Darling Ingredients’ health brand Rousselot, the global leader in collagen-based solutions, announced today that a new study has found that utilization of highly purified gelatin biomaterials for 3D in vitro models can significantly enhance the reliability and reproducibility in these models, creating new possibilities for replacing preclinical animal trials.
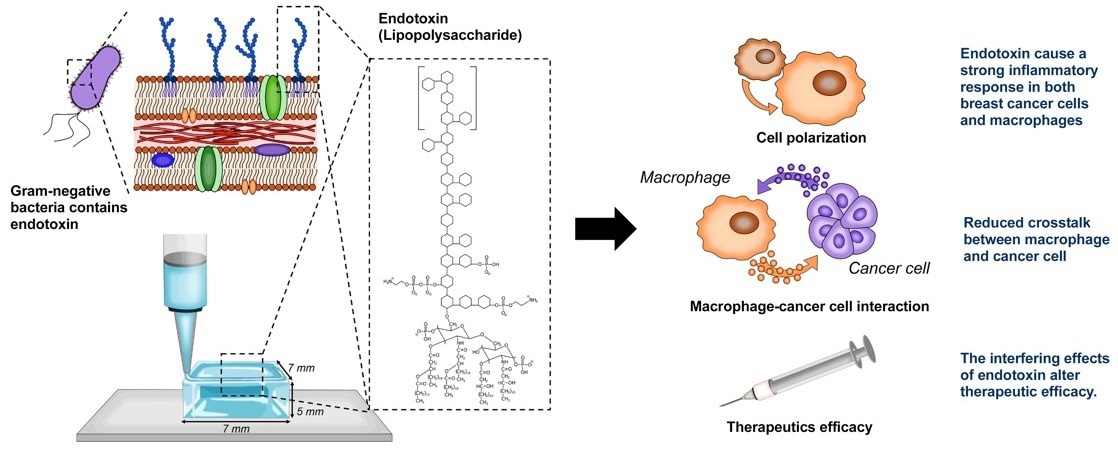 Image 1: Illustration shows how the presence of endotoxins impacts the credibility of 3D models. This figure is a modified version of the original graphic in Heinrich, M. A., Heinrich, L., Ankone, M. J. K., Vergauwen, B., & Prakash, J. (2023). Endotoxin contamination alters macrophage-cancer cell interaction and therapeutic efficacy in pre-clinical 3D in vitro models. Biomaterials advances, 144, 213220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioadv.2022.213220 Available under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). Image Credit: Rousselot Biomedical
Image 1: Illustration shows how the presence of endotoxins impacts the credibility of 3D models. This figure is a modified version of the original graphic in Heinrich, M. A., Heinrich, L., Ankone, M. J. K., Vergauwen, B., & Prakash, J. (2023). Endotoxin contamination alters macrophage-cancer cell interaction and therapeutic efficacy in pre-clinical 3D in vitro models. Biomaterials advances, 144, 213220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioadv.2022.213220 Available under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). Image Credit: Rousselot Biomedical
“This study revealed that 3D models of novel breast cancer immunotherapies display clear therapeutic efficacy differences depending on the level of endotoxins in gelatins and methacryloyl gelatins (GelMA) used in in vitro systems,” said Dr. Kathleen Jacobs, Global Regulatory Affairs Director, Rousselot. “Biomaterials with low endotoxin content could lead to a more accurate representation of the safety and potency of novel therapeutics. This can improve the validity of 3D in vitro models and help to reduce animal testing.”
The joint study done by the University of Twente, The Netherlands, and Rousselot Biomedical investigated for the first time the impact of endotoxins on 3D breast tumor-immune cancer models. The research compared 3D models using standard gelatins and GelMAs or Rousselot’s X-PURE® gelatin and X-PURE® GelMA – purified biomaterials with low endotoxin levels (<10 EU/g).
The study demonstrated that endotoxin levels had a marked effect on the validity of the 3D-printed model in three aspects:
- Inflammatory reaction: The presence of high levels of endotoxins caused a strong inflammatory response in immune cells (macrophages) in contaminated models.
- Receptivity of immune cells to cancer cells: Crosstalk between macrophages and cancer cells was significantly reduced in the presence of high endotoxin levels.
- Reliability of therapeutic outcomes: The high endotoxin environment artificially increased the measured efficacy of the therapy designed to inhibit the expression of anti-inflammatory markers.
Recent changes in European Union and US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) legislation, combined with increased ethical considerations and efficacy demands, are driving the rapid replacement of pre-clinical animal trials with 3D biofabrication models.
Dr Bjorn Vergauwen, Scientific Director, Product and Process Development, Rousselot concluded, “The use of purified biomaterials such as Rousselot’s X-Pure or X-Pure GelMA in in vitro 3D models is critical in producing a biologically relevant environment, while also helping to reduce the costs, time and ethical concerns associated with drug development.”