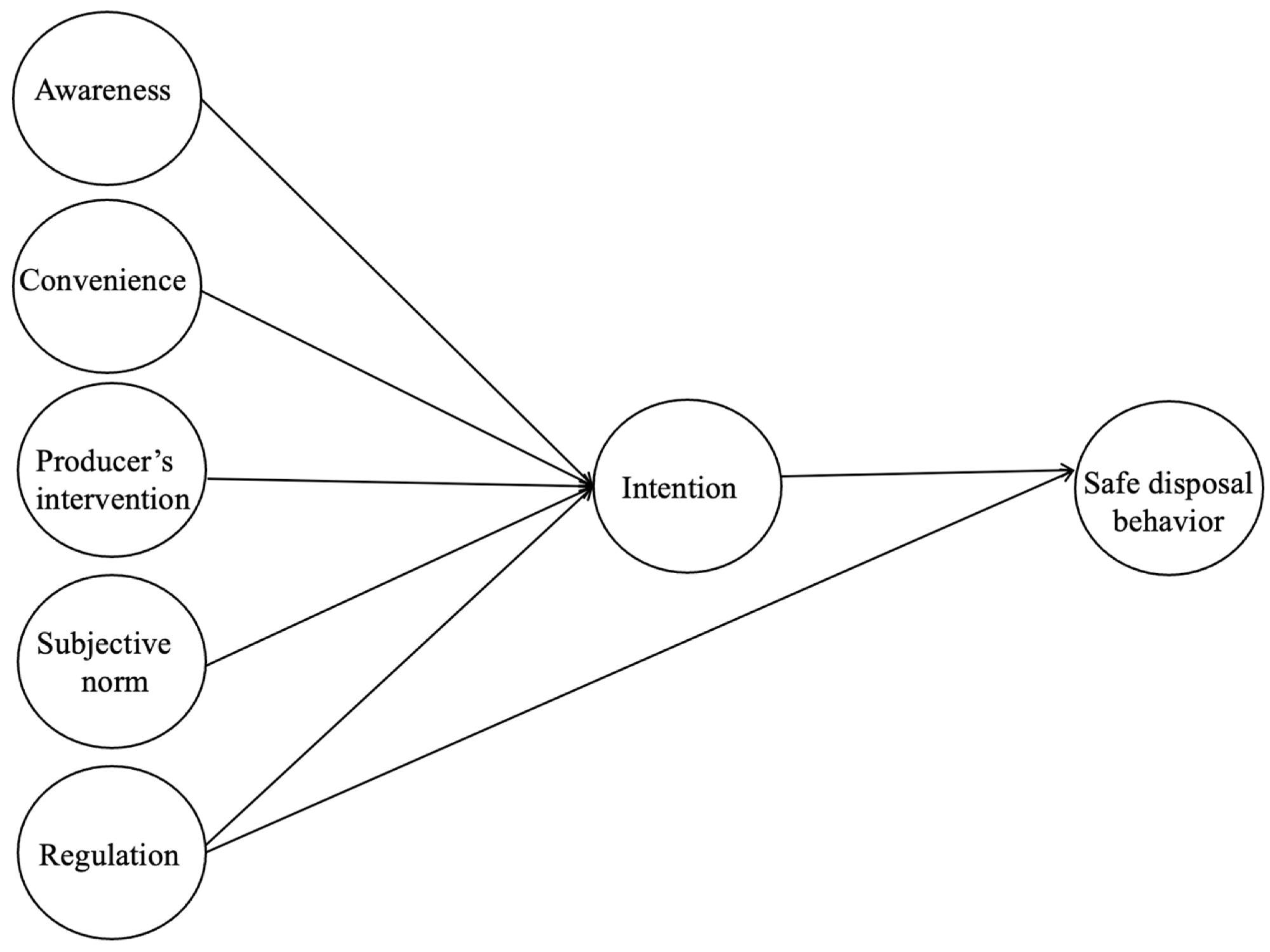
Relationship between factors impacting e-waste safe disposal intentions and behavior. Image Credit: Laeequiddin, E et al., Sustainability
Data were analyzed for measurement properties and descriptive statistics. Modeling was employed to further test the research hypotheses. The findings of the questionnaire and survey were explored in depth in the paper, providing pertinent information for the field of e-waste recycling.
Findings and Ways Forward
A comprehensive understanding of the factors which influence behaviors and intentions of consumers for safe electronic waste disposal was achieved by the authors using the survey approach in the context of the Indian market.
The broad findings of the research are that all the factors, except the direct effect of government regulation, have a significant impact on consumer behavior and intent. A positive correlation between awareness of the issue and safe disposal intentions of consumers was identified. Using mobile phones, which are a major electronics product that consumers periodically replace, as the study example, the authors found that consumer knowledge of the consequences of electronic waste increases their intention to dispose of these products safely.
A previous study on e-waste in African nations has suggested that improving education will have a positive effect on e-waste attitudes amongst consumers. Based on this study, the authors have suggested that governments, educational institutions, and manufacturers can play a key role in raising awareness of the issue.
Based on the findings that convenience has an impact on e-waste intentions, which agrees with previous studies, the authors have suggested that investing in infrastructure, collection points, incentive schemes, and management systems will improve e-waste recycling by making it easier for consumers. People’s willingness to pay for convenience is governed by their environmental beliefs, which are statistically significant.
Subjective norms were found to be influenced by factors such as peer pressure and societal norms. The study authors have suggested that educational institutions, community leaders, and community groups can play a role in helping to influence consumers and organize collection efforts. Furthermore, interventions by manufacturers such as buy-back incentives could have a positive impact to help overcome the current issues with e-waste.
The research has identified that the problem of influencing consumers' safe disposal behavior and intentions is a complex one, but with a coordinated strategy between governments, industry, educational institutions, and community organizations and leaders, the problem of e-waste disposal can be overcome.
Further Reading
Laeequiddin, E et al. (2022) Factors That Influence the Safe Disposal Behavior of E-Waste by Electronics Consumers Sustainability 14(9) 4981 | mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/9/4981
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.