The Clearview db photometer can be used for the accurate and cost-effective identification of fuel products in pipelines. The information collected by the photometer can be used to reduce wastage and help with product movements.
Experimental
The ClearView db photometer was equipped with 2 x 2 m low-0H fiber optic cables connected to a fiber-optic probe with a 1 cm flow path.
The near-infrared (NIR) spectrum of a fuel provides a wealth of information about its chemical constitution. The majority of hydrocarbon compounds absorb at the wavelengths 1,190 nm and 1,230 nm, whereas aromatic compounds produce a peak structure similar to the one displayed in the below spectra.
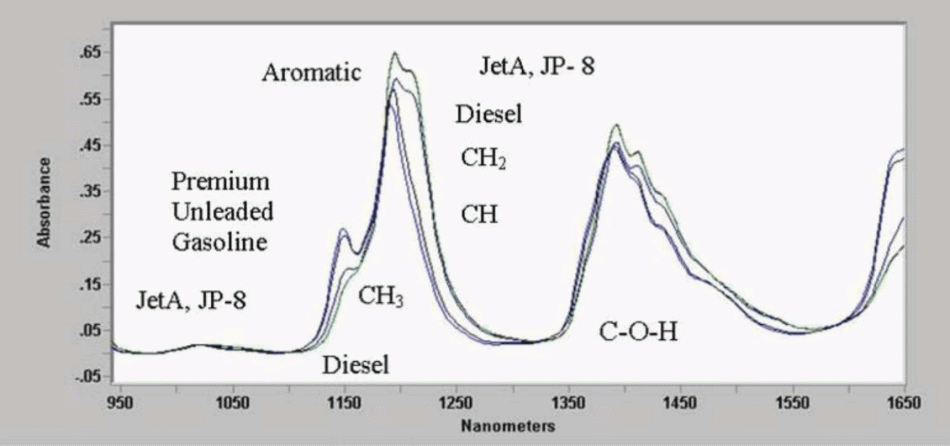
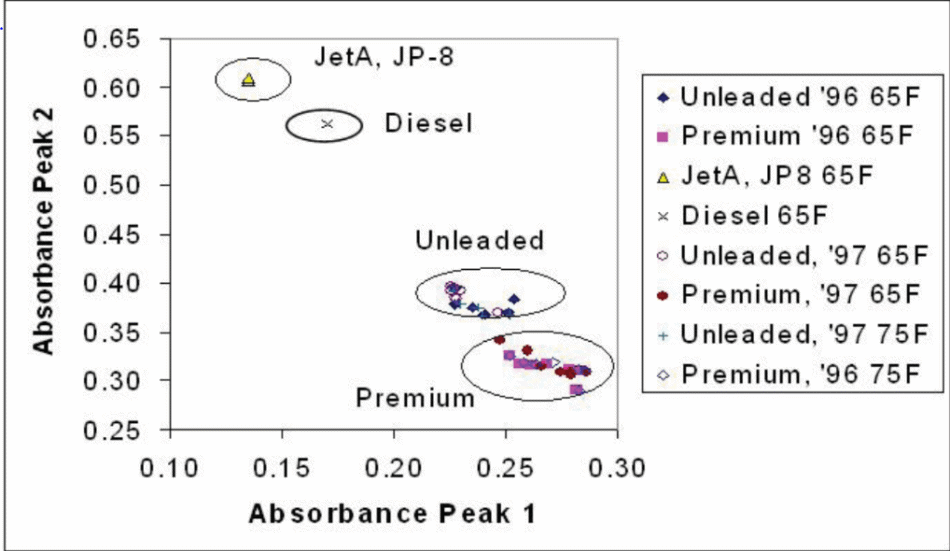
These characteristic absorptions make it possible to identify fuel components with more certainty than with single parameter measurements.
Samples
Samples used were R+M/2 87 and 93 octane with monthly blend changes at a range of temperatures (65 -75 ° F) and RVPs (8 – 13).
Outputs
An analog output of 4-20 mA for every fuel type and the mixing areas between fuels (4-bit digital output optional).
Lamp replacements and probe fouling alarms used optoswitch circuits.
Conclusions
Real-time analysis of fuel components is possible using the ClearView db.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Process Insights – Optical Absorption Spectroscopy.
For more information on this source, please visit Process Insights – Optical Absorption Spectroscopy.